Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly (PISA) – control over the morphology of nanoparticles for drug delivery applications†
Bunyamin
Karagoz
a,
Lars
Esser
bcd,
Hien T.
Duong
b,
Johan S.
Basuki
b,
Cyrille
Boyer
*b and
Thomas P.
Davis
*bcd
aIstanbul Technical University, Department of Chemistry, Maslak 34469, Istanbul, Turkey. Fax: +90 212 285 6386; Tel: +90 212 285 3261
bAustralian Centre for Nanomedicine, The University of New South Wales, Sydney NSW2052, Australia. E-mail: cboyer@unsw.edu.au; Fax: +61 2 9385 5966; Tel: +61 2 9385 4333
cMonash Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences (MIPS), Monash University, VIC 3052, Australia. E-mail: Thomas.P.Davis@monash.edu; Fax: +61 3 9903 9581; Tel: +61 3 9903 9635
dDepartment of Chemistry, University of Warwick, Coventry CV47AL, UK
First published on 22nd October 2013
Abstract
In this paper, we describe the synthesis of asymmetric functional POEGMA-b-P(ST-co-VBA) copolymers in methanol, yielding in one-pot polymerization a range of nanoparticle morphologies, including spherical micelles, worm-like, rod-like micelles and vesicles. The presence of the aldehyde group was then exploited to form crosslinks or to conjugate chemotherapy compounds, such as doxorubicin, via pH-breakable bonds (Schiff base or imine) directly to the preformed nanoparticles. The influence of the nanoparticle morphologies on the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line uptake was investigated using flow cytometry and confocal microscopy. Finally, the IC50 of DOX, following nanoparticle delivery, was studied showing significant influence of the nanoparticle carrier morphology on therapeutic efficacy for breast cancer.
Drug delivery carriers, such as polymeric nanoparticles, organic/inorganic nanoparticles, and dendrimers, have been widely used for therapeutic treatments in oncology and cardiovascular disease, as they can increase therapeutic efficacy by changing biodistribution via passive or active targeting.1 A number of different polymeric drug delivery platforms have already been used in human trials with very promising results.2 Most commonly, spherical nanoparticles have been used for drug delivery, whilst in contrast, other morphologies have received little attention, despite evidence that not only size but also morphology can make a considerable difference to the efficacy of drug delivery.1b,3 DeSimone and co-workers4 prepared different polymeric nanoparticles using top-down lithography fabrication, and subsequently, demonstrated that cylindrical sub-micromic particles presented higher cell uptake than equivalent cubic particles. In a more recent study by Ruoslahti, Mitragotri and co-workers,5 a higher cell uptake of polystyrene (PST) rods (compared to PST nanospheres) was reported. The same authors also demonstrated a preferential cell uptake of nanorods in targeted tissues using in vivo studies.5a Thus, the published evidence strongly indicates that the nanoparticle morphology can play a key role in governing biodistribution and bioactivity.
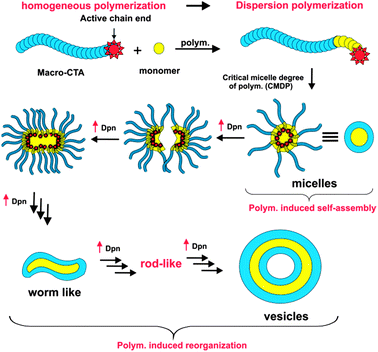
In the current study, we prepared different morphologies of polymeric nanoparticles using self-assembly of asymmetric block copolymers.6 The first studies highlighting self-assembly of asymmetric block copolymers in solution were reported by Eisenberg's group,7 using self-assembly of polystyrene-b-polyacrylic acid diblock copolymers; different nanoparticle morphologies (spherical micelles,8 worm-like micelles3c,9 and vesicles10) were obtained by self-assembly using co-solvency manipulation. One of the main drawbacks of the Eisenberg approach is the low polymer concentrations required (around 1%, w/w), limiting scale-up. There have been a number of recent synthetic developments addressing the problem of low concentration, as described in papers by An,11 Charleux,12 Armes13 and Pan.14 The common feature of the three new approaches is the exploitation of simultaneously inducing self-assembly during the actual polymerization process. We were inspired by the initial work of Armes13 and Pan14 to develop a new approach to synthesize polymeric nanoparticles with morphological control, using “polymerization induced self-assembly” (PISA). The PISA concept is based on the chain extension of homopolymers with a co-monomer to yield asymmetric block copolymers. During the chain extension with the second block, self-assembly is induced by the insolubility of the second block in the polymerization solution. The PISA approach can be used to prepare families of nanoparticles varying in morphology using a single initial homopolymer via a simple one-pot reaction.
