Low temperature synthesis of Ag@anatase TiO2 nanocomposites through controlled hydrolysis and improved degradation of toxic malachite green under both ultra-violet and visible light
Abstract
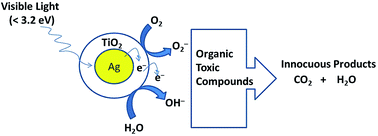
The nanocomposite material of titania coated silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) was prepared by employing a combination of two different synthetic routes. The proposed strategy demonstrates the utilization of a radiation chemical route to synthesize natural biopolymer gum acacia capped AgNPs at a very low pH followed by the controlled hydrolysis of Ti-tetra isopropoxide (TiPP) at low temperature for better growth of the titania shell on the AgNPs. The formation of the hybrid Ag–TiO2 nanocomposites was confirmed through UV-Vis spectroscopic analysis, which showed a red shift in the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) peak of the Ag NPs (about 15 nm) and a blue shift in the case of TiO2 (about 10 nm) with concomitant reduction in the intensity of peak of the AgNPs at 410 nm. In addition, the synthesized materials were characterized by dynamic light scattering (DLS), Fourier transform infra-red (FTIR) spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The as-synthesized TiO2 NPs and Ag@TiO2 nanocomposites were subsequently applied to the photochemical degradation of the toxic dye molecule, malachite green (MG), chosen as a model pollutant. The apparent photocatalytic degradation rate constants in regard to the Ag@TiO2 and TiO2 nanomaterials were calculated to be 0.25 and 0.05 min−1, respectively. The photocatalytic degradation rates of MG by the Ag@TiO2 nanocomposites under visible light illumination were found to be nearly 42 times higher than that of the TiO2 NPs implicating its great promise for the improved degradation of toxic materials such as azo dyes using visible solar light.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...