Induction of hepatocyte functional protein expression by submicron/nano-patterning substrates to mimic in vivo structures
Abstract
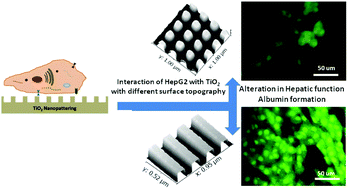
To investigate the influence of bio-inspired metallic superficial topography on the cellular behaviour of a hepatocyte cell line, TiO2 nanopatterns with diversified shapes and heterotropic lateral dimensions were fabricated using electron beam lithography and atomic layer deposition. The dimensional uniformity and shape diversity of the nanopatterns were confirmed using scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy. These topographical nanocues provide good tools for controlling and regulating multiple hepatocellular functions. The expressions of functional proteins such as albumin, transferrin and cytochrome P450 were tested as functional markers. In addition, the change in cellular orientation, cell alignment and native extracellular matrix (ECM) assembly induced by these well-defined nanotopographies were observed. Twelve hours after cell seeding, TiO2 nanogratings with a lateral dimension of 240 nm showed a higher degree of functional protein expression compared to other nanotopographical substrates and a flat surface. These findings suggest that the TiO2 surface resembles a hierarchically-extended collagen nanofibrillar surface and could be recognized by hepatocytes, allowing the proper cytoskeletal orientation and cellular integrity. This TiO2 nanopattern with a specific shape and dimension (240 nm) might therefore emulate ECM biophysical cues, and the intrinsic topography of TiO2 surfaces might evoke enhanced cellular responses. These unique surfaces could be further exploited for tissue engineering and bioreactor technology.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...