In the present work, a one-pot RAFT dispersion polymerization with simultaneous self-assembly into controlled structures is reported. Morphologies such as worm-like and rod-like vesicles and micelles were all formed from well-defined amphiphilic block copolymers, poly[oligo(ethyleneglycol) methacrylate]-block-[poly(styrene)-co-poly(vinyl benzaldehyde)] (POEGMA-b-P(ST-co-VBA)), synthesized by chain extension of dithiobenzoate functional POEGMA using RAFT polymerization. Morphology control was achieved by manipulating the number-average degree of polymerization (DPn) of the P(ST-co-VBA) blocks in the methanol polymerization medium. As the DPn of the core polymer increased (with conversion) the block copolymers assembled sequentially into spherical micelles → worm-like micelles → rod-like → vesicles, as determined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements. The aldehyde groups positioned in the core of the micellar structures were subsequently reacted with various amino compounds to either conjugate chemotherapy drugs or to crosslink the nanostructures. Diamino compounds were employed to crosslink the core nanoparticles using pH-responsive bonds (imines). The aldehyde groups were also exploited to conjugate doxorubicin (DOX, a commonly employed chemotherapy drug) via pH breakable bonds (Schiff base or imine), with a drug loading of 5 wt%. The drug-loaded, self-assembled nanoparticles were then used to deliver DOX to breast cancer cells (MCF-7). Flow cytometry and confocal microscopy revealed different cell uptake mediated by the different nanoparticle morphologies. Cell viability assays using MCF-7 breast cancer cells were also conducted showing a significant effect of morphology on cytotoxicity.
Initially, we successfully synthesized POEGMA homopolymers using RAFT polymerization15 (Scheme S1 in the ESI†) with CPADB as a RAFT agent for 12 h at 70 °C (Fig. S1 and S2 in the ESI and Table S1†). The homopolymerization reactions were stopped at a conversion of around 60% to minimize the formation of dead polymers, yielding POEGMA with Mn, NMR = 11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 100 g mol−1 and PDI = 1.09 (Fig. S2 in the ESI†). POEGMA was then chain extended using a mixture of ST and VBA (95–5 mol%) in methanol. The solvent, methanol, was deliberately chosen as the P(ST-co-VBA) block is insoluble in methanol, while in contrast, the monomers ST and VBA are soluble. The dispersion polymerization reactions were carried out at 70 °C using different polymerization times to control conversion and hence molecular weight (Scheme 1). To maintain good control over polymerization, it is important to maintain high RAFT end-group fidelity and a constant radical concentration even under phase separation conditions. This high-level of control was maintained using a high molar feed ratio 1
100 g mol−1 and PDI = 1.09 (Fig. S2 in the ESI†). POEGMA was then chain extended using a mixture of ST and VBA (95–5 mol%) in methanol. The solvent, methanol, was deliberately chosen as the P(ST-co-VBA) block is insoluble in methanol, while in contrast, the monomers ST and VBA are soluble. The dispersion polymerization reactions were carried out at 70 °C using different polymerization times to control conversion and hence molecular weight (Scheme 1). To maintain good control over polymerization, it is important to maintain high RAFT end-group fidelity and a constant radical concentration even under phase separation conditions. This high-level of control was maintained using a high molar feed ratio 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5000 of POEGMA:ST-VBA in methanol (wsolvent
5000 of POEGMA:ST-VBA in methanol (wsolvent![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) wmonomer = 1
wmonomer = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
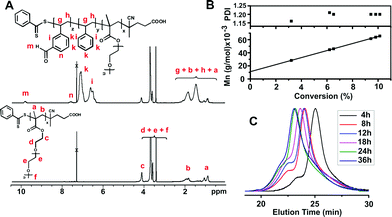
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). After chain extension, the amphiphilic block copolymer structure was characterized by comparing 1H-NMR spectra of the polymer chains before and after chain extension (Fig. 1A). Characteristic aldehyde proton and aromatic proton signals of PVBA were clearly observed at 9.9 ppm (m) and at 7.5 ppm (n), adjacent to polystyrene protons, confirming successful chain extension.
