A facile hydrothermal etching process to in situ synthesize highly efficient TiO2/Ag nanocube photocatalysts with high-energy facets exposed for enhanced photocatalytic performance
Abstract
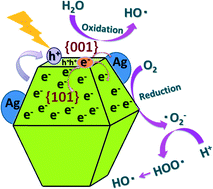
A facile hydrothermal etching process was developed to synthesize TiO2/Ag nanocubes for enhanced photocatalytic application. The synthesis was carried out by chemically etching hollow @TiO2 spheres in the presence of an AgF or AgF/NaF solution under hydrothermal conditions. Utilizing F− as a morphology-directing agent and Ag+ as an Ag source during the etching process, TiO2 nanocubes can be easily formed with their active high-energy facets exposed and Ag nanoparticles can be in situ deposited simultaneously on the surface of the TiO2 nanocubes to generate hybrid TiO2/Ag nanocubes. The resulting TiO2/Ag nanocubes were well controlled with Ag nanoparticles uniformly distributed on the surface of the TiO2 nanocubes. The morphologies of TiO2/Ag can be altered from ellipsoidal to cubic shapes depending on the amounts of AgF or AgF/NaF used for chemical etching. Due to the exposure of the active high-energy facets of TiO2 and the uniform deposition of Ag nanoparticles, the obtained TiO2/Ag nanocubes showed superior catalytic performance for the photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B under visible-light radiation. It is proposed that the surface plasmon resonance effect arisen from Ag nanoparticles on TiO2 nanocubes can effectively enhance the visible-light driven photocatalytic properties of TiO2/Ag photocatalysts. Meanwhile, due to the etching of F ions during the synthetic process, the morphology variation of TiO2 from spherical to cubic shapes may be beneficial to the exposure of high energy {001} facets, which is liable to produce more electron–hole pairs in the photocatalytic process, and electron–hole pairs can combine with OH− to produce large amounts of hydroxyl radicals, eventually accelerating the decomposition of the organic dye.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...