Features of S-nitrosylation based on statistical analysis and molecular dynamics simulation: cysteine acidity, surrounding basicity, steric hindrance and local flexibility†
Abstract
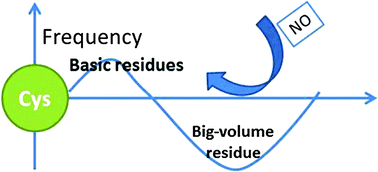
S-Nitrosylation is involved in protein functional regulation and cellular signal transduction. Although intensive efforts have been made, the molecular mechanisms of S-nitrosylation have not yet been fully understood. In this work, we carried out a survey on 213 protein structures with S-nitrosylated cysteine sites and molecular dynamic simulations of hemoglobin as a case study. It was observed that the S-nitrosylated cysteines showed a lower pKa, a higher population of basic residues, a lower population of big-volume residues in the neighborhood, and relatively higher flexibility. The case study of hemoglobin showed that, compared to that in the T-state, Cysβ93 in the R-state hemoglobin possessed the above structural features, in agreement with the previous report that the R-state was more reactive in S-nitrosylation. Moreover, basic residues moved closer to the Cysβ93 in the dep-R-state hemoglobin, while big-volume residues approached the Cysβ93 in the dep-T-state. Using the four characteristics, i.e. cysteine acidity, surrounding basicity, steric hindrance, and local flexibility, a 3-dimensional model of S-nitrosylation was constructed to explain 61.9% of the S-nitrosylated and 58.1% of the non-S-nitrosylated cysteines. Our study suggests that cysteine deprotonation is a prerequisite for protein S-nitrosylation, and these characteristics might be useful in identifying specificity of protein S-nitrosylation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...