1). After chain extension, the amphiphilic block copolymer structure was characterized by comparing 1H-NMR spectra of the polymer chains before and after chain extension (Fig. 1A). Characteristic aldehyde proton and aromatic proton signals of PVBA were clearly observed at 9.9 ppm (m) and at 7.5 ppm (n), adjacent to polystyrene protons, confirming successful chain extension.
During the chain extension of POEGMA, molecular weight values and polydispersity indices of sample block copolymers were determined by 1H-NMR spectroscopy and SEC measurements taken at different polymerization times (Table S2 in the ESI†). VBA was observed to polymerize faster than ST, indicating the formation of pseudo-gradient polymers. The molecular weight values determined by NMR and SEC were in accord with theoretical values showing a linear increase with conversion (Fig. 1B) and low PDIs, consistent with the known traits of living polymerization.16 SEC traces of the block copolymers taken at increasing polymerization times (Fig. 1C) indicate unimodal molecular weight distributions and incremental shifts to lower retention times. The presence of molecular weight shoulders at lower retention times is consistent with the formation of dead polymers by coupling reactions, in accordance with a slight increase in PDI (1.16 to 1.20) (Table S2 in the ESI†).
During the polymerization, we observed that the polymerization solution became cloudy-milky, indicating the formation of nanoparticles. This result motivated us to determine the size of the nanoparticles by DLS. The diameters of the nanoparticles obtained from the dispersion block copolymerization/self-organization were measured at different polymerization times using DLS (Fig. 2B). The measurements were done following dilutions in methanol of the polymerization solutions prepared with a feed molar ratio of POEGMA:ST–VBA:AIBN = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4750–250
4750–250![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.1. The sizes of the nanoparticles were found to steadily increase with polymerization time; the number average sizes of the block copolymers increased from 25 nm to finally attain 144 nm (Fig. 2B), with relatively low dispersities (<0.2). We observed an anomaly in the DLS results, in which the sample taken at 36 h gave smaller diameter nanoparticles than the previous sample taken at 24 h reaction time. We believe that this anomaly can be attributed to a morphology switch from rod-like to vesicle structures.
0.1. The sizes of the nanoparticles were found to steadily increase with polymerization time; the number average sizes of the block copolymers increased from 25 nm to finally attain 144 nm (Fig. 2B), with relatively low dispersities (<0.2). We observed an anomaly in the DLS results, in which the sample taken at 36 h gave smaller diameter nanoparticles than the previous sample taken at 24 h reaction time. We believe that this anomaly can be attributed to a morphology switch from rod-like to vesicle structures.
Nanoparticle morphologies were investigated using TEM before and after purification using dialysis against methanol. The images (Fig. 2C, see Fig. S3 in the ESI† for additional TEM images) showed that core functional asymmetric block copolymer aggregates first formed spherical micelles after 4 h, and subsequently, worm-like and rod-like vesicles with increasing polymerization times. TEM micrographs confirmed the existence of four different morphologies, ranging from micelle to vesicles, from a single polymerizing system, with sizes in accordance with DLS data (Fig. 2C). SEM also confirmed the formation of different morphologies observed by TEM (data not shown) (Fig. 3).
