Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleSynthesis of dihydroisoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11-ones, their in silico ADMET properties and in vitro antitumor activities†
Diego R. Merchán-Arenas *a,
Felipe Sojobc,
Francisco Arvelobc and
Vladimir V. Kouznetsov
*a,
Felipe Sojobc,
Francisco Arvelobc and
Vladimir V. Kouznetsov a
a
aLaboratorio de Química Orgánica y Biomolecular, Universidad Industrial de Santander, Parque Tecnológico Guatiguará, Km 2 vía refugio, Piedecuesta, A.A. 681011, Colombia. E-mail: dmerchan605@gmail.com; Tel: +57 76 344000 ext. 3593
bCentro de Biociencias, Fundación Instituto de Estudios Avanzados-IDEA, Caracas, Venezuela
cLaboratorio de Cultivo de Tejidos y Biología de Tumores, Instituto de Biología Experimental, Universidad Central de Venezuela, código postal 1041, Caracas, Venezuela
First published on 19th November 2020
Abstract
We evaluated the antitumoral activity of diverse series of 5-aryl-dihydroisoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11-ones, AIIQ (Aryl IsoIndolo-Quinoline, 4a–m), and 5-vinyl dihydroisoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11-ones, VIIQ (Vinyl IsoIndolo-Quinoline, 6a–l), obtained using three component imino Diels–Alder (DA) reaction of anilines, o-phthalaldehyde and dienophiles. The first series was obtained in previous work employing isoeugenol and anethole as dienophiles, whereas the vinyl series was synthesized in high yields (75–90%) using isoprene as a dienophile. The cytotoxic activity of both AIIQ and VIIQ series was evaluated against four cancer lines, identifying a new lead compound 4h from the AIIQ series, active against MCF-7 (310 nM), SKBR3 (1434 nM), PC3 (210 nM) and HeLa (79 nM) cells with high selectivity. In addition, in silico ADMET properties for the two series were assessed and discussed.
Introduction
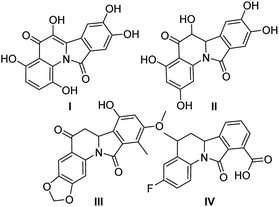
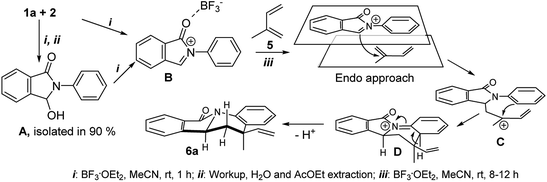
Nitrogen-containing polycyclic aromatic compounds stand out as promising bioactive entities. Molecular architectures such as isoindolo[2,1-a]quinolines (IIQ, I–III) have been synthesized and these molecules showed important applications in the treatment against cancer and bacterial infection as they have potent Topo II and DNA gyrase inhibitory activities1,2 (Fig. 1). Recently, a new isoindoloquinoline compound IV was identified as a selective ligand of telomeric RNA G-quadruplexes, a potential therapeutic target for cancer treatment.3Furthermore, presence of the tetrahydro and dihydroindoloquinoline moieties on secondary metabolites has been highlighted in several reports, including representative compounds like the alkaloid camptothecin, isolated from Camptotheca acuminata.4 Due to that few natural and synthetic examples of isoindoloquinoline models have been identified, their synthesis continues being attractive. Therefore, some methodologies as Grignard reaction,5,6 ortho-aromatic metallation,7 Suzuki coupling,8 Friedel–Crafts reaction from phthalimides,9 Barbier-type allylation,10 among others; have been effective for the isoindolo[2,1-a]quinoline synthesis. Moreover, phthalimide building block has showed an important role in almost all synthetic tools, becoming easily obtained from anilines and phthalic anhydride, further its derivatization towards IIQ synthesis. The synthetic development of these systems during the period of 1966–2004 has been reviewed.11
Another recent approach to access to this isoindolo[2,1-a]quinoline topology had been gaining importance. In this case, the imino-Diels–Alder reaction (DAR) (Povarov reaction) in its intramolecular12 and intermolecular13 version was the synthetic tool to afford different nitrogen-containing polycyclic heterocycles. One more efficient way to obtain the isoindoloquinolines was proposed by Khadem group using a couple of anilines and phthaldehydic acid in a multicomponent reaction [4 + 2] catalysed by TFA.14 Despite of several reports about this core synthesis, the reaction parameters have shown some drawbacks related with high temperatures (200 °C), toxic and harmful solvents (acetonitrile, dichloromethane, xylene, among others), additives and metal (Pd) catalysed conditions. Our group recently reported the free-solvent synthesis of highly functionalized 6,6a-dihydroisoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11(5H)-one derivatives, using natural β-styrenes (isoeugenol, anethole and isosafrole) as dienophiles (Scheme 1).15
 | ||
| Scheme 1 Previous work, synthesis of aryl isoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11-ones used in this research to test as potential antitumoral compounds. | ||
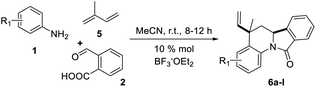
This type of DAR is a bulk synthetic tool since it is possible to use different commercial starting materials, catalysts, promoters, solvents; in general, a great variety of conditions.16 Moreover, this reaction has shown the importance of several activated alkenes, as their structural features allow to act as dienes or dienophiles, depending on the established reaction conditions and molecular energy barriers. Among the different dienes reported, the 1,3-butadiene derivatives have served as ideal precursors in natural products synthesis.17 However, the role of this diene on the synthesis of heterocycles with this frame in the final product is reduced, especially when electron-deficient aza-dienes are employed. Some studies in which these dienes are used as dienophiles, have permitted to obtain alkaloid analogues with the 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline scaffold with a high regio and diastereoselectivity.18,19 Based on these evidences, in the present work we focused our research towards the cytotoxic evaluation of new 5-methyl-5-vinyl substituted isoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11-ones (VIIQ series) synthesized using isoprene as dienophile in an imino-DAR. In addition, a 5-aryl-6-methyl substituted isoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11-ones (AIIQ series) series prepared by our own protocol was evaluated as potential antitumoral agent. We propose its plausible reaction mechanism where a preformed iminium ion is involved to react with the isoprene through of an imino-DAR, instead of mentioned cascade reaction and accessing their ADMET properties for both series.
Results and discussion
Chemistry
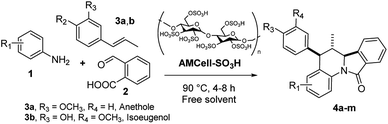
Synthesis of isoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11-ones has been preceded for the motivation of their interesting biological activity and rigid polycyclic architecture. Therefore, in this research we focused our task in the construction of this core, using the three component imino-DAR as synthetic tool. As we mentioned above, in a previous work we obtained a series of AIIQ, employing anilines 1, phthalic aldehyde 2 and (E)-prop-1-en-1-ylbenzenes 3; in the presence of sulfonated amorphous milled cellulose (AMCell-SO3H) as promoter (Scheme 1) to synthesize a series of isoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11-ones 4a–m (Fig. 2).15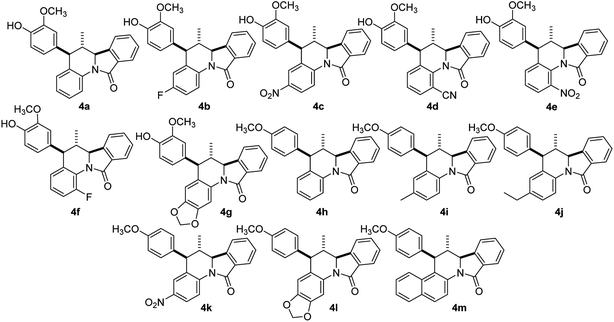 | ||
| Fig. 2 The 5-aryl-6-methyl isoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11-ones (AIIQ series) synthesized in a previous work.15 | ||
These scaffolds were created integrating fragments with potential pharmacophore groups, closely relationship with biological interesting isoindoloquinolines (Fig. 1) and other bioactive molecules reported in our researches.20 Thus, alkene phenolic molecules 3 available from natural sources, were used to include guaiac oil, 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl fragment (from isoeugenol 3a) and anisyl, 4-methoxyphenyl moiety (from anethole 3b).20 The desired molecules 4a–m with C-5 aryl moieties (AIIQ series), were easily prepared without any solvents in good to excellent yields (see ESI†).
