Synthesis of lipase nano-bio-conjugates as an efficient biocatalyst: characterization and activity–stability studies with potential biocatalytic applications†
Abstract
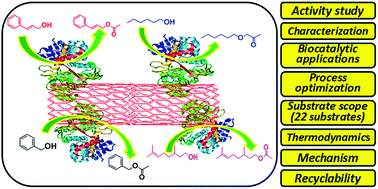
In the present study, we have synthesized lipase-nano-bio-conjugates via immobilization of various lipases on multiwall carbon nano-tubes (MCNT), in order to construct an efficient and recyclable biocatalytic system. In a screening study lipase Pseudomonas fluorescens (PFL) acted as an efficient biocatalyst (lipase-nano-bio-conjugates) which showed higher retention of lipase activity and protein loading. Consequently the immobilization support : lipase (MCNT : PFL) composition was screened in which MCNT : PFL (2 : 1) was calculated as a robust biocatalyst composition which showed higher activity retention and protein loading. This nano-bio-conjugate was then characterized in detail with physical and biochemical techniques using SEM, TEM, FTIR, Km, Vmax, catalytic efficiency and (%) water content analysis. This developed biocatalyst was further used for practical biocatalytic applications such as O-acylation reactions. Various reaction parameters were optimized in detail like reactant molar ratio (2 : 3.5), solvent, MCNT : PFL biocatalyst amount (36 mg), temperature (50 °C) etc. The developed biocatalytic protocol was then extended to synthesize several (twenty-two) industrially important acylated moieties with an excellent yield, these products are well characterized by 1HNMR, 13CNMR and GCMS analysis. Moreover in the present study, we have reviewed the potential industrial applications of various synthesized compounds. Also, we have studied the thermodynamic aspect which demonstrated more feasibility of use of immobilized MCNT : PFL lipase over free lipase. Interestingly, immobilized MCNT : PFL lipase showed 2.3 fold higher catalytic activity than free PFL. Besides this, the biocatalyst was efficiently recycled for up to five cycles. Thus the present protocol demonstrated, (i) synthesis of nano-bio-conjugates as a bio-catalyst, (ii) detailed physical-biochemical characterization of nano-bio-conjugates, (iii) optimization of the biocatalytic protocol (iv) practical biocatalytic applications along with a mechanistic study (v) a thermodynamic feasibility study and (vi) recyclability study.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...