The morphology changes were governed by the P(ST-co-VBA) chain lengths during the polymerization reaction. Spherical micelles formed from the block copolymer aggregates when DPn of the P(ST-co-VBA) block reached 175 units (Fig. 2A). A morphology transition from micelles to worm and rod-like structures was observed for P(ST-co-VBA) blocks greater than 340 repeating units. Finally vesicles were formed when DPn of the second block reached over 500. Scheme 2 summarizes the different phases of self-assembly that we observed during the polymerization.
Core-crosslinking of the POEGMA-b-P(ST-co-VBA) asymmetric block copolymer was achieved by reacting aldehyde groups with 1,3-diaminopropane in methanol at room temperature, followed by reduction in the presence of sodium borohydrate to yield secondary amine (Scheme 3). In this way, we could stabilize the self-assembled block copolymer nanoparticles via unbreakable bonds.
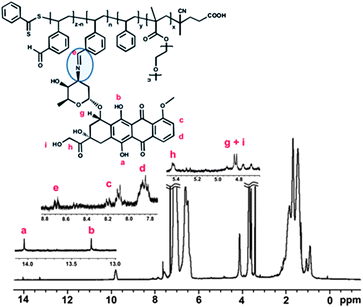
The structural changes after core-crosslinking of the block copolymer were studied using FT-IR spectroscopy (Fig. S4 in ESI†). The FT-IR spectra shown in Fig. S4A in the ESI,† are taken from the block copolymer solution before crosslinking; characteristic aldehyde and methacrylate ester carbonyl peaks can be observed at 1700 and 1740 cm−1. After crosslinking (Fig. S4B in the ESI†) a new absorption peak appears at 1650 cm−1, corresponding to imine (C·N) stretching vibrations. Furthermore, a decrease of the aldehyde carbonyl absorption at 1700 cm−1 is consistent with successful crosslinking of the block copolymers via reaction of the aldehyde group. The imine bond was successively converted to secondary amine by reduction in the presence of sodium borohydride. In addition, TEM was performed on the vesicles after core cross-linking using THF as solvent. THF has been chosen because it can solubilize both blocks. TEM confirmed the integrity of the vesicles in THF after cross-linking (Scheme 3 and Fig. S5 in the ESI† for additional TEM pictures).
The presence of aldehyde groups in the core of the nanoparticles was exploited to conjugate a widely used chemotherapy drug, doxorubicin (DOX), via pH-responsive bonds. The amino groups intrinsic to HCl/DOX (commercial form) were reacted overnight with the aldehyde groups (in methanol) in the presence of triethylamine to neutralize the HCl (Scheme S2 in the ESI†). This synthetic strategy was previously reported by us to successfully conjugate DOX to star polymers and other nanoparticles without any loss in DOX cytotoxicity.17 After DOX was loaded into the nanoparticles and subsequent careful purification, the amount of DOX conjugated was determined by UV-visible spectroscopy using the strong absorption at 495 nm together with a calibration curve (Fig. S6 and S7 in the ESI†). The drug loading efficiency was determined to be ∼67%. 1H NMR spectroscopy confirmed the decrease in the aldehyde signal at 9.9 ppm. The drug loading values, independently measured, using both NMR and UV-visible spectroscopy methods were in good agreement. A new signal in the NMR spectra (at 8.7 ppm) was attributed to imine formation. TEM analysis on the nanoparticles, after drug conjugation, indicated no significant size or morphological changes in water and in methanol (Fig. S8 in the ESI†).
We compared the drug delivery potential of the four different nanoparticle morphologies, i.e. micelle, worm-like, rod-like and vesicle. The drug loading was fixed at 5% w/w. Firstly, the nanoparticle cell-uptake in breast cancer cells (MCF-7) was investigated using both flow cytometry and confocal microscopy (Fig. S9 and S10 in the ESI†). DOX accumulation is easy to monitor as it has fluorescence emissions at 565 and 630 nm permitting direct tracking in cells.