Looking for expand our molecular series, we wanted to introduce a vinyl fragment instead of the aryl group on C-5 position to obtain a vinyl substituted derivatives, i.e., VIIQ series 6. For this aim, we employed the same imino-DAR of arylamines 1 and phthalic aldehyde 2, with participation of isoprene 5 that allowed generating different and varied molecular diversity (Table 1).
| Entry | Catalyst | Solvent | Isoprene eq. | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Reaction was carried out for 0.5 mmol of substrate, aniline (0.5 mmol), phthalic aldehyde (0.6 mmol) and isoprene to room temperature; catalyst load was 10% mol using 5 mL of solvent in a 20 mL flask under N2 atmosphere. Reported yields are from isolated products after chromatography column purification. | ||||
| 1 | BF3·OEt2 | MeCN | 1.2 | 55 |
| 2 | CAN | MeCN | 1.2 | 42 |
| 3 | AlCl3 | MeCN | 1.2 | 48 |
| 4 | BF3·OEt2 | DCM | 1.2 | 52 |
| 5 | BF3·OEt2 | DCE | 1.2 | 50 |
| 6 | BF3·OEt2 | MeCN | 1.5 | 67 |
| 7 | BF3·OEt2 | MeCN | 3 | 80 |
Noteworthy, that isoprene 5 has been used before in normal DAR as diene and dienophile, but poorly employed in imino-DAR as dienophile.18,19 One of few works on this theme reports that tetrahydroquinoline (THQ) molecules, obtained from aldimines and different dienophiles, including the isoprene, could be used as potential antidiabetic compounds through of modulation of (adenosine monophosphate)-activated protein kinase (AMPK).21
On that way, isoprene is an interesting precursor, not explored in imino-DA reaction and could be used to incorporate favourable bioactive groups in IIQ skeleton for our diversity-oriented synthesis. According to the above statements and considering the high volatility of this alkene (bp = 34 °C), the reaction had to be performed at room temperature (25 °C). Based on our group's experience in account and knowing that BF3·OEt2 (10 mol%, previous work),15 cerium ammonium nitrate (CAN) and AlCl3, are commonly used as catalysts for imino-DA reactions,22 we anticipate good results in the synthesis of VIIQ series. Thus, assuming a possible volatilization of isoprene from the reaction media, we realized a small set of experiments using these catalysts to optimize the reaction conditions (Table 1).
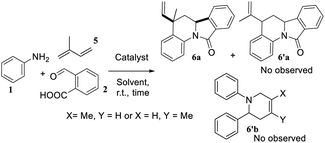
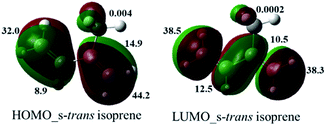
At first, we examined all potential products according with the isoprene reactivity, this kind of butadiene can also produce six members adducts when it acts as diene. According to Kobayashi et al.,23 the diene behaviour of 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene was observed when a bi-aryl substituted pyridine such as 6′b was obtained in a 37%. On the other hand, despite isoprene (2-methyl-1,3-butadiene) and derivatives as 2-trimethylsilyloxybutadiene, commonly used in hetero DA reaction, have showed low site selectivity acting as dienophile, obtaining pyridines and THQs as inseparable mixtures;24 in our research compound 6′b was not observed. Therefore, we obtained selectively the main product VIIQ structure. However, according to others studies,25 reaction could be occurring via two possible π-sites, the methyl substituted double bond or the second one unsubstituted and two possible products 6a and 6′a can be formed. Nevertheless, structure 6′a was not observed and it can be explained because orbital coefficient contribution to the frontiers orbital (HOMO) of isoprene for the structure s-trans are higher on the methylated double bond (16.30, 31.13), than the no methylated double bond (17.7, 30.9).26 We realized a similar approach using a semiempirical basis set as 3-21G by the second-order Møller–Plesset perturbation (MP2) (Fig. 3), where numbers indicate the percentual contribution of all orbital coefficients (see ESI†).26
Then, using this theoretical semiempirical analysis for the isoprene, we prove that C1–C2 (methylated carbon) and C3–C4 double bonds have more electronic density for the HOMO and LUMO frontier orbitals (FO). Nevertheless, the HOMO for the isoprene is the directly implied FO in imino DA reaction as an energetic inverse demand reaction. Thus, we concluded that this highest coefficient contribution for C1 (44.2) and C2 (14.9) for the HOMO_s-trans configuration, explains preliminary the site-selectivity reaction, yielding exclusively the 6a product.
After identification of the final product, we followed the optimization process using mainly the above-mentioned Lewis acids. The best behaviour was observed initially for the BF3·OEt2 in MeCN (Table 1, entry 1), this catalyst has been widely studied,27 where it proposed interaction with the diene has showed an influence of the HOMO, LUMO energies calculated28 and this complex has showed good results in our investigations.29 On the other hand, used solvents haven no influence over reaction yields in this reaction. However, when the number of isoprene equivalents were enlarged, a considerable increase in the reaction yield up to 80% was observed (Table 1, entry 7). Based on these results, three equivalents of isoprene, relative to the starting aniline, were employed for the synthesis of VIIQ products.
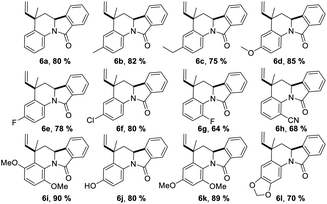
Having the reaction conditions in hands, different functional groups were included into the final isoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11(5H)-one skeleton 6a–l, employing various anilines in combination with phthalic aldehyde and isoprene as the alkene (Table 2). The cycloaddition reaction occurred with complete regio and stereoselectivity to give only one isomer in each reaction in good to high yields (68–90%).
| a Reaction run for 0.5 mmol of substrate, aniline (0.5 mmol), phthalic aldehyde (0.6 mmol) and isoprene to room temperature; catalyst load was 10% mol using 5 mL of solvent in a 20 mL flask under N2 atmosphere. |
|---|
 |
The mechanistic elucidation of such cycloaddition30 processes has been studied and is still under discussion, debating between a concerted or a step-wise mechanisms.31,32 However, numerous practical studies and theoretical investigations support a non-concerted mechanism for the Lewis acid catalysed aza DA reaction.33–36
In our previous work on AIIQ products 4a–m we mentioned that amide formation (γ-lactamization) may occur directly after aldimine formation and prior to [4 + 2] cycloaddition of the acyliminium intermediate.15 In this present study, in order to elucidate this mechanistic route, we achieved isolation of N-phenyl-3-hydroxy-isoindolinone (A) under the same reaction conditions (see ESI†). Noteworthy that A is known as an excellent starting material for isoindolo[2,1-a]-quinolin-11-ones synthesis.13 Thus, the reasonable mechanism can be envisioned as initial de-hydroxylation of isoindolinones type A by a Lewis acid, BF3·OEt2, to generate N-acyliminium cation B followed by electrophilic attack of cation B to isoprene 5, leading to a new cation C (Scheme 2). Then, its intramolecular Friedel–Crafts reaction can afford intermediate D which gives isoindolo[2,1-a]-quinolinone ring 6a through 1,3-H shift step.13
Looking for an evidence of the reaction mechanism, we used the trapping control strategy.33,34 Thus, BF3·OEt2-catalysed reaction of isoindolinone (A) and isoprene (5) in methanol was carried out (see ESI†). Unfortunately, the obtained results were insufficient to draw definite conclusions. It was observed that methanol affected drastically on over the course of the reaction, decreasing the yield of the final product 6a to 20% and generating an unseparated mixture of poly-methoxylated adducts of B in which isoprene moiety was not incorporated. This indicates that there was an interaction between the molecules of methanol and intermediate ionic species like B–C during the cycloaddition process. With this outcome, we believed that formation of final isoindolo[2,1-a]-quinolin-11-ones 6 using the three-component reaction of 1, 2 and 5 occurs via generation of N-acyliminium cations which react with isoprene following a step-wise addition–cyclisation mechanism as indicated in Scheme 2.
Regarding to the obtention of two possible diastereomers cis/trans, associated to the vinyl and methyl position, we performed a structural elucidation using monocrystal X-ray analysis (Fig. 4). Thus, we observed that the reference proton 6a-H is oriented in axial position as same as methyl group and vinyl group is pseudo-equatorial oriented. As it is known, DA reaction, normal and inverse version, are favoured though of an endo approach because it maximizes the secondary orbital overlap.37 Therefore, explanation of this behaviour could be associated with no covalent interaction between aryl moiety and vinyl group in the endo approach (Scheme 2).
