Antimicrobial silica particles synthesized via ring-opening grafting of cationic amphiphilic cyclic carbonates: effects of hydrophobicity and structure†
Abstract
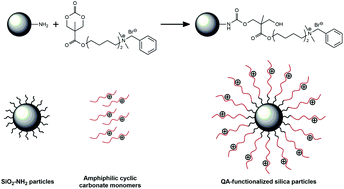
In this study, cationic amphiphilic cyclic carbonates with varying hydrophobicity and structure were synthesized and grafted onto amine-containing silica surface via a ring-opening nucleophilic addition reaction to impart antimicrobial properties. The presence of the coated layer on silica surface was verified by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The effects of the alkyl chain length and the cationic group structure of the surface-grafted carbonate on the antimicrobial efficacy against Gram-positive S. aureus, and Gram-negative E. coli and P. aeruginosa were examined to understand the structure–activity relationship of the surface-coated silica particles. Results indicated that an optimal chain length of the hydrophobic alkyl tail, and the position of the cationic center and benzyl group were crucial in imparting high antimicrobial efficacy especially against difficult-to-kill P. aeruginosa. These quaternary ammonium-functionalized silica particles have various potential antimicrobial applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...