Chlorine/UV induced photochemical degradation of total ammonia nitrogen (TAN) and process optimization
Abstract
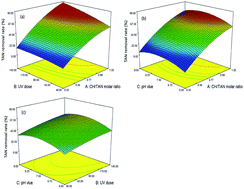
Total ammonia nitrogen (TAN) is a pollutant which is spread throughout the world in surface water systems, and this leads to a reduction in water treatment efficiency and the generation of highly toxic disinfection by-products. Although the chlorine/UV process has been demonstrated to be effective for TAN degradation, no information is available to describe the effects of the reaction parameters on TAN control. In this study, experiments were conducted to investigate the effects of the chlorine : TAN molar ratio, UV dose and pH on TAN removal efficiency. Experimental results indicated that both the chlorine : TAN molar ratio and UV dose represented positive effects, while pH showed a complex effect on TAN removal. The interaction between the chlorine : TAN molar ratio and UV dose was also significant, implying a synergistic effect in the chlorine/UV process. Response surface methodology (RSM) was applied to establish the regression model and optimize the chlorine/UV process. Based on the optimization parameter, the combined process was used to treat TAN-containing raw water. The experimental results matched well with the predicted response, indicating the proposed model was accurate and reliable. The main photodecomposition products were nitrate, accompanied with a little amount of nitrite. The mechanism of TAN decomposition in the chlorine/UV process was proposed as UV induced photolysis of chloramine and intermediate radical oxidation. This study demonstrated the chlorine/UV process as an effective strategy for TAN control in water treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...