The four different DOX-loaded nanoparticles were incubated with MCF-7 cells for 24 h (concentration of 0.125 μM based on DOX). At different time points (1 h, 5 h and 24 h), the cells were analyzed by flow cytometry to monitor the uptake of DOX (Fig. S9 in the ESI†). After 1 h, different nanoparticle cell uptake processes were observed (higher uptake to less): rod-like ∼ worm-like > vesicle ∼ micelle. As the incubation time increased (24 h), the results indicated that nanoparticle cell uptake was enhanced for worm and rod-like structures (in comparison to micelles and vesicles). Prior observations made on hard-core nanoparticles (such as gold nanorods) and soft-nanoparticles (PST nanoparticles) seem consistent with our findings.18 For example, Tang and co-workers investigated the influence of the silica nanoparticle shapes on the cell uptake using human melanoma cells (A375).19a The authors demonstrated that worm and rod-like (cylindrical) shapes, presenting a higher aspect ratio compared to spherical shape, showed a greater adhesion of nanoparticles to the cell membrane due to their high surface of contact. This high adhesion of these cylindrical nanoparticles stimulated the cell uptake. Dawson, Aberg and co-workers obtained a similar result using PST nanoparticles.19b The authors correlated the adhesion of these nano-objects with the cell membranes with their cell uptake. In conclusion, the higher aspect ratio of cylindrical nanoparticles (worm or rod-like) compared to spherical nanoparticles results in a higher surface of contact with the cell membranes, promoting cell uptake.
Confocal microscopy confirmed the accumulation of DOX in the cytoplasm for all the different nanoparticles (Fig. S10 in the ESI†). Cytotoxicity studies were also performed using the 4 different nanostructures loaded with DOX using the MCF-7 cell-line.
Firstly, the 4 polymeric nanoparticles without DOX were all non-toxic at the concentrations employed in this study up to 10 mg mL−1 in good agreement with our previous studies using similar polymers (data not shown).20 After DOX conjugation, we observed differences in cytotoxicity dependent on the nanoparticle morphology, with the lowest IC50 values obtained for worm and rod-like structures (7 times lower than spherical micelles), while the highest IC50 was observed for micelles and vesicles. The enhancement in toxicity of the worm and rod-like nanoparticles might be related to higher cell uptake (although further studies would be required to clarify this result). Over ∼80% of DOX was released from the nanoparticles at pH 5.0 after 72 h, while very slow release was observed at pH 7.4 (∼10%) demonstrating that DOX released in a controlled manner. Interestingly, no significant difference of DOX released was observed between the different morphologies (Fig. S11 in the ESI†) at pH 5.0 and at pH 7.4. As a comparison, we determined IC50 of Dox for MCF-7. The IC50 value of Dox is in good agreement with published values (Table 1).21
| Shapes | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|
| Dox | 0.093 (± 0.008) |
| Micelles-Dox | 2.193 (± 0.1) |
| Vesicles-Dox | 1.928 (± 0.2) |
| Rod-like-Dox | 0.796 (± 0.1) |
| Worm-Dox | 0.302 (± 0.02) |
Conclusions
In this study, we successfully prepared four different functional POEGMA-b-P(ST-co-VBA) block copolymer nanoparticles using one-pot polymerization induced self-assembly. Aldehyde groups in the nanoparticle cores were exploited to both crosslink, imparting stability, and conjugate doxorubicin. Using MCF-7 cells, we demonstrated a significant effect of morphology on nanoparticle cell uptake, with the highest cell uptake observed for worm-like and rod-like structures. The changes in cell uptake were reflected in changes to the cytotoxicity of DOX-loaded nanoparticles.Acknowledgements