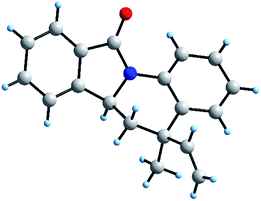 | ||
| Fig. 4 Stick-ball model of 6a asymmetric unit from monocrystal X-ray diffraction (see ESI†). | ||
Having a complete structural description of IIQ molecules, and following our medicinal chemistry program, we evaluated their in silico and in vitro, molecular properties and activity as antitumoral compounds.
Biology
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 commercially available chemicals, yielding a complete list of all available orally fragments.38
000 commercially available chemicals, yielding a complete list of all available orally fragments.38
| IIQ | Molecular formula | Molecular properties | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
c![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) log log![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) P P |
TPSA | MW, g mol−1 | nNO | nOHNH | nRB | Viol. | ||
| 4a | C24H21NO3 | 4.307 | 49.771 | 371.44 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 4b | C24H20FNO3 | 4.446 | 49.771 | 389.43 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 4c | C24H20N2O5 | 4.241 | 95.595 | 416.43 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| 4d | C25H20N2O3 | 4.013 | 73.563 | 396.45 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 4e | C24H20N2O5 | 4.217 | 95.595 | 416.43 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| 4f | C24H20FNO3 | 4.422 | 49.771 | 389.43 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 4g | C25H21NO5 | 4.173 | 68.239 | 415.44 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 4h | C24H21NO2 | 5.024 | 29.543 | 355.44 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| 4i | C25H23NO2 | 5.449 | 29.543 | 369.46 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| 4j | C26H25NO2 | 5.916 | 29.543 | 383.49 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 1 |
| 4k | C24H20N2O4 | 4.959 | 75.367 | 400.43 | 6 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| 4l | C25H21NO4 | 4.890 | 48.011 | 399.45 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 4m | C28H23NO2 | 6.183 | 29.543 | 405.50 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| 6a | C19H17NO | 4.167 | 20.309 | 275.35 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 6b | C20H19NO | 4.592 | 20.309 | 289.38 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 6c | C21H21NO | 5.06 | 20.31 | 303.40 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| 6d | C20H19NO2 | 4.200 | 29.543 | 305.38 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 6e | C19H16FNO | 4.307 | 20.309 | 293.34 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 6f | C19H16ClNO | 4.821 | 20.309 | 309.80 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 6g | C24H16FNO | 4.283 | 20.309 | 293.34 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 6h | C20H16N2O | 3.870 | 44.10 | 300.36 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 6i | C21H21NO3 | 4.185 | 38.777 | 335.40 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| 6j | C19H17NO2 | 4.18 | 29.54 | 305.38 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 6k | C21H21NO3 | 5.18 | 38.78 | 335.40 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| 6l | C20H17NO3 | 4.034 | 38.777 | 319.36 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Adr | C27H29NO11 | 0.567 | 206.08 | 543.52 | 12 | 7 | 5 | 3 |
Conversely to the Adriamycin (Adr) as reference, the obtained calculations demonstrated that all synthesized compounds contain high bioavailability properties, and they are between almost all parameters established by this rule of five (molecular weight = 275.35–416.43 g mol−1, c![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) log
log![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) P = 3.870–6.183, nNO = 2–7, and nOHNH = 0–1)40 (Table 3). Compounds with c
P = 3.870–6.183, nNO = 2–7, and nOHNH = 0–1)40 (Table 3). Compounds with c![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) log
log![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) P, higher than five units (4h–4j, 4m, 6c and 6k), showed just one violation, maintaining their potential bioavailability to permeate the lipidic membrane. In this case, c
P, higher than five units (4h–4j, 4m, 6c and 6k), showed just one violation, maintaining their potential bioavailability to permeate the lipidic membrane. In this case, c![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) log
log![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) P property is especially affected by the inclusion of apolar groups as methyl (4i) and ethyl (4j), compounds with highest c
P property is especially affected by the inclusion of apolar groups as methyl (4i) and ethyl (4j), compounds with highest c![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) log
log![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) P.
P.
In the AIIQ series, 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl moiety (4a–4g) provides a better solubility than the 4-methoxyphenyl (4h–4m) in the IIQ core.
The TPSA values minor to 140 Å2 are associated to good cell membrane permeability. Values below to 60 Å2 are accepted for those compounds able to cross the hematoencephalic barrier. Considering this, the TPSA values obtained for the synthesized compounds (20.309–95.595 Å2) allow us to confirm their drug-relevant properties regarding to cell membrane permeation. The TPSA value has been shown to be a very good descriptor characterizing drug absorption, including intestinal absorption, bioavailability, Caco-2 permeability and blood–brain barrier penetration.41 Chemotherapy cancer treatment showed several side effects in drug treatment and reveals a diminution in the life quality of patient, showing hair fall out, vomit, not remember things, among others.42
These side effects are produced because anticancer drugs are generally toxic and kill normal cells due to their low selectivity.
Therefore, in order to assess preliminary to these kind of possible pharmacological properties of compounds 4a–m and 6a–l, their toxicity profile evaluation was performed employing the DataWarrior software.39 It may point to the presence of certain fragments generally responsible for the irritant, mutagenic, tumorigenic, or reproductive effects in these molecules.43 As shown in Table 4, any of the structural frames included in the final products afford a high toxic property.
| IIQ | Potential riska | Drug-likeness | Drug-score | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mut. | Tum. | Irr. | Rep. eff. | |||
a  , drug-like properties; , drug-like properties;  , moderate risk; , moderate risk;  , high risk. , high risk. |
||||||
| 4a |  |
 |
 |
 |
0.13 | 0.47 |
| 4b |  |
 |
 |
 |
−1.73 | 0.33 |
| 4c |  |
 |
 |
 |
−6.85 | 0.27 |
| 4d |  |
 |
 |
 |
−4.28 | 0.27 |
| 4e |  |
 |
 |
 |
−7.05 | 0.22 |
| 4f |  |
 |
 |
 |
−1.34 | 0.34 |
| 4g |  |
 |
 |
 |
−0.33 | 0.36 |
| 4h |  |
 |
 |
 |
0.01 | 0.43 |
| 4i |  |
 |
 |
 |
−1.51 | 0.30 |
| 4j |  |
 |
 |
 |
−0.44 | 0.32 |
| 4k |  |
 |
 |
 |
−6.92 | 0.26 |
| 4l |  |
 |
 |
 |
−0.47 | 0.33 |
| 4m |  |
 |
 |
 |
−2.47 | 0.15 |
| 6a |  |
 |
 |
 |
−4.77 | 0.28 |
| 6b |  |
 |
 |
 |
−3.35 | 0.26 |
| 6c |  |
 |
 |
 |
−2.08 | 0.11 |
| 6d |  |
 |
 |
 |
−4.97 | 0.28 |
| 6e |  |
 |
 |
 |
−6.62 | 0.26 |
| 6f |  |
 |
 |
 |
−4.79 | 0.23 |
| 6g |  |
 |
 |
 |
−6.25 | 0.26 |
| 6h |  |
 |
 |
 |
−6.16 | 0.03 |
| 6i |  |
 |
 |
 |
−6.68 | 0.27 |
| 6j |  |
 |
 |
 |
−6.56 | 0.23 |
| 6k |  |
 |
 |
 |
−5.85 | 0.26 |
| 6l |  |
 |
 |
 |
−5.32 | 0.24 |
| Adr |  |
 |
 |
 |
7.19 | 0.55 |
A moderate risk was observed for some compounds in the irritant subject, mainly the vinyl isoindoloquinoline series. On the other hand, a moderate mutagenic risk was observed for compounds 4e, 4m and 6a. Ciano group at the C-1 position afford a potential high risk regarding to reproductive effects.
Apparently, obtained compounds have not functional groups that could be attributed to them potential toxicity and drug score values are closer to the Adriamycin value. In the same sense, there is remarkable that mostly AIIQ showed better drug score values than VIIQ molecules. Adriamycin evaluation in DataWarrior platform afford us a high drug likeness value, in agreement with its widely recognized properties and thus to have a good molecular properties theoretical approach. On the other hand, as complement of this preliminary high throughput screening, in silico analysis, we performed the evaluation of the growth inhibitory activity against four cancer cell lines, for the synthetic compounds 4a–m, 6a–l.
