An ESIPT-based fluorescent probe for sensitive detection of hydrazine in aqueous solution†
Abstract
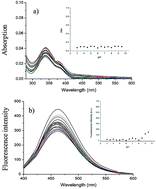
A fluorescent probe for sensitive detection of hydrazine based on an ESIPT mechanism and a substitution–cyclization–elimination cascade was developed. After the addition of hydrazine, an approximately 50-fold enhancement in fluorescence intensity at 465 nm was observed and the subsequent decrease at 375 nm was observed in 10 min with a detection limit of 0.147 μM. We also detected hydrazine in HeLa cells successfully.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...