Bunyamin Karagoz is thankful to the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) for financial support. Cyrille Boyer is thankful for his ARC-APD and Future Fellowship from Australian Research Council (ARC-FT 120100096).Notes and references
- (a) S. Bamrungsap, Z. Zhao, T. Chen, L. Wang, C. Li, T. Fu and W. Tan, Nanomedicine, 2012, 7, 1253–1271 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) E. J. Cho, H. Holback, K. C. Liu, S. A. Abouelmagd, J. Park and Y. Yeo, Mol. Pharmaceutics, 2013, 10, 2093–2110 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Duncan and R. Gaspar, Mol. Pharmaceutics, 2011, 8, 2101–2141 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) A. Albanese, P. S. Tang and W. C. W. Chan, Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng., 2012, 14, 1–16 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) M. Avila-Olias, C. Pegoraro, G. Battaglia and I. Canton, Ther. Delivery, 2013, 4, 27–43 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) Y. Geng, P. Dalhaimer, S. Cai, R. Tsai, M. Tewari, T. Minko and D. E. Discher, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2007, 2, 249–255 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) A. Kunzmann, B. Andersson, C. Vogt, N. Feliu, F. Ye, S. Gabrielsson, M. S. Toprak, T. Buerki-Thurnherr, S. Laurent, M. Vahter, H. Krug, M. Muhammed, A. Scheynius and B. Fadeel, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 2011, 253, 81–93 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) S. Park, Y. J. Son, K. W. Leong and H. S. Yoo, Nano Today, 2012, 7, 76–84 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) L. Tang, N. P. Gabrielson, F. M. Uckun, T. M. Fan and J. Cheng, Mol. Pharmaceutics, 2013, 10, 883–892 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) S. Venkataraman, J. L. Hedrick, Z. Y. Ong, C. Yang, P. L. R. Ee, P. T. Hammond and Y. Y. Yang, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2011, 63, 1228–1246 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) W. K. Oh, S. Kim, H. Yoon and J. Jang, Small, 2010, 6, 872–879 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) C. Pegoraro, D. Cecchin, L. S. Gracia, N. Warren, J. Madsen, S. P. Armes, A. Lewis, S. MacNeil and G. Battaglia, Cancer Lett., 2013, 334, 328–337 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (j) C. LoPresti, M. Massignani, C. Fernyhough, A. Blanazs, A. J. Ryan, J. Madsen, N. J. Warren, S. P. Armes, A. L. Lewis, S. Chirasatitsin, A. J. Engler and G. Battaglia, ACS Nano, 2011, 5, 1775–1784 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. E. A. Gratton, P. A. Ropp, P. D. Pohlhaus, J. C. Luft, V. J. Madden, M. E. Napier and J. M. DeSimone, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2008, 105, 11613–11618 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) P. Kolhar, A. C. Anselmo, V. Gupta, K. Pant, B. Prabhakarpandian, E. Ruoslahti and S. Mitragotri, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2013, 110(26), 10753–10758 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) J. A. Champion, Y. K. Katare and S. Mitragotri, J. Controlled Release, 2007, 121, 3–9 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) S. Muro, C. Garnacho, J. A. Champion, J. Leferovich, C. Gajewski, E. H. Schuchman, S. Mitragotri and V. R. Muzykantov, Mol. Ther., 2008, 16, 1450–1458 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) F. H. Schacher, P. A. Rupar and I. Manners, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 7898–7921 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) B. L. Sanchez-Gaytan, W. Cui, Y. Kim, M. A. Mendez-Polanco, T. V. Duncan, M. Fryd, B. B. Wayland and S.