A moderate risk was observed for some compounds in the irritant subject, mainly the vinyl isoindoloquinoline series. On the other hand, a moderate mutagenic risk was observed for compounds 4e, 4m and 6a. Ciano group at the C-1 position afford a potential high risk regarding to reproductive effects. Apparently, obtained compounds have not functional groups that could be attributed to them potential toxicity and drug score values are closer to the Adriamycin value. In the same sense, there is remarkable that mostly AIIQ showed better drug score values than VIIQ molecules. On the other hand, as complement of this preliminary high throughput screening, in silico analysis, we performed the evaluation of the growth inhibitory activity against four cancer cell lines, for the synthetic compounds 4a–m, 6a–l.
| IIQ | Cancer cells lines, cytotoxicity, IC50 (μM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCF-7 | SKBR3 | PC3 | HeLa | Fibroblasts | |
| a Marked in bold parameters indicated notable interesting anticancer activity. | |||||
| 4a | 41.65 ± 1.02 | 76.67 ± 1.02 | 21.48 ± 1.05 | 24.90 ± 1.02 | >100 |
| 4b | >100 | 92.24 ± 1.04 | 35.85 ± 1.03 | >100 | >100 |
| 4c | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 4d | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 4e | >100 | >100 | 65.77 ± 1.25 | >100 | >100 |
| 4f | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 4g | >100 | >100 | 47.47 ± 1.00 | 23.16 ± 1.02 | >100 |
| 4h | 0.31 ± 1.03 | 14.34 ± 1.03 | 0.21 ± 1.00 | 0.079 ± 1.18 | >100 |
| 4i | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 4j | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 4k | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 4l | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 4m | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 6a | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 6b | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 6c | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 6d | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 6e | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 6f | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 6g | >100 | >100 | 83.48 ± 1.00 | >100 | >100 |
| 6h | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 6i | >100 | 96.48 ± 1.05 | 64.61 ± 1.00 | >100 | >100 |
| 6j | >100 | 79.23 ± 1.00 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 6k | >100 | 40.14 ± 1.00 | 23.89 ± 1.05 | >100 | >100 |
| 6l | >100 | >100 | 63.47 ± 1.06 | >100 | >100 |
| Adr | 0.74 ± 0.05 | 1.65 ± 0.08 | 2.35 ± 0.4 | 3.62 ± 0.12 | 2.45 ± 0.37 |
We also observed that both series, AIIQ and VIIQ showed positive response in the assay where five AIIQ (4a, 4b, 4e, 4g and 4h) and four VIIQ (6g, 6i, 6k and 6l) have activity at least against PC3, pancreas cancer cell line and SKBR3 (breast carcinoma, overexpresses the HER2/c-erb-2 gene). Noteworthy, that any tested compounds are toxic for normal human dermis fibroblasts (Table 5).
According with our previous report, phenolics, i.e., 4-methoxyphenyl and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl groups in the tetrahydroquinoline derivatives are responsible for anticancer properties.20 Similarly, these functionalized aromatic fragments in the IIQ core provide biological activity against malignant tumour. As results, there have been discovered two AIIQ molecules, 4a and 4h, which showed potent cytotoxicity against four cancer cell lines, being non-toxic for normal cells. Moreover, comp. 4a with 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl moiety derived from starting eugenol molecule, resulted in a less active anticancer agent than its analogue 4h with 4-methoxyphenyl fragment that is resulting from anethole. This analogue displays the best activity of all series, reaching a 79 nM IC50 value against HeLa cancer cell line. In addition, its great antitumor action was obtained for the other cell lines MCF-7, 310 nM; SKBR3, 1434 nM and PC3, 210 nM (Table 5). Interesting to note, one, an additional hydroxy group in C-5 aryl moiety of comp. 4a worthens anticancer activity highlighting its MCF-7, PC3 and HeLa cells inhibition that is more effective that Adriamycin, a reference compound.
According to the in silico calculations (Table 3), comp. 4a is less lipophilic molecule and possesses more TPSA values, i.e., less capacity of cell membrane permeability than comp. 4h. Moreover, both molecules showed the best drug score values of the series for these two compounds and their toxicity values for fibroblasts using MTT assay were chord with the risk properties obtained from DataWarrior platform (Table 4). Due to the importance of this new potential anticancer compounds, more studies are performed in advance to demonstrate more biological properties based on cancer diseases.
Conclusion
In this research, we developed mild, efficient synthesis of novel vinyl isoindoloquinoline derivatives. In addition, we prepared and tested analogous aryl isoindoloquinoline molecules. Bio inspection of new molecules of both series against cancer cell lines in different studies confirmed that they are promising anticancer agents.Among them, 5-(4-methoxyphenyl)isoindoloquinoline 4h was shown to be more positioned as a new potential compound, which is under ongoing researches in our laboratories, displaying an excellent cytotoxic activity (79–1434 nM), even more in three cancer cell lines (MCF-7, PC3 and HeLa) than the reference compound, the Adriamycin.
Experimental
Chemistry
General information and NMR spectra are reported in ESI.†Aryl isoindolo[2,1-a]quinolines 4a–m were easily prepared via three-component reaction of respective anilines, isoeugenol/trans-anethole and ortho-phthalaldehydic acid following described procedure.15 Characterization data and spectra information for these series are reported in ESI.† The new vinyl derivatives are reported here and in the ESI.† All compounds were purified and characterized before biological tests.
Trans-5-methyl-5-vinyl-6,6a-dihydroisoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11(5H)-one (6a). Were obtained 400 mg (1.45 mmol, 80%), white solid; mp: 182–183 °C; IR (KBr): 2947, 1682 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 1.43 (3H, d, J = 1.0 Hz, CH3), 2.24 (1H, dd, J = 12.4, 7.1 Hz, CH2), 2.36 (1H, dd, J = 12.4, 7.0 Hz, CH2), 4.86–4.66 (1H, m, CH), 4.97 (1H, dd, J = 10.0, 2.5 Hz,
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.03 (1H, d, J = 2.6 Hz,
CH2), 5.03 (1H, d, J = 2.6 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.97 (1H, ddd, J = 16.7, 9.9, 0.9 Hz,
CH2), 5.97 (1H, ddd, J = 16.7, 9.9, 0.9 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH), 7.07 (1H, td, J = 7.2, 1.7 Hz, 3-H), 7.21–7.12 (3H, m, 1-H and 2-H), 7.34 (1H, td, J = 7.4, 1.6 Hz, 8-H), 7.38 (1H, dd, J = 7.4, 1.8 Hz, 9-H), 7.44–7.39 (1H, m, 7-H), 7.65 (1-H, dd, J = 7.3, 1.6 Hz, 10-H). 13C NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 24.4, 40.6, 42.9, 54.1, 112.1, 122.2, 124.0, 124.3, 125.0, 125.7, 125.8, 129.2, 130.2, 132.2, 133.9, 137.7, 142.8, 147.4, 164.9; GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 24.117 min, m/z (%) 275 (M+˙, 70), 260 (100), 232 (10); anal. calc. for C19H17NO: C, 82.88; H, 6.22; N, 5.09. Found: C, 82.80; H, 6.12; N, 5.19.
CH), 7.07 (1H, td, J = 7.2, 1.7 Hz, 3-H), 7.21–7.12 (3H, m, 1-H and 2-H), 7.34 (1H, td, J = 7.4, 1.6 Hz, 8-H), 7.38 (1H, dd, J = 7.4, 1.8 Hz, 9-H), 7.44–7.39 (1H, m, 7-H), 7.65 (1-H, dd, J = 7.3, 1.6 Hz, 10-H). 13C NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 24.4, 40.6, 42.9, 54.1, 112.1, 122.2, 124.0, 124.3, 125.0, 125.7, 125.8, 129.2, 130.2, 132.2, 133.9, 137.7, 142.8, 147.4, 164.9; GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 24.117 min, m/z (%) 275 (M+˙, 70), 260 (100), 232 (10); anal. calc. for C19H17NO: C, 82.88; H, 6.22; N, 5.09. Found: C, 82.80; H, 6.12; N, 5.19.
