The growth mechanism of zinc oxide and hydrozincite: a study using electron microscopies and in situ SAXS†
Abstract
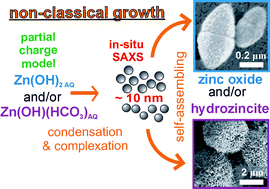
The growth mechanism of ZnO is investigated by a combination of
* Corresponding authors
a
National Institute of Chemistry Slovenia, Hajdrihova 19, Ljubljana, Slovenia
E-mail:
zorica.crnjak.orel@ki.si
Fax: +386 1 476 0300
Tel: +386 1 476 0236
b Centre of Excellence for Polymer Materials and Technologies, Tehnološki park 24, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia
c Materials Research Dept., Ruđer Bošković Institute, P.O. Box 180, Zagreb, Croatia
d Sincrotrone Trieste, S.C.p.A., I-34012 Basovizza, TS, Italy
e Jožef Stefan Institute, Jamova 39, Ljubljana, Slovenia
f Faculty of Computer and Information Science, University of Ljubljana, Tržaška cesta 25, Ljubljana, Slovenia
The growth mechanism of ZnO is investigated by a combination of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
M. Bitenc, P. Podbršček, P. Dubček, S. Bernstorff, G. Dražić, B. Orel and Z. C. Orel, CrystEngComm, 2012, 14, 3080 DOI: 10.1039/C2CE06134A
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
