Lignin extraction from biomass with protic ionic liquids†
Abstract
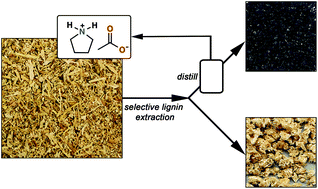
A highly effective method has been developed for the simple extraction of lignin from lignocellulosic biomass using a potentially inexpensive protic ionic liquid (PIL). After the lignin-extraction step, the PIL is easily recovered using distillation leaving the separated lignin and cellulose-rich residues available for further processing. Biopolymer solubility tests indicate that increasing the xylan (i.e., hemicellulose) solubility in the PIL results in greater fiber disruption/penetration, which significantly enhances the effectiveness of the lignin extraction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...