A polymer in a crowded and confined space: effects of crowder size and poly-dispersity
Abstract
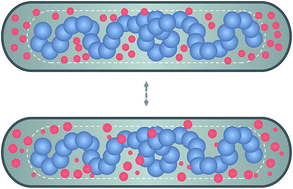
DNA compaction in a bacterial cell is in part carried out by entropic (depletion) forces induced by “free” proteins or crowding particles in the cytoplasm. Indeed, recent in vitro experiments highlight these effects by showing that they alone can condense the E. coli chromosome to its in vivo size. Using molecular dynamics simulations and a theoretical approach, we study how a flexible chain molecule can be compacted by crowding particles with variable sizes in a (cell-like) cylindrical space. Our results show that with smaller crowding agents the compaction occurs at a lower volume fraction but at a larger concentration such that doubling their size is equivalent to increasing their concentration fourfold. Similarly, the effect of polydispersity can be correctly mimicked by adjusting the size of crowders in a homogeneous system. Under different conditions, however, crowding particles can induce chain adsorption onto the cylinder wall, stretching the chain, which would otherwise remain condensed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...