-J. Park, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2007, 46, 9235–9238 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Zhang and A. Eisenberg, Macromolecules, 1996, 29, 8805–8815 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) L. Zhang and A. Eisenberg, Science, 1995, 268, 1728–1731 CAS; (b) R. Savić, L. Luo, A. Eisenberg and D. Maysinger, Science, 2003, 300, 615–618 CrossRef PubMed; (c) Z. Li, E. Kesselman, Y. Talmon, M. A. Hillmyer and T. P. Lodge, Science, 2004, 306, 98–101 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) Y.-Y. Won, H. T. Davis and F. S. Bates, Science, 1999, 283, 960–963 CrossRef CAS; (b) H. A. Klok and S. Lecommandoux, Adv. Mater., 2001, 13, 1217–1229 CrossRef CAS; (c) J. Rodríguez-Hernández, F. Chécot, Y. Gnanou and S. Lecommandoux, Prog. Polym. Sci., 2005, 30, 691–724 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) B. M. Discher, Y.-Y. Won, D. S. Ege, J. C.-M. Lee, F. S. Bates, D. E. Discher and D. A. Hammer, Science, 1999, 284, 1143–1146 CrossRef CAS; (b) D. E. Discher and A. Eisenberg, Science, 2002, 297, 967–973 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) M. Marguet, L. Edembe and S. Lecommandoux, Angew. Chem., 2012, 124, 1199–1202 CrossRef; (d) J. Rodríguez-Hernández and S. Lecommandoux, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 2026–2027 CrossRef PubMed; (e) F. Chécot, S. Lecommandoux, Y. Gnanou and H.-A. Klok, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2002, 41, 1339–1343 CrossRef.
- (a) G. Liu, Q. Qiu, W. Shen and Z. An, Macromolecules, 2011, 44, 5237–5245 CrossRef CAS; (b) G. Liu, Q. Qiu and Z. An, Polym. Chem., 2012, 3, 504–513 RSC.
- (a) B. Charleux, G. Delaittre, J. Rieger and F. D'Agosto, Macromolecules, 2012, 45, 6753–6765 CrossRef CAS; (b) S. Boisse, J. Rieger, K. Belal, A. Di-Cicco, P. Beaunier, M.-H. Li and B. Charleux, Chem. Commun., 2010, 46, 1950–1952 RSC; (c) G. Delaittre, C. Dire, J. Rieger, J.-L. Putaux and B. Charleux, Chem. Commun., 2009, 2887–2889 RSC; (d) G. Delaittre, M. Save, M. Gaborieau, P. Castignolles, J. Rieger and B. Charleux, Polym. Chem., 2012, 3, 1526–1538 RSC; (e) X. Zhang, J. Rieger and B. Charleux, Polym. Chem., 2012, 3, 1502–1509 RSC.
- (a) A. Blanazs, J. Madsen, G. Battaglia, A. J. Ryan and S. P. Armes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 16581–16587 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) A. Blanazs, A. J. Ryan and S. P. Armes, Macromolecules, 2012, 45, 5099–5107 CrossRef CAS; (c) A. Blanazs, R. Verber, O. O. Mykhaylyk, A. J. Ryan, J. Z. Heath, C. W. I. Douglas and S. P. Armes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 9741–9748 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) L. A. Fielding, M. J. Derry, V. Ladmiral, J. Rosselgong, A. M. Rodrigues, L. P. D. Ratcliffe, S. Sugihara and S. P. Armes, Chem. Sci., 2013, 4, 2081–2087 RSC; (e) Y. Li and S. P. Armes, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 4042–4046 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) H. Lomas, M. Massignani, K. A. Abdullah, I. Canton, C. Lo Presti, S. MacNeil, J. Du, A. Blanazs, J. Madsen, S. P. Armes, A. L. Lewis and G. Battaglia, Faraday Discuss., 2008, 139, 143–159 RSC; (g) S. Sugihara, S. P. Armes, A. Blanazs and A. L. Lewis, Soft Matter, 2011, 7, 10787–10793 RSC; (h) S. Sugihara, A. Blanazs, S. P. Armes, A. J. Ryan and A. L. Lewis, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 15707–15713 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) V. Ladmiral, M. Semsarilar, I. Canton and S. Armes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(36), 13574–13581 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) W. M. Wan, C. Y. Hong and C. Y. Pan, Chem. Commun., 2009, 5883–5885 RSC; (b) J.