Activation helix orientation of the estrogen receptor is mediated by receptor dimerization: evidence from molecular dynamics simulations†
Abstract
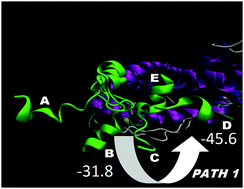
In recent years, the nuclear receptors (NR) dynamics have been studied extensively by various approaches. However, the transition path of helix 12 (H12) to an agonist or an antagonist conformation and the exchange pathway between these states is not clear yet. A number of accelerated molecular dynamics (aMD) runs were performed on both an ERα monomer and a homodimer with a total length of 2.2 μs. We have been able to sample reasonably well the H12 conformational landscape to reproduce precisely both the agonist and the antagonist conformations, starting from an unfolded position, and to describe the transition path between them, even in the presence of an agonist ligand. These conformations were the most prevalent, suggesting that the extended H12 state is not likely to exist and that the natural ERα H12 position might exist in both the agonist and antagonist states. Remarkably, the H12 transition occurs and is regulated only in a dimer form and the proper agonist or antagonist H12 conformation can be achieved solely in one of the dimer subunits. These results clearly demonstrate that clusters of the two well-known H12 states exist by themselves in the protein free energy landscape, i.e. they are not constituted directly by the ligands, and dimerization favors the switch between them. Conversely, in a monomer, no transitions have been observed. Thus, the dimer formation helps the constitution of populations of discrete H12 conformational states and reshapes the conformational landscape. Further analyses have shown that these observations can be explained by specific interface and long range protein–protein interactions, resulting in conformational fluctuations in helices 5 and 11. Based on these results, a new ERα activation/deactivation mechanism and a sequence of binding events during receptor activity modulation have been suggested according to which ligands control the H12 conformation via alterations of the inter-dimer interactions. These findings agree with the HDX and fluorescence experiments and provide an explanation on a structural basis of these data, demonstrating that the dynamics of H12 are not altered greatly upon ligand binding and large fluctuations at the end of H11 are present.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...