Asp-containing actinomycin and tetracyclic chromophoric analogues from the Streptomyces sp. strain S22†
Abstract
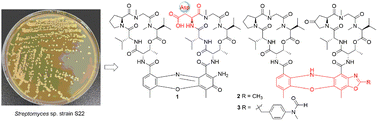
Three novel actinomycins, actimomycin S (1), neo-actinomycins C and D (2 and 3), and one new benzo[d]oxazole alkaloid (4) were isolated from the Streptomyces sp. strain S22, along with three known congeners F9 (5), X2 (6) and X0β (7) and 2-acetylamino-3-hydroxyl-4-methyl-benzoic acid methyl ester (8). The structures of the new products were elucidated by spectroscopic methods, and the absolute configuration of amino acid residues was determined by Marfey's analysis. Actinomycin S contains an aspartic acid (Asp) residue in the β-peptidolactone ring. This is the first report of an Asp residue within an actinomycin-type natural product. Notably, neo-actinomycins C and D feature a rare tetracyclic 5H-oxazolo[4,5-b]phenoxazine chromophore. Among these, neo-actinomycin D, with an unprecedented molecular formula, represents the highest molecular weight member in the actinomycin family. Actinomycins 1–3 exhibited antimicrobial activity against multiple resistant “ESKAPE” pathogens with MIC values ranging from 1.25 to 80.0 μg mL−1. In addition, 1–3 showed potent cytotoxic activities against the HepG2 liver carcinoma cell line with IC50 values of 0.10, 0.32, and 0.024 μM, respectively. Furthermore, 1 inhibited cell proliferation by inducing G0–G1 phase arrest in the cell cycle.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...