Theoretical study on catalyzed selective photoreduction mechanism for 4-bromobenzaldehyde in two different solvents
Abstract
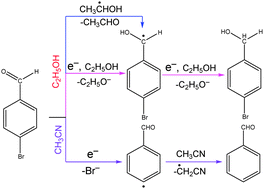
The density functional theory (M06-2X) method has been employed to investigate the selective photoreduction mechanism in ethanol and acetonitrile solvents for 4-bromobenzaldehyde (4-BBA) reduced by photoelectrons, which are produced by illumination of TiO2. The solvent effects of ethanol and acetonitrile are considered by the SMD solvent model. The computational results show that the reaction is selective in different solvents. In ethanol solvent, the carbonyl reduction process is favored both in thermodynamics and kinetics, and 4-BBA could be reduced to the product, 4-bromobenzyl alcohol. However, owing to it not being a good proton donor solvent, the debromination reduction process in acetonitrile is favored. These results are consistent with the experimental observations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...