Trans-3,5-dimethyl-5-vinyl-6,6a-dihydroisoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11(5H)-one (6b). Were obtained 410 mg (1.41 mmol, 82%), white solid; mp: 193–195 °C; IR (KBr): 2940, 1660 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 1.63–1.50 (4H, m, CH3 and CH2), 2.26 (3H, s, 3-CH3), 2.38 (1H, d, J = 12.3 Hz, CH2), 5.08 (1H, d, J = 12.2 Hz, 6a-H), 5.16 (1H, d, J = 10.9 Hz,
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.30 (1H, d, J = 17.3 Hz,
CH2), 5.30 (1H, d, J = 17.3 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.93 (1H, dd, J = 17.0, 10.5 Hz,
CH2), 5.93 (1H, dd, J = 17.0, 10.5 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH), 7.03 (1H, s, 4-H), 7.09 (1H, d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2-H), 7.57 (1H, d, J = 7.3 Hz, 9-H), 7.69 (1H, d, J = 7.4 Hz, 8-H), 7.75 (1H, d, J = 7.4 Hz, 7-H), 7.80 (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz, 10-H), 8.27 (1H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1-H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 20.7, 22.1, 27.2, 40.0, 40.5, 54.9, 112.5, 119.7, 122.8, 123.4, 127.4, 128.6, 128.9, 131.9, 132.3, 132.5, 132.8, 145.0, 146.7, 165.1; GC/MS (70 eV): tR = 25.042 min, m/z (%) 289 (M+˙, 80), 274 (100), 246 (5); anal. calc. for C20H19NO: C, 83.01; H, 6.62; N, 4.84. Found: C, 82.95; H, 6.59; N, 4.75.
CH), 7.03 (1H, s, 4-H), 7.09 (1H, d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2-H), 7.57 (1H, d, J = 7.3 Hz, 9-H), 7.69 (1H, d, J = 7.4 Hz, 8-H), 7.75 (1H, d, J = 7.4 Hz, 7-H), 7.80 (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz, 10-H), 8.27 (1H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1-H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 20.7, 22.1, 27.2, 40.0, 40.5, 54.9, 112.5, 119.7, 122.8, 123.4, 127.4, 128.6, 128.9, 131.9, 132.3, 132.5, 132.8, 145.0, 146.7, 165.1; GC/MS (70 eV): tR = 25.042 min, m/z (%) 289 (M+˙, 80), 274 (100), 246 (5); anal. calc. for C20H19NO: C, 83.01; H, 6.62; N, 4.84. Found: C, 82.95; H, 6.59; N, 4.75.
Trans-3-ethyl-5-methyl-5-vinyl-6,6a-dihydroisoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11(5H)-one (6c). Were obtained 375 mg (1.23 mmol, 75%) white solid; mp: 187–188 °C; IR (KBr): 2809, 1666 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 1.56 (4H, br. s, CH3 and CH2), 1.78 (1H, s, CH2), 2.27 (3H, s, CH3), 2.43–2.28 (2H, m, CH2), 5.1 (1H, d, J = 10.1,
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.17 (1H, d, J = 10.2 Hz,
CH2), 5.17 (1H, d, J = 10.2 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.31 (1H, d, J = 17.4 Hz, 6a-H), 5.96 (1H, br. d, J = 17.1 Hz,
CH2), 5.31 (1H, d, J = 17.4 Hz, 6a-H), 5.96 (1H, br. d, J = 17.1 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH), 7.04 (1H, s, 4-H), 7.10 (1H, d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2-H), 7.59 (1H, br. s, 9-H), 7.69 (1H, br. s, 8-H), 7.75 (1H, s, 7-H), 7.82 (1H, s, 1-H), 8.29 (1H, d, J = 8.2 Hz, 10H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 20.7, 27.2, 29.4, 40.0, 40.5, 54.9, 68.2, 112.5, 119.7, 122.8, 123.4, 127.4, 128.6, 128.9, 131.9, 132.3, 132.5, 132.8, 145.0, 146.7, 165.1; GC/MS (70 eV): tR = 25.014 min, m/z (%) 303 (M+˙, 70), 274 (100), 246 (5); anal. calc. for C21H21NO: C, 83.13; H, 6.98; N, 4.62. Found: C, 83.08; H, 7.06; N, 4.55.
CH), 7.04 (1H, s, 4-H), 7.10 (1H, d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2-H), 7.59 (1H, br. s, 9-H), 7.69 (1H, br. s, 8-H), 7.75 (1H, s, 7-H), 7.82 (1H, s, 1-H), 8.29 (1H, d, J = 8.2 Hz, 10H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 20.7, 27.2, 29.4, 40.0, 40.5, 54.9, 68.2, 112.5, 119.7, 122.8, 123.4, 127.4, 128.6, 128.9, 131.9, 132.3, 132.5, 132.8, 145.0, 146.7, 165.1; GC/MS (70 eV): tR = 25.014 min, m/z (%) 303 (M+˙, 70), 274 (100), 246 (5); anal. calc. for C21H21NO: C, 83.13; H, 6.98; N, 4.62. Found: C, 83.08; H, 7.06; N, 4.55.
Trans-5-methyl-3-methoxy-5-vinyl-6,6a-dihydroisoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11(5H)-one (6d). Were obtained 425 mg (1.39 mmol, 85%), white solid; mp: 178–179 °C; IR (KBr): 2947, 1680 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 1.56 (4H, m, 5-CH3 and CH2), 2.44–2.29 (1H, m, CH2), 3.72 (3H, s, CH3O), 5.05 (1H, d, J = 12.5, 2.6 Hz, 6a-H), 5.17 (1H, J = 10.1,
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2) 5.31 (1H, d, J = 17.4,
CH2) 5.31 (1H, d, J = 17.4, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.96 (1H, dd, J = 17.4, 10.6 Hz,
CH2), 5.96 (1H, dd, J = 17.4, 10.6 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH), 6.76 (1H, d, J = 3.0, 4-H), 6.90 (1H, dd, J = 9.0, 3.0 Hz, 2-H), 7.55 (1H, ‘t’, J = 7.4 Hz, 9-H), 7.67 (1H, ‘t’, J = 7.4 Hz, 8-H), 7.74 (1H, br. d, J = 7.6 Hz, 7-H), 7.79 (1H, br. d, J = 7.5 Hz, 10-H), 8.33 (1H, d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1-H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 27.6, 40.7, 40.9, 55.3, 55.6, 112.6, 113.1, 114.2, 121.4, 123.2, 123.7, 128.8, 129.0, 132.4, 132.6, 134.9, 145.3, 147.0, 155.9, 165.2; GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 26.638 min, m/z (%) 305 (M+˙, 90), 290 (100), 262 (10); anal. calc. for C20H19NO2: C, 78.66; H, 6.27; N, 4.59. Found: C, 78.59; H, 6.19; N, 4.67.
CH), 6.76 (1H, d, J = 3.0, 4-H), 6.90 (1H, dd, J = 9.0, 3.0 Hz, 2-H), 7.55 (1H, ‘t’, J = 7.4 Hz, 9-H), 7.67 (1H, ‘t’, J = 7.4 Hz, 8-H), 7.74 (1H, br. d, J = 7.6 Hz, 7-H), 7.79 (1H, br. d, J = 7.5 Hz, 10-H), 8.33 (1H, d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1-H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 27.6, 40.7, 40.9, 55.3, 55.6, 112.6, 113.1, 114.2, 121.4, 123.2, 123.7, 128.8, 129.0, 132.4, 132.6, 134.9, 145.3, 147.0, 155.9, 165.2; GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 26.638 min, m/z (%) 305 (M+˙, 90), 290 (100), 262 (10); anal. calc. for C20H19NO2: C, 78.66; H, 6.27; N, 4.59. Found: C, 78.59; H, 6.19; N, 4.67.
