Hepatoprotective effect of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. lignans and its formula with Rubus idaeus on chronic alcohol-induced liver injury in mice
Abstract
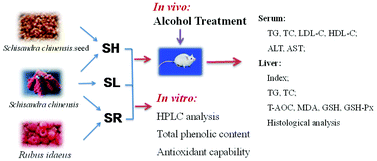
This study aimed to investigate the liver protection effect of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. (SC) lignans and its combination with Rubus idaeus (RI) on chronic alcohol-induced mice. A low level of SC lignans (SL) was prepared from the clear juice of sarcocarp. Lignans were further extracted from the SC seeds and added to the SL to form high-level SC lignans (SH). Moreover, RI clear juice lyophilized powder was mixed with SL (SR), and the liver protection effects of SL, SH and SR were investigated. Male ICR mice were administered with the corresponding samples and gastrically infused with 50% alcohol (1 h later) once per day for 60 d. In the in vitro study, the characteristic lignans in the SC clear juice and the seed extract were analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The total phenolic content (TPC) and antioxidant capability of SL, SH, and SR were determined. The results of the in vivo study showed that SC lignans exhibited a dose-dependent effect on the regulation of hepatic antioxidant status, serum transaminases levels, hyperlipidemia and hepatic fat deposition in mice. However, hepatic lesions were observed in the SH mice, which indicated a potential side effect caused by long-term consumption of SH under chronic alcohol administration. By contrast, SR exhibited a similar hepatoprotective effect as SH without any abnormality found in the histological analysis. After analysis with HPLC, Schizandrol A and Schizandrol B were identified in the SC clear juice, and two more kinds of lignans, Schisandrin A and Schisandrin B, were identified in the seed extracts. The SR sample had the highest TPC and exhibited the best antioxidant capability. In conclusion, RI strengthened the liver protection effect of SC lignans effectively and safely, which was probably achieved by enhancing the antioxidant status and the positive effect of their combination was possibly attributed to both lignans and polyphenols. This study demonstrated that the combination of low-level SC lignans and RI might be used as a potential safe formula for beverage development to alleviate the adverse effects of long-term alcohol consumption.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...