Dynamic metabonomic and microbiological response of rats to lincomycin exposure: an integrated microbiology and metabonomics analysis†‡
Abstract
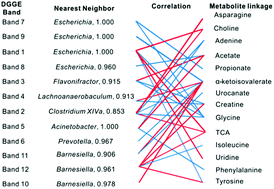
Humans are associated with a consortium of gut microbiome and individual variations in the microbes influence host metabolism. To probe the relationship between microbiome and the host metabolic changes, we analyzed the metabonomic and microbiological response of rats exposed to lincomycin (LM) by an integrated approach combining 16S rRNA gene sequencing and 1H NMR-based metabolomics profiling. LM exposure resulted in decreased levels of hippurate, short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and primary bile acids and increased levels of choline and oligosaccharides. Levels of Barnesiella and Prevotella decreased sharply, whereas level of Clostridium cluster XIVa increased slightly. In addition, strong correlations were observed between metabolites and the levels of Barnesiella, Prevotella and Escherichia coli. Meanwhile, some metabolites, such as N-methylnicotinate and trigonelline, showed association with osmotic homeostasis and nucleic acid synthesis. These results suggest that LM exposure lead to significantly suppressed fermentation, gut microbial modification of bile acids and influenced liver and kidney homeostasis. This applicable method reveals the effects regarding metabonomic and microbiological responses of LM, and the combination of microbiology and metabonomics as a powerful approach offers a non-invasive means to elucidate the progression of drugs and diet. The correlation between the host and gut microbiota identifies potential biomarkers and provides substantial insight into the bacterial function, which in turn could provide a rationale for development of potential microbiota-based early prevention and therapeutic interventions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...