A novel supramolecular aggregated liquid–solid microextraction method for the preconcentration and determination of trace amounts of lead in saline solutions and food samples using electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry
Abstract
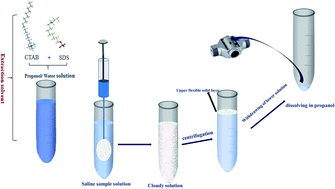
A novel supramolecular aggregated liquid–solid microextraction method was developed for the preconcentration and determination of trace amounts of lead in saline solutions and food samples. The technique was based on catanionic assemblies of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide and sodium dodecyl sulphate surfactants as a new green extraction solvent for use in a dispersive microextraction method coupled with electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. This technique benefits from the safe and green properties of the supramolecular aggregates rather than the hazardous and volatile organic solvents commonly used in liquid–liquid microextraction methods. The main component of the dispersive solvent is water and a direct interaction between the extraction solvent and the analyte is possible. The separation behaviour of the sodium dodecyl sulphate/cetyltrimethylammonium bromide solvent phase and various parameters influencing the extraction efficiency of lead (e.g. pH, salt concentration, centrifugation time, amount of ligand and extraction solvent) were investigated and optimized. Under the optimum conditions, linearity was observed in the range 0.1–2.0 ng mL−1 lead with a correlation coefficient of 0.996 and a limit of detection (S/N = 3) of 0.047 ng mL−1. The relative standard deviations were 6.5 and 5.2% for five repeated measurements of 0.4 and 1.0 ng mL−1 lead solutions, respectively. The effects of some common anions and cations on the lead signal were investigated. The proposed method was successfully applied to the determination of lead in sea water and some food samples. The accuracy of the method was confirmed by analysing a certified reference material.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...