A water-soluble fluorescent pH probe and its application for monitoring lysosomal pH changes in living cells†
Abstract
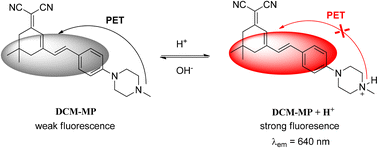
Intracellular pH plays a crucial role in many cellular processes, and abnormal intracellular pH has been linked to common diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer's. To address this issue, a water-soluble fluorescent pH probe was designed based on the protonation/deprotonation of the 4-methylpiperazin-1-yl group, using dicyanoisophorone as the fluorophore. In the neutral form of the probe, fluorescence is quenched due to charge transfer from the 4-methylpiperazin-1-yl group to the fluorophore upon excitation. Under acidic conditions, protonation of the 4-methylpiperazin-1-yl group inhibits the photoinduced electron transfer process, leading to an increase in fluorescence intensity. Density-functional theory calculations also verified the fluorescence OFF–ON mechanism. The probe exhibits high selectivity, photostability, fast response to pH changes, and low cytotoxicity to cells. Additionally, the probe selectively accumulates in lysosomes, with a high Pearson coefficient (0.95) using LysoTracker Green DND-26 as a reference. Notably, the probe can monitor lysosomal pH changes in living cells and track pH changes stimulated by chloroquine. We anticipate that the probe has potential for diagnosing pH-related diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...