The anti-infective activity of Salvia miltiorrhiza against Staphylococcus aureus by attenuating accessory gene regulator system-mediated virulence†
Abstract
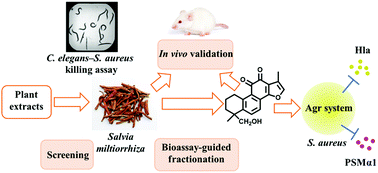
Due to the rapid evolution of antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus, antivirulence therapy may be a promising alternative for the effective control of the spread of resistant pathogens. The Chinese Materia Medica has been widely used for the treatment of diseases and production of health foods, and it remains a valuable resource for the discovery of compounds possessing antivirulence activity. Through a Caenorhabditis elegans infection model, an EtOAc-soluble fraction of 80% EtOH extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (SMEA) was found to possess potential anti-infective activity against S. aureus. Then, several in vitro assays indicated that SMEA had robust antivirulence activity at the dose of 400 μg mL−1, reducing hemolytic activity and α-hemolysin expression in S. aureus. Furthermore, at 100 mg kg−1, SMEA reduced abscess formation in the main organs of mice challenged with S. aureus. In order to identify the bioactive components of SMEA and investigate the mechanisms underlying the antivirulence activity, SMEA was separated using bioassay-guided fractionation. As a result, eight compounds were identified in SMEA. Among them, tanshinone IIB (TNB) showed strong antivirulence activity both in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, at 24 μg mL−1, TNB significantly reduced the expression of RNAIII and psmα, indicating that the mechanism underlying TNB activity was related to the accessory gene regulator quorum sensing system. In conclusion, TNB's antivirulence properties make it a promising candidate for drug development against S. aureus infections.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...