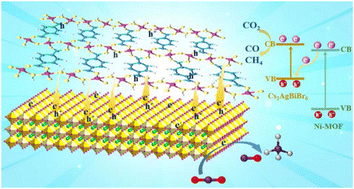
A lead-free Cs2AgBiBr6 double perovskite is emerging as a promising candidate to replace toxic lead halide perovskites because of its environmental friendliness and impressive stability. However, the applications of Cs2AgBiBr6 (CABB) in photocatalytic CO2 reduction are restricted by its poor charge separation and low CO2 capturing ability. Herein, we report a novel inorganic/organic hybrid photocatalyst by coupling two-dimensional (2D) CABB nanosheets (NSs) with 2D Ni-based metal–organic framework (Ni-MOF) NSs. Systematic studies suggest the formation of an S-scheme heterojunction between CABB and the Ni-MOF, which facilitates the separation of photogenerated charge carriers and preserves the high redox potential of the hybrid. The Ni-MOF also serves as a CO2 capturing agent to facilitate the surface reaction. These remarkable features endow the CABB/Ni-MOF hybrid with significantly enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction performance, which is 6.43 and 8.79 times higher than that of solitary CABB and Ni-MOF, respectively. This study offers a novel photocatalytic system based on lead-free double perovskites and MOFs, which sheds light on fabricating highly efficient photocatalysts for artificial photosynthesis.