Binding multidentate ligands to Ni2+: kinetic identification of preferential binding sites†
Abstract
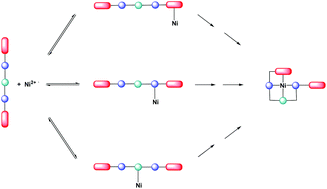
The kinetics of the reactions between [Ni(MeOH)6]2+ (hereafter Ni2+) and a variety of neutral Schiff base multidentate ligands have been measured in methanol at 25.0 °C using stopped-flow spectrophotometry. The ligands contain a variety of different potential donor sites (phenolic OH, imine N, pyridyl N and NH groups), different structural components and substituents. The kinetic studies explore how systematic changes to the composition of the ligands affect the rates of binding. The results are consistent with the Eigen–Wilkins mechanism in which the ligand initially forms an outer-sphere association with Ni2+ prior to dissociation of a coordinated solvent molecule and binding to the metal ion. The general features that emerge from these studies are as follows. (i) For ligands with the same donor set, the rates of binding are all similar irrespective of changes to the ligand framework (bridge and substituents). (ii) Comparison of structurally analogous ligands shows that the presence of pyridyl or NH groups in the multidentate results in significantly faster reactions. (iii) With ligands containing multiple NH groups, the rate of ligand binding increases as the number of NH groups increases. The extent to which these kinetic features can be attributed to preferential binding of particular donor groups is discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...