-T. Sun, C.-Y. Hong and C.-Y. Pan, Soft Matter, 2012, 8, 7753–7767 RSC; (c) J.-T. Sun, C.-Y. Hong and C.-Y. Pan, Polym. Chem., 2013, 4, 873–881 RSC; (d) W.-M. Wan, X.-L. Sun and C.-Y. Pan, Macromolecules, 2009, 42, 4950–4952 CrossRef CAS; (e) W.-M. Wan, X.-L. Sun and C.-Y. Pan, Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2010, 31, 399–404 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) C. Boyer, V. Bulmus, T. P. Davis, V. Ladmiral, J. Liu and S. Perrier, Chem. Rev., 2009, 109, 5402–5436 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) C. Boyer, M. H. Stenzel and T. P. Davis, J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem., 2011, 49, 551–595 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Goto and T. Fukuda, Prog. Polym. Sci., 2004, 29, 329–385 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) J. Liu, H. Duong, M. R. Whittaker, T. P. Davis and C. Boyer, Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2012, 33, 760–766 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) H. T. T. Duong, F. Hughes, S. Sagnella, M. Kavallaris, A. MacMillan, R. Whan, J. Hook, T. P. Davis and C. Boyer, Mol. Pharmaceutics, 2012, 9, 3046–3061 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) W. Zhou, X. Liu and J. Ji, J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 13969–13976 RSC; (b) A. Arnida, A. Malugin and H. Ghandehari, J. Applied Toxicology, 2010, 30, 212–217 CAS; (c) E. Oh, J. B. Delehanty, K. E. Sapsford, K. Susumu, R. Goswami, J. B. Blanco-Canosa, P. E. Dawson, J. Granek, M. Shoff, Q. Zhang, P. L. Goering, A. Huston and I. L. Medintz, ACS Nano, 2011, 5, 6434–6448 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) A. Albanese and W. C. W. Chan, ACS Nano, 2011, 5, 5478–5489 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) B. D. Chithrani, A. A. Ghazani and W. C. W. Chan, Nano Lett., 2006, 6, 662–668 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) B. Duncan, C. Kim and V. M. Rotello, J. Controlled Release, 2010, 148, 122–127 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) T. Wang, J. Bai, X. Jiang and G. U. Nienhaus, ACS Nano, 2012, 6, 1251–1259 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) M. Elsabahy and K. L. Wooley, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41, 2545–2561 RSC; (i) J. Zhu, S. Zhang, K. Zhang, X. Wang, J. W. Mays, K. L. Wooley and D. J. Pochan, Nat. Commun., 2013, 4, 2297 Search PubMed.
- (a) X. Huang, X. Teng, D. Chen, F. Tang and J. He, Biomaterials, 2010, 31, 438 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) A. Lesniak, A. Salvati, M. J. Santos-Martinez, M. W. Radomski, K. A. Dawson and C. Åberg, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 1438–1444 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) D. Pissuwan, C. Boyer, K. Gunasekaran, T. P. Davis and V. Bulmus, Biomacromolecules, 2010, 11, 412–420 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) H. T. T. Duong, C. P. Marquis, M. Whittaker, T. P. Davis and C. Boyer, Macromolecules, 2011, 44, 8008–8019 CrossRef CAS; (c) H. T. T. Duong, Z. M. Kamarudin, R. B. Erlich, Y. Li, M. W. Jones, M. Kavallaris, C. Boyer and T. P. Davis, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 4190–4192 RSC.
- (a) S. A. Akman, G. Forrest, F.-F. Chu, R. Steven Esworthy and J. H. Doroshow, Cancer Res., 1990, 50, 1397–1402 CAS; (b) F. A. Fornari, J. K. Randolph, J. C. Yalowich, M. K. Ritke and D. A. Gewirtz, Mol. Pharmacol., 1994, 45, 649–656 CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c3py01306e |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 |