Kinetics of the (salen)Cr(iii)- and (salen)Co(iii)-catalyzed copolymerization of epoxides with CO2, and of the accompanying degradation reactions†
Abstract
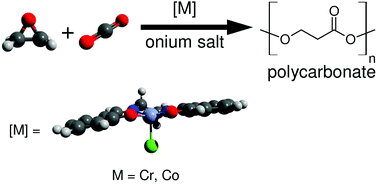
The (salen)Cr(III)- and (salen)Co(III)-catalyzed copolymerization reactions between a variety of epoxides with CO2 were studied by computational methods, and these findings were compared with experimental observations. The displacement of a polymeric carbonate by an epoxide, followed by epoxide ring-opening, was found to be the overall rate determining step (ΔG‡ = 22–27 kcal mol−1), whereas carboxylation of the metal-bound alkoxide is fast (ΔG‡ = 6–8 kcal mol−1). Chromium(III)-catalyzed systems have higher free energy barriers than cobalt(III) systems, consistent with the fact that (salen)Cr(III)-catalyzed polymerization reactions have to be performed at higher temperatures; such differences are attributed to enthalpy. The metal-bound polymer carbonate and alkoxide backbiting reactions generally have higher barriers than when unbound, due to the terminal oxygen atoms’ reduced nucleophilicity. Homopolymerization of epoxides to give polyether defects is negligible in both chromium- and cobalt-catalyzed systems. This is due to carboxylation (metal-bound or metal-free) being competitive, and because displacement of a polymeric alkoxide from the metal center by an epoxide is strongly endergonic.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...