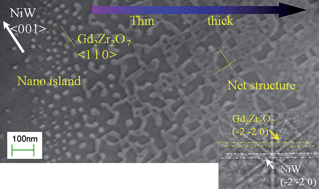
The surface texture and morphology of thin films play an essential role in determining their properties. In this study, local features in the film surface of crystallized Gd2Zr2O7 (GZO) films with a thickness gradient are investigated by means of scanning electron microscopy and electron backscatter diffraction. A strong dependence of the morphology and texture on the film thickness is observed, mainly due to (i) the transition of growth mode associated with the critical film thickness, i.e., increasing the film thickness leads to the grain morphology changing from 2-dimensional discs (highly ordered nanoislands or network) to 3-dimensional domes (equiaxed nanograins), and (ii) the segregation of residual carbon in the surface layer. The epitaxial nuclei forming at the interface hardly further develop by consuming the polycrystalline grains in the surface layer. A two-step annealing procedure is proposed to improve the surface texture in the GZO/NiW system, according to the influence of PO2 on the texture formation of GZO films. A GZO film with strong biaxial texture is achieved, as evidenced by the high indexing rate of Kikuchi patterns on the film surface, as well as by the highly ordered crystal structure along the film thickness observed by a transmission electron microscope. On the basis of the enhanced understanding of the crystallization processes, we demonstrate a possibility of engineering the surface morphology and texture in the film deposited on technical substrates using a chemical solution deposition route.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...