Synthesis of end-functionalized poly(methyl methacrylate) by organocatalyzed group transfer polymerization using functional silyl ketene acetals and α-phenylacrylates†
Abstract
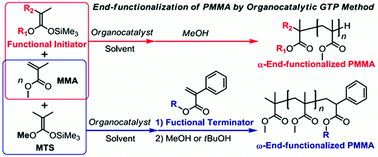
The present study describes the α- and ω-end-functionalization of poly(methyl methacrylate)s (PMMAs) by organocatalyzed group transfer polymerization (GTP) using both functional silyl ketene acetal (SKA) initiators and α-phenylacrylate terminators. The syntheses of structurally defect-free α-end-functionalized PMMAs with hydroxyl, ethynyl, vinyl, and norbornenyl groups (HO-PMMA, HC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C-PMMA, H2C
C-PMMA, H2C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH-PMMA, and NB-PMMA, respectively) were achieved by either the N-(trimethylsilyl)bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide-(Me3SiNTf2-) or t-Bu-P4-catalyzed GTP of MMA using functional trimethyl SKAs (1a–1d). On the other hand, the ω-end-functionalized PMMAs with ethynyl, hydroxyl, vinyl, and bromo groups (PMMA-C
CH-PMMA, and NB-PMMA, respectively) were achieved by either the N-(trimethylsilyl)bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide-(Me3SiNTf2-) or t-Bu-P4-catalyzed GTP of MMA using functional trimethyl SKAs (1a–1d). On the other hand, the ω-end-functionalized PMMAs with ethynyl, hydroxyl, vinyl, and bromo groups (PMMA-C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CH, PMMA-OH, PMMA-CH
CH, PMMA-OH, PMMA-CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2, and PMMA-Br, respectively) were for the first time obtained by the Me3SiNTf2-catalyzed GTP of MMA followed by a termination reaction using functional α-phenylacrylates (2a–2d). All the polymerizations produced end-functionalized PMMAs with controlled molar masses, narrow dispersities, and defect-free polymer structures as designed. The quantitative incorporation of functionalities into the α- or ω-end of the PMMAs was confirmed by the 1H NMR and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) measurements.
CH2, and PMMA-Br, respectively) were for the first time obtained by the Me3SiNTf2-catalyzed GTP of MMA followed by a termination reaction using functional α-phenylacrylates (2a–2d). All the polymerizations produced end-functionalized PMMAs with controlled molar masses, narrow dispersities, and defect-free polymer structures as designed. The quantitative incorporation of functionalities into the α- or ω-end of the PMMAs was confirmed by the 1H NMR and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) measurements.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...