Iron-catalyzed aerobic difunctionalization of alkenes: a highly efficient approach to construct oxindoles by C–S and C–C bond formation†
Abstract
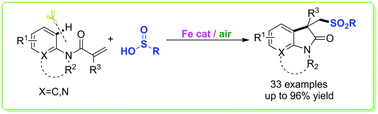
A novel iron-catalyzed efficient approach to construct sulfone-containing oxindoles, which play important roles in the structural library design and drug discovery, has been developed. The use of readily available benzenesulfinic acids, an inexpensive iron salt as the catalyst, and air as the oxidant makes this sulfur incorporation protocol very efficient and practical.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...