Experimental and theoretical study of weak intermolecular interactions in crystalline tertiary squaramides†
Abstract
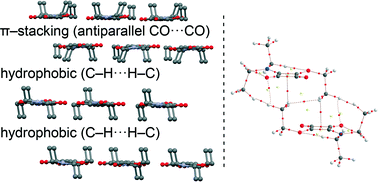
We report the X-ray solid state structures of two tertiary squaramides, i.e. 3-(diethylamino)-4-ethoxy-cyclobutene-1,2-dione (1) and bis-3,4-(diethylamino)-cyclobutene-1,2-dione (2). Compound 1 forms electrostatically compressed dimers in the solid state. Moreover, compound 2 exhibits a remarkable solid state architecture resembling a lipid bilayer. This supramolecular assembly has been analyzed using high level DFT calculations and Bader's theory of “atoms-in-molecules”. The antiparallel CO⋯CO interactions of the cyclobutenedione rings and hydrophobic interactions involving the ethyl chains are crucial for the formation of the bilayer assembly in the solid state.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...