Targeted and efficient activation of channelrhodopsins expressed in living cells via specifically-bound upconversion nanoparticles†
Abstract
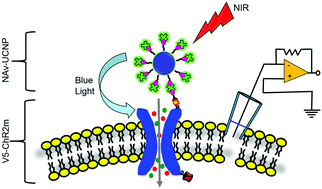
Optogenetics is an innovative technology now widely adopted by researchers in different fields of biological sciences. However, most light-sensitive proteins adopted in optogenetics are excited by ultraviolet or visible light which has a weak tissue penetration capability. Upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs), which absorb near-infrared (NIR) light to emit shorter wavelength light, can help address this issue. In this report, we demonstrated the target selectivity by specifically conjugating the UCNPs with channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2). We tagged the V5 epitope to the extracellular N-terminal of ChR2 (V5-ChR2m) and functionalized the surface of UCNPs with NeutrAvidin (NAv-UCNPs). After the binding of the biotinylated antibody against V5 onto the V5-ChR2m expressed in the plasma membrane of live HEK293T cells, our results showed that the NAv-UCNPs were specifically bound to the membrane of cells expressing V5-ChR2m. Without the V5 epitope or NAv modification, no binding of UCNPs onto the cell membrane was observed. For the cells expressing V5-ChR2m and bound with NAv-UCNPs, both 488 nm illumination and the upconverted blue emission from UCNPs by 980 nm excitation induced an inward current and elevated the intracellular Ca2+ concentration. Our design reduces the distance between UCNPs and light-sensitive proteins to the molecular level, which not only minimizes the NIR energy required but also provides a way to guide the specific binding for optogenetics applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...