Pomegranate juice alters the microbiota in breast milk and infant stool: a pilot study†
Abstract
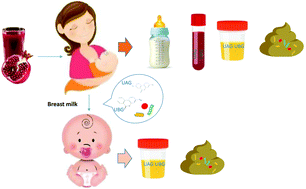
Pomegranate juice (PomJ) contains ellagitannins (ETs) that are metabolized to ellagic acid (EA). Intestinal bacteria convert EA further to urolithins that are absorbed into the circulation and may provide health benefits. PomJ consumption by pregnant women was reported to be neuroprotective for their infants. In order to determine whether EA and metabolites are transferred from breast milk of mothers consuming PomJ to nursing infants, we performed an interventional pilot study and enrolled ten healthy women with full-term, exclusively breast-fed infants, consuming 8 oz. of PomJ daily for two weeks. Breast milk, plasma, urine and stool samples were collected from the mothers and the urine and stool samples from the infants before and after two weeks of PomJ consumption. Samples were analyzed using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry to identify EA metabolites and 16S rRNA sequencing to determine changes in the microbiota. EA metabolite conjugates (dimethyl EA-glucuronide DMEAG and urolithin A-glucuronide UAG) were found in breast milk, plasma and urine from mothers and in urine of infants after 14 days of PomJ consumption. In addition, urolithin B-glucuronide (UBG) was found in breast milk, plasma and urine from two participants and urine from their infants. PomJ consumption was associated with a significant decrease in breast milk of Lactococcus, Subdoligranulum, and Acinetobacter, while the abundance of Firmicutes/Faecalibacterium increased significantly. In breast milk Escherichia/Shigella was inversely correlated to breast milk UAG. In infant stools, the abundance of Lachnoclostridium and Staphylococcus was increased. Infant stool Blautia was positively correlated to breast milk and mother plasma UBG. This pilot study demonstrates that EA and its metabolites are absorbed by the nursing infant from breast milk, excreted in urine and impact the infant gut microbiome. The concentration of EA metabolites in breast milk increased over time. Phenolic compounds in breast milk could be a way to promote neuroprotective, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory health benefits in infants.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...