The postprandial glucose response to some varieties of commercially available gluten-free pasta: a comparison between healthy and celiac subjects
Abstract
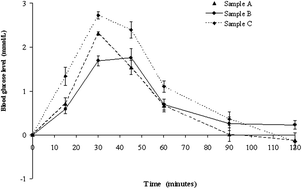
The objective of the present paper is to evaluate the post-prandial response to some varieties of gluten free (GF) pasta that are commonly consumed in Italy. The glycaemic responses were compared with a glucose standard in healthy subjects and gluten-free diet celiac subjects. Subjects were served portions of the test foods and a standard food (glucose), on separate occasions, each containing 50 g available carbohydrates. Capillary blood glucose was measured from finger-prick samples in fasted subjects and at 15, 30, 45, 60, 90 and 120 minutes after the consumption of each test food. For each type of pasta, the glycaemic index (GI) was calculated by expressing the incremental area under the blood glucose curve as a percentage of each subject's average incremental area under the blood glucose curve (AUC) for the standard food. Gluten free pasta exhibited a range of GI values from 46 to 66. The glycaemic load (GL) and glycaemic profile (GP) were also calculated. A higher GI value was observed in pasta containing rice flour as the main ingredient. Lower values were observed in pasta obtained using corn or a mixture of corn and rice flour as the main ingredients. The results were confirmed in celiac subjects. The information presented in this paper may be useful in helping celiac people to select low-GI pasta.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...