Micro-patterned polymer brushes by a combination of photolithography and interface-mediated RAFT polymerization for DNA hybridization†
Abstract
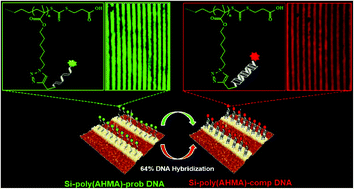
The fabrication of micro-patterned polymer brushes for DNA attachment and subsequent hybridization were investigated by ellipsometry, confocal microscopy and atomic force microscopy. The attachment of TTC5 ([2-(2-carboxyethylsulfanylthiocarbonylsulfanyl)propionic acid]) to the aminodecane functionalized surface (Si–NH2) was achieved by an amide reaction in the presence of N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) and EDC (N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride). The RAFT agent layer on the silicon substrate (Si-TTC5) was then exposed to UV radiation and oxygen plasma through a patterned photoresist. Micro-patterned polymer brushes were obtained by interface-mediated RAFT polymerization of AHMA (6-azidohexylmethacrylate) and followed a click reaction to attach the amine groups for the immobilization of biotin-functionalized DNA probes. Cy3-labelled single stranded DNA probes were first bound to amino-functionalized photopatterned polymer brushes. DNA immobilization was studied by using laser scanning confocal microscopy. Probe DNA immobilized photopatterned surfaces were then hybridized with Cy5-labelled complementary and non-complementary DNA probes to investigate the hybridization efficiencies. Hybridization experiments reveal that the DNA-modified substrates demonstrate a high specificity for the recognition of complementary DNA (Cy5-labelled) under hybridization conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...