Selective adsorption and separation of dyes from an aqueous solution on organic–inorganic hybrid cyclomatrix polyphosphazene submicro-spheres†
Abstract
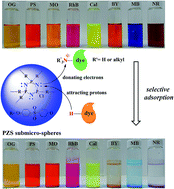
Nitrogen-enriched and organic–inorganic hybrid polymer submicro-spheres based on highly cross-linked poly(cyclotriphosphazene-co-4,4′-sulfonyldiphenol) (PZS) were prepared using one-step precipitation copolymerization route. The chemical structure and morphology of the submicro-spheres were characterized. The adsorption behaviors of the submicro-spheres towards different organic dyes in an aqueous solution were investigated systematically. The results showed that PZS submicro-spheres could effectively adsorb methylene blue (MB), Bismarck brown Y (BY), neutral red (NR), rhodamine B (RhB), and calcein (Cal) with high adsorption capacities, but they could hardly adsorb orange G (OG), Ponceau S (PS), and methyl orange (MO), indicating that PZS submicro-spheres could adsorb guest dyes selectively. The adsorption process was found to follow the pseudo-second-order kinetic model rather than the pseudo-first-order one. Isotherm studies revealed that the Langmuir model was more suitable for describing the adsorption behavior of the PZS submicro-spheres than the Freundlich model. A probable mechanism based on the unique host–guest interactions between the submicro-spheres and the dyes was proposed and experimentally verified to explain the selective adsorption. The nitrogen-enriched PZS submicro-spheres possess electron-donating and proton-attracting abilities and could act as bases, and thus the dyes that are classified as Lewis acids (electron acceptor) and/or Brønsted acids (proton donor) could be selectively adsorbed onto the submicro-spheres by acid–base interactions. Because of the selective adsorption behavior towards different organic dyes, PZS submicro-spheres also exhibited a strong ability for separating dye mixtures in an aqueous solution.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...