In situ-forming robust chitosan-poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels prepared by copper-free azide–alkyne click reaction for tissue engineering†
Abstract
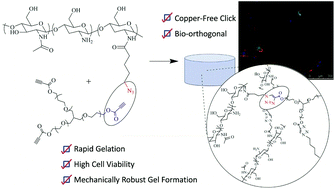
A water-soluble azide-functionalised chitosan was crosslinked with propiolic acid ester-functional poly(ethylene glycol) using copper-free click chemistry. The resultant hydrogel materials were formed within 5–60 min at 37 °C and resulted in mechanically robust materials with tuneable properties such as swelling, mechanical strength and degradation. Importantly, the hydrogels supported mesenchymal stem cell attachment and proliferation and were also non-toxic to encapsulated cells. As such these studies indicate that the hydrogels have potential to be used as injectable biomaterials for tissue engineering.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating our 2018 prize and award winners

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...