Facile synthesis of polymethionine oxides through polycondensation of activated urethane derivative of α-amino acid and their application to antifouling polymer against proteins and cells†
Abstract
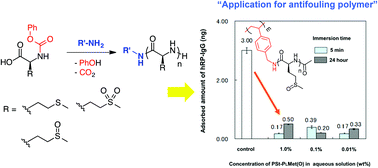
We have developed a facile route for the synthesis of poly(methionine) and poly(methionine oxide), including poly(methionine sulfoxide), and poly(methionine sulfone) through polycondensation of the corresponding N-phenoxycarbonyl derivatives of α-amino acids in the presence of amines. These urethane derivatives were readily synthesized through N-carbamylation of onium salt of methionine with diphenyl carbonate. Oxidation of sulfide on the urethane derivative with a hydrogen peroxide selectively provided the corresponding sulfoxide and sulfone in high yield. Heating of their urethane derivative 60 °C successfully obtained the corresponding polypeptide through polycondensation accompanying the elimination of phenol and CO2 in high yield. The molecular weight of polypeptide was adjusted by varying the feed ratio of urethane derivative to amine. MALDI-TOF mass analysis revealed that the added amine was successfully incorporated into the terminal end of the polypeptide. Taking advantage of our facile synthetic route to synthesize a polypeptide, we have synthesized a polystyrenes bearing oligo(L-methionine sulfoxide) in the side chain, and investigated their application as a surface-coating polymer that leads to antifouling property against proteins and cells. The polystyrene was readily synthesized through polycondensation of a urethane derivative of L-methionine sulfoxide in the presence of 4-vinylbenzylamine, followed by radical polymerization with water-soluble azo initiator. The inhibition of protein (hRP-IgG) adsorption and F9 cells adhesion was observed on the surface of the polymer-coated PS plate because of the hydrophilic nature of L-methionine sulfoxide segment. In addition, the result of CCK-8 assay reveals a low cytotoxicity against F9 cells, indicating that the polymer possesses a high biocompatibility.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...