Renewable-power-assisted production of hydrogen and liquid hydrocarbons from natural gas: techno-economic analysis†
Abstract
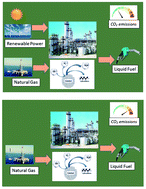
The declining cost of renewable power has engendered growing interest in leveraging this power for the production of chemicals and synthetic fuels. Here, renewable power is added to the gas-to-liquid (GTL) process through Fischer–Tropsch (FT) synthesis in order to increase process efficiency and reduce CO2 emissions. Accordingly, two realistic configurations are considered which differ primarily in the syngas preparation step. In the first configuration, solid oxide steam electrolysis cells (SOEC) in combination with an autothermal reformer (ATR) are used to produce synthesis gas with the right composition, while in the second configuration, an electrically-heated steam methane reformer (E-SMR) is utilized for syngas production. The results support the idea of adding power to the GTL process, mainly by increased process efficiencies and reduced process emissions. Assuming renewable power is available, the process emissions would be 200 and 400 gCO2 L−1 syncrude for the first and second configurations, respectively. Configuration 1 and 2 show 8 and 4 times less emission per liter syncrude produced, respectively, compared to a GTL plant without H2 addition with a process emission of 1570 gCO2 L−1 syncrude. By studying the two designs based on FT production, carbon efficiency, and FT catalyst volume, a better alternative is to add renewable power to the SOEC (configuration 1) rather than using it in an E-SMR (configuration 2). Given an electricity price of $100/MW h and natural gas price of 5 $ per GJ, FT syncrude and H2 can be produced at a cost between $15/MW h and $16/MW h. These designs are considered to better utilize the available carbon resources and thus expedite the transition to a low-carbon economy.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Open Access Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...