Trans-3-fluor-5-methyl-5-vinyl-6,6a-dihydroisoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11(5H)-one (6e). Were obtained 390 mg (1.33 mmol, 78%), white solid; mp: 163–165 °C; IR (KBr): 2979, 1660 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 1.72–1.50 (4H, m, 5-CH3 and CH2), 2.41 (1H, d, J = 12.4 Hz, CH2), 5.10 (1H, d, J = 12.5 Hz, 6a-H), 5.19 (1H, d, J = 10.1 Hz,
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.33 (1H, d, J = 17.1 Hz,
CH2), 5.33 (1H, d, J = 17.1 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 6.01–5.98 (1H, m,
CH2), 6.01–5.98 (1H, m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH), 7.04 (1H, d, J = 8.3 Hz, 4-H), 7.16 (1H, m, 2-H), 7.71 (1H, br. s, 9-H), 7.77 (1H, s, 8-H), 7.82 (2H, br. s, 7-H and 10-H), 8.41 (1H, br. s, 1-H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 27.1, 39.9, 40.4, 54.9, 113.2, 113.7, 113.9, 114.8, 121.6, 122.8, 123.5, 128.7, 131.4, 131.6, 132.5, 135.6, 144.8, 146.0, 165.2; GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 24.055 min, m/z (%) 293 (M+˙, 80), 278 (100), 250 (5); anal. calc. for C19H16FNO: C, 77.80; H, 5.50; F, 6.48, N, 4.77. Found: C, 77.86; H, 5.42; N, 4.66.
CH), 7.04 (1H, d, J = 8.3 Hz, 4-H), 7.16 (1H, m, 2-H), 7.71 (1H, br. s, 9-H), 7.77 (1H, s, 8-H), 7.82 (2H, br. s, 7-H and 10-H), 8.41 (1H, br. s, 1-H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 27.1, 39.9, 40.4, 54.9, 113.2, 113.7, 113.9, 114.8, 121.6, 122.8, 123.5, 128.7, 131.4, 131.6, 132.5, 135.6, 144.8, 146.0, 165.2; GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 24.055 min, m/z (%) 293 (M+˙, 80), 278 (100), 250 (5); anal. calc. for C19H16FNO: C, 77.80; H, 5.50; F, 6.48, N, 4.77. Found: C, 77.86; H, 5.42; N, 4.66.
Trans-3-chloro-5-methyl-5-vinyl-6,6a-dihydroisoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11(5H)-one (6f). Were obtained 400 mg (1.29 mmol, 80%), white solid; mp: 225–226 °C; IR (KBr): 2948, 1682 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 1.44 (3H, d, J = 1.1 Hz, CH3), 2.26 (1H, dd, J = 12.4, 7.1 Hz, CH2), 2.37 (1H, dd, J = 12.5, 7.0 Hz, CH2), 4.77–4.53 (1H, m, 6a-H), 4.96 (1H, dd, J = 10.0, 2.5 Hz,
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.03 (1H, d, J = 2.6 Hz,
CH2), 5.03 (1H, d, J = 2.6 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.99 (1H, ddq, J = 16.8, 10.1, 1.1 Hz,
CH2), 5.99 (1H, ddq, J = 16.8, 10.1, 1.1 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH), 7.16 (1H, d, J = 1.1 Hz, 4-H), 7.20 (2H, d, J = 1.1 Hz, 1-H and 2-H), 7.39–7.33 (2H, m, 8-H and 9-H), 7.41 (1H, ddd, J = 6.9, 2.1, 0.7 Hz, 7-H), 7.65 (1H, dd, J = 7.1, 1.8 Hz, 10-H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 24.1, 39.6, 40.1, 42.5, 53.6, 111.5, 124.8, 125.1, 125.3, 125.5, 129.5, 129.7, 129.8, 131.3, 136.1, 136.6, 142.0, 146.8, 163.7; GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 25.855 min, m/z (%) 309 (M+˙, 80), 294 (100), 259 (20); anal. calc. for C19H16ClNO: C, 73.66; H, 5.21; Cl, 11.44; N, 4.52. Found: C, 73.71; H, 5.29; N, 4.59.
CH), 7.16 (1H, d, J = 1.1 Hz, 4-H), 7.20 (2H, d, J = 1.1 Hz, 1-H and 2-H), 7.39–7.33 (2H, m, 8-H and 9-H), 7.41 (1H, ddd, J = 6.9, 2.1, 0.7 Hz, 7-H), 7.65 (1H, dd, J = 7.1, 1.8 Hz, 10-H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 24.1, 39.6, 40.1, 42.5, 53.6, 111.5, 124.8, 125.1, 125.3, 125.5, 129.5, 129.7, 129.8, 131.3, 136.1, 136.6, 142.0, 146.8, 163.7; GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 25.855 min, m/z (%) 309 (M+˙, 80), 294 (100), 259 (20); anal. calc. for C19H16ClNO: C, 73.66; H, 5.21; Cl, 11.44; N, 4.52. Found: C, 73.71; H, 5.29; N, 4.59.
Trans-1-fluor-5-methyl-5-vinyl-6,6a-dihydroisoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11(5H)-one (6g). Were obtained 320 mg (1.1 mmol, 64%); white solid; mp: 150–152 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 1.33 (3H, d, J = 1.1 Hz, CH3), 2.34 (1H, dd, J = 12.5, 7.0 Hz, CH2), 2.43 (1H, dd, J = 12.5, 7.0 Hz, CH2), 4.91 (1H, t, J = 6.9 Hz, 6a-H), 4.96 (1H, dd, J = 10.0, 2.5 Hz,
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.03 (1H, dd, J = 16.9, 2.4 Hz,
CH2), 5.03 (1H, dd, J = 16.9, 2.4 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 6.05–5.93 (1H, m,
CH2), 6.05–5.93 (1H, m, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH), 6.94 (1H, td, J = 7.8, 1.5 Hz, 2-H), 7.02 (1H, dd, J = 7.5, 1.6 Hz, 4-H), 7.15 (1H, td, J = 7.5, 5.0 Hz, 3H), 7.40–7.31 (2H, m, 8-H and 9-H), 7.45–7.40 (1H, m, 7-H), 7.70–7.60 (1H, m, 10-H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 25.1, 40.0, 41.0, 42.4, 58.7, 112.0, 116.6, 122.1, 125.0, 125.7, 126.5, 130.2, 132.0, 134.8, 141.9, 146.1, 156.3, 158.3, 164.4; GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 10.9 min, m/z (%) 293 (M+˙, 100), 278 (80), 250 (30); anal. calc. for C19H16FNO: C, 77.80; H, 5.50; F, 6.48, N, 4.77. Found: C, 77.85; H, 5.45; N, 4.85.
CH), 6.94 (1H, td, J = 7.8, 1.5 Hz, 2-H), 7.02 (1H, dd, J = 7.5, 1.6 Hz, 4-H), 7.15 (1H, td, J = 7.5, 5.0 Hz, 3H), 7.40–7.31 (2H, m, 8-H and 9-H), 7.45–7.40 (1H, m, 7-H), 7.70–7.60 (1H, m, 10-H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 25.1, 40.0, 41.0, 42.4, 58.7, 112.0, 116.6, 122.1, 125.0, 125.7, 126.5, 130.2, 132.0, 134.8, 141.9, 146.1, 156.3, 158.3, 164.4; GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 10.9 min, m/z (%) 293 (M+˙, 100), 278 (80), 250 (30); anal. calc. for C19H16FNO: C, 77.80; H, 5.50; F, 6.48, N, 4.77. Found: C, 77.85; H, 5.45; N, 4.85.
Trans-1-ciano-5-methyl-5-vinyl-6,6a-dihydroisoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11(5H)-one (6h). Were obtained 340 mg (1.13 mmol, 68%), white solid; mp: 198–199 °C; IR (KBr): 2950, 1660 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 1.34 (3H, d, J = 1.1 Hz, CH3), 2.34 (1H, dd, J = 12.5, 7.0 Hz, CH2), 2.43 (1H, dd, J = 12.5, 7.0 Hz, CH2), 4.94–4.90 (1H, m, CH), 4.97 (1H, dd, J = 10.0, 2.5 Hz,
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.04 (1H, dd, J = 16.9, 2.4 Hz,
CH2), 5.04 (1H, dd, J = 16.9, 2.4 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.99 (1H, ddd, J = 16.7, 9.9, 0.9 Hz, CH), 7.35–7.27 (2H, m, 3-H and 4-H), 7.44–7.35 (3H, m, 7-H, 8-H and 9-H), 7.48 (1H, dd, J = 7.0, 2.0 Hz, 2-H), 7.68–7.62 (1H, m, 10-H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 25.0, 40.0, 42.1, 42.4, 57.7, 109.6, 112.2, 115.8, 125.2, 125.7, 125.9, 129.1, 130.2, 131.5, 134.0, 135.9, 138.6, 141.6, 145.2, 164.4; GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 25.1 min, m/z (%) 300 (M+˙, 100), 285 (80), 254 (30); anal. calc. for C20H16NO: C, 79.98; H, 5.37; N, 9.33. Found: C, 80.01; H, 5.42; N, 9.29.
