The sodium ion-assisted memory behaviour of a silicon nanowire partial composite field-effect transistor†
Abstract
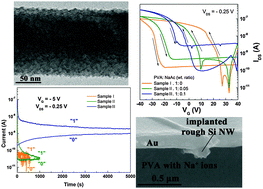
A partial composite consisting of rough silicon nanowires and a polymer dielectric layer with sufficient Na+ ions was used to create a field-effect transistor based memory device. Addition of Na+ ions helped compensate for water molecule trapped charges leading to narrow hysteresis characteristics and stable memory retention stability of the resulting device.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...