CH2), 5.99 (1H, ddd, J = 16.7, 9.9, 0.9 Hz, CH), 7.35–7.27 (2H, m, 3-H and 4-H), 7.44–7.35 (3H, m, 7-H, 8-H and 9-H), 7.48 (1H, dd, J = 7.0, 2.0 Hz, 2-H), 7.68–7.62 (1H, m, 10-H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 25.0, 40.0, 42.1, 42.4, 57.7, 109.6, 112.2, 115.8, 125.2, 125.7, 125.9, 129.1, 130.2, 131.5, 134.0, 135.9, 138.6, 141.6, 145.2, 164.4; GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 25.1 min, m/z (%) 300 (M+˙, 100), 285 (80), 254 (30); anal. calc. for C20H16NO: C, 79.98; H, 5.37; N, 9.33. Found: C, 80.01; H, 5.42; N, 9.29.
Trans-1,4-dimethoxy-5-methyl-5-vinyl-6,6a-dihydroisoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11(5H)-one (6i). Were obtained 450 mg (1.34 mmol, 90%), white solid; mp: 180–181 °C; IR (KBr): 2948, 1660 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 1.27 (1H, ‘t’, J = 12.6 Hz, CH2), 1.56 (3H, s, CH3), 2.28 (1H, dd, J = 13.2, 2.6 Hz, CH2), 3.69 (3H, s, OCH3), 3.77 (3H, s, OCH3), 5.06–4.81 (3H, m,
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2, and 6a-H), 6.07 (1H, dd, J = 17.5, 10.6 Hz,
CH2, and 6a-H), 6.07 (1H, dd, J = 17.5, 10.6 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH), 6.89 (1H, d, J = 9.1 Hz, 3-H), 7.01 (1H, d, J = 9.1 Hz, 2-H), 7.55 (1H, t, J = 7.0 Hz, 9-H), 7.65 (1H, m, 8-H), 7.70 (1H, d, J = 7.5 Hz, 7-H), 7.77 (1H, d, J = 7.5 Hz, 10-H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 25.2, 41.1, 47.3, 55.0, 55.9, 56.1, 110.1, 110.2, 111.8, 122.9, 123.6, 124.9, 125.3, 128.4, 131.8, 131.9, 146.4, 147.1, 147.3, 151.6, 163.4; GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 26.678 min, m/z (%) 335 (M+˙, 100), 320 (30), 306 (10), 361 (25); anal. calc. for C21H21NO3: C, 75.20; H, 6.31; N, 4.18. Found: C, 75.29; H, 6.40; N, 4.08.
CH), 6.89 (1H, d, J = 9.1 Hz, 3-H), 7.01 (1H, d, J = 9.1 Hz, 2-H), 7.55 (1H, t, J = 7.0 Hz, 9-H), 7.65 (1H, m, 8-H), 7.70 (1H, d, J = 7.5 Hz, 7-H), 7.77 (1H, d, J = 7.5 Hz, 10-H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 25.2, 41.1, 47.3, 55.0, 55.9, 56.1, 110.1, 110.2, 111.8, 122.9, 123.6, 124.9, 125.3, 128.4, 131.8, 131.9, 146.4, 147.1, 147.3, 151.6, 163.4; GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 26.678 min, m/z (%) 335 (M+˙, 100), 320 (30), 306 (10), 361 (25); anal. calc. for C21H21NO3: C, 75.20; H, 6.31; N, 4.18. Found: C, 75.29; H, 6.40; N, 4.08.
Trans-5-hydroxy-5-vinyl-6,6a-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoindolo[2,1-a]-quinolin-11(5H)-one (6j). Were obtained 390 mg (1.34 mmol, 78%), white solid; mp: 150–152 °C; IR (KBr): 3435, 2890, 1682 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 1.54 (4H, d, J = 8.5 Hz, CH3 and CH2), 2.41–2.23 (1H, m, CH2), 5.02 (1H, d, J = 11.9 Hz, 6a-H), 5.15 (1H, d, J = 10.6 Hz,
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.29 (1H, d, J = 17.3 Hz,
CH2), 5.29 (1H, d, J = 17.3 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.91 (1H, dd, J = 17.3, 10.5 Hz,
CH2), 5.91 (1H, dd, J = 17.3, 10.5 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 6.65 (1H, d, J = 2.9 Hz, 4-H), 6.71 (1H, dd, J = 8.8, 2.8 Hz, 2-H), 7.54 (1H, d, J = 7.5 Hz, 9-H), 7.65 (1H, d, J = 7.4 Hz, 8-H), 7.71 (1H, d, J = 7.2 Hz, 7-H), 7.77 (1H, d, J = 7.3 Hz, 10-H), 8.20 (1H, d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1-H), 9.28 (1H, s, OH); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 18.0, 27.6, 31.1, 40.6, 41.2, 55.3, 112.8, 115.2, 121.5, 123.6, 127.4, 128.9, 132.4, 132.6, 134.8, 145.2, 147.2, 154.1, 165.1 GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 35.56 min, m/z (%) 291 (M+˙, 100), 276 (55), 246 (90); anal. calc. For C19H17NO2: C, 78.33; H, 5.88; N, 4.81. Found: C, 78.44; H, 5.97; N, 4.75.
CH2), 6.65 (1H, d, J = 2.9 Hz, 4-H), 6.71 (1H, dd, J = 8.8, 2.8 Hz, 2-H), 7.54 (1H, d, J = 7.5 Hz, 9-H), 7.65 (1H, d, J = 7.4 Hz, 8-H), 7.71 (1H, d, J = 7.2 Hz, 7-H), 7.77 (1H, d, J = 7.3 Hz, 10-H), 8.20 (1H, d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1-H), 9.28 (1H, s, OH); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 18.0, 27.6, 31.1, 40.6, 41.2, 55.3, 112.8, 115.2, 121.5, 123.6, 127.4, 128.9, 132.4, 132.6, 134.8, 145.2, 147.2, 154.1, 165.1 GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 35.56 min, m/z (%) 291 (M+˙, 100), 276 (55), 246 (90); anal. calc. For C19H17NO2: C, 78.33; H, 5.88; N, 4.81. Found: C, 78.44; H, 5.97; N, 4.75.
Trans-1,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-5-vinyl-6,6a-dihydroisoindolo[2,1-a]quinolin-11(5H)-one (6k). Were obtained 400 mg (1.19 mmol, 80%), white solid; mp: 160–161 °C; IR (KBr): 2948, 1660 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 1.35 (3H, d, J = 0.9 Hz, CH3), 2.35 (1H, dd, J = 12.4, 7.1 Hz, CH2), 2.43 (1H, dd, J = 12.4, 7.0 Hz, CH2), 3.71 (3H, s, OCH3), 3.78 (3H, s, OCH3), 4.92 (1H, t, J = 6.9 Hz, 6a-H), 4.97 (1H, dd, J = 10.1, 2.4 Hz,
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.04 (1H, dd, J = 16.9, 2.4 Hz,
CH2), 5.04 (1H, dd, J = 16.9, 2.4 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 6.00 (1H, ddq, J = 16.8, 10.1, 1.0 Hz,
CH2), 6.00 (1H, ddq, J = 16.8, 10.1, 1.0 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH), 6.54 (1H, d, J = 1.4 Hz, 4-H), 6.84 (1H, d, J = 1.4 Hz, 2-H), 7.37 (2H, dd, J = 5.4, 3.6 Hz, 8H and 9H), 7.43–7.39 (1H, m, 7-H), 7.75–7.63 (1H, m, 10H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 25.1, 39.4, 42.4, 42.7, 55.7, 57.3, 58.5, 100.1, 107.1, 111.9, 122.5, 125.6, 125.7, 130.2, 131.9, 135.8, 141.3, 145.0, 155.1, 157.0, 164.5; GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 25.138 min, m/z (%) 335 (M+˙, 70), 320 (100), 288 (50), 256 (50); anal. calc. For C21H21NO3: C, 75.20; H, 6.31; N, 4.18. Found: C, 75.27; H, 6.38; N, 4.27.
CH), 6.54 (1H, d, J = 1.4 Hz, 4-H), 6.84 (1H, d, J = 1.4 Hz, 2-H), 7.37 (2H, dd, J = 5.4, 3.6 Hz, 8H and 9H), 7.43–7.39 (1H, m, 7-H), 7.75–7.63 (1H, m, 10H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 25.1, 39.4, 42.4, 42.7, 55.7, 57.3, 58.5, 100.1, 107.1, 111.9, 122.5, 125.6, 125.7, 130.2, 131.9, 135.8, 141.3, 145.0, 155.1, 157.0, 164.5; GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 25.138 min, m/z (%) 335 (M+˙, 70), 320 (100), 288 (50), 256 (50); anal. calc. For C21H21NO3: C, 75.20; H, 6.31; N, 4.18. Found: C, 75.27; H, 6.38; N, 4.27.
Trans-5-methyl-5-vinyl-6,6a-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoindolo[2,1-a]-quinolin-11(5H)-one (6l). Were obtained 350 mg (1.10 mmol, 70%), white solid; mp: 193–194 °C; IR (KBr): 2890, 1682 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 1.55–1.47 (4H, m, CH3 and CH2), 2.40–2.34 (1H, dd, J = 13.4, 2.28 Hz, CH2), 5.02 (1H d, J = 11.0 Hz, 6a-H), 5.13 (1H, d, J = 10.6 Hz,
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.26 (1H, d, J = 17.5 Hz,
CH2), 5.26 (1H, d, J = 17.5 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 5.88 (2H, dd, J = 17.3, 10.5 Hz,
CH2), 5.88 (2H, dd, J = 17.3, 10.5 Hz, ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH), 6.02–5.96 (2H, m,
CH), 6.02–5.96 (2H, m, 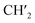 ), 6.72 (1H, s, 4-H), 7.54 (1H, t, J = 7.2 Hz, 9-H), 7.67 (1H, t, J = 7.1 Hz, 8-H), 7.73 (1H, d, J = 7.3 Hz, 7-H), 7.77 (1H, d, J = 7.3 Hz, 10-H), 7.94 (1H, s, 1-H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 27.7, 40.3, 40.5, 55.1, 100.8, 101.2, 107.9, 112.6, 122.7, 123.3, 126.2, 128.6, 128.9, 131.8, 132.3, 143.6, 144.7, 145.6, 146.7, 165.0; GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 28.88 min, m/z (%) 319 (M+˙, 100), 304 (55), 274 (55), 246 (90); anal. calc. For C20H17NO3: C, 75.22; H, 5.37; N, 4.39. Found: C, 75.30; H, 5.43; N, 4.46.
), 6.72 (1H, s, 4-H), 7.54 (1H, t, J = 7.2 Hz, 9-H), 7.67 (1H, t, J = 7.1 Hz, 8-H), 7.73 (1H, d, J = 7.3 Hz, 7-H), 7.77 (1H, d, J = 7.3 Hz, 10-H), 7.94 (1H, s, 1-H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 27.7, 40.3, 40.5, 55.1, 100.8, 101.2, 107.9, 112.6, 122.7, 123.3, 126.2, 128.6, 128.9, 131.8, 132.3, 143.6, 144.7, 145.6, 146.7, 165.0; GC/MS (70 eV), tR = 28.88 min, m/z (%) 319 (M+˙, 100), 304 (55), 274 (55), 246 (90); anal. calc. For C20H17NO3: C, 75.22; H, 5.37; N, 4.39. Found: C, 75.30; H, 5.43; N, 4.46.
Biology
Human tumour cell lines and culture media: PC3 (prostate carcinoma), HeLa (cervical epithelial carcinoma) were grown in RPMI 1640 medium (Invitrogen) supplemented with 10% heat inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), 1% of L-glutamine, 1% streptomycin, 100 units per mL penicillin (all obtained from Sigma Aldrich USA). MCF-7 (breast carcinoma, no overexpresses the HER2/c-erb-2 gene), SK-BR-3 (breast carcinoma, overexpresses the HER2/c-erb-2 gene) and primary culture of normal human dermis fibroblast used as control cells were grown in DMEM medium (GIBCO). Cells were grown in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2 and 95% air at 37 °C until they reach the exponential growth phase. For treatments exponentially growing cells were collected, counted, re-suspended in fresh culture medium, and incubated in 96 sterile well plates.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.Acknowledgements
Financial support from Patrimonio Autónomo Fondo Nacional de Financiamiento para la Ciencia, la Tecnología y la Innovación, Francisco José de Caldas (Project No. 007-2017, cod. 110274558597), is gratefully acknowledged. D. R. M. A. thanks COLCIENCIAS for the doctoral fellowship. The authors also thank Dr Carlos A. Echeverry-Gonzalez for his help in carrying out some experiments on mechanistic details and XRD group lab from UIS for his support in monocrystal X-ray analysis.Notes and references
- Z. Sui, J. Altom, V. Nguyen, J. Fernandez, J. Bernstein, J. J. Hiliard, J. F. Barrett, B. L. Podlogar and K. A. Ohemeng, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 1998, 6, 735–742 CAS.
- T. Lübbers, P. Angehrn, A. Gmünder and S. Herzig, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2007, 17, 4708–4714 Search PubMed.
- M. Garavís, B. López-Méndez, A. Somoza, J. Oyarzabal, C. Dalvit, A. Villasante, R. Campos-Olivas and C. González, ACS Chem. Biol., 2014, 9, 1559–1566 Search PubMed.
- M. Wall, M. C. Wani, C. E. Cook, K. H. Palmer, A. T. McPhail and G. A. Sim, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1966, 88, 3888–3890 CAS.
- P. Pigeon and B. Decroix, Synth. Commun., 1998, 28(13), 2507–2516 CAS.
- P. Pigeon, M. Othman, P. Netchitaïlo and B. Decroix, J. Heterocycl. Chem., 1999, 36, 691–695 CAS.
- J. Epsztajn, A. Jóźwiak, P. Kołuda, I. Sadokierska and I. Wilkowska, Tetrahedron, 2000, 56, 4837–4844 CAS.
- V. Mamane and Y. Fort, Tetrahedron Lett., 2006, 47, 2337–2340 CAS.
- Y. Zhou, L. Qian and W. Zhang, Synlett, 2009, 5, 0843–0847 Search PubMed.
- Ch. Reddy, S. Babu and R. Padmavathi, ChemistrySelect, 2016, 1, 2952–2959 CAS.
- E. V. Boltukhina, F. I. Zubkov and A. V. Varlamov, Chem. Heterocycl. Compd., 2006, 42, 971–1001 CAS.
- F. I. Zubkov, E. V. Boltukhina, K. F. Turchin, R. S. Borisova and A. V. Varlamov, Tetrahedron, 2005, 61, 4099–4113 CAS.
- (a) W. Zhang, A. Zheng, Z. Liu, L. Yang and Z. Liu, Tetrahedron Lett., 2005, 46, 5691–5694 CAS; (b) Z. Al-Jaroudi, P. P. Mohapatra, T. S. Cameron and A. Jha, Synthesis, 2016, 48, 4477–4488 CAS; (c) M. O'Brien, R. Weagle, D. Corkum, M. Kuanar, P. Mohapatra and A. Jha, Mol. Diversity, 2017, 21, 455–462 Search PubMed.
- S. Khadem, K. Udachin, G. Enright, M. Prakesch and P. Arya, Tetrahedron Lett., 2009, 50, 6661–6664 CAS.
- D. R. Merchán-Arenas and V. V. Kouznetsov, J. Org. Chem., 2014, 79, 5327–5333 Search PubMed.
- O. Ghashghaei, C. Masdeu, C. Alonso, F. Palacios and R. Lavilla, Drug Discov. Today Technol., 2018, 29, 71–79 Search PubMed.
- U. Hsing-Janlgi, C. Ericn, A. Browne and E. Sewy, Can. J. Chem., 1988, 66, 2345–2347 Search PubMed.
- P. J. Gregoire, J. M. Mellor and G. D. Merriman, Tetrahedron, 1995, 51, 6133–6144 CAS.
- A. Katritzky and M. F. Gordeev, J. Org. Chem., 1993, 58, 4049–4053 CAS.
- A. Muñoz, F. Sojo, D. R. Merchán Arenas, V. V. Kouznetsov and F. Arvelo, Chem.-Biol. Interact., 2011, 189, 215–221 Search PubMed.
- L. Chen, L. Feng, Y. He, M. Huang, Y. Liu, H. Yun and M. Zhuo, WO 2012/001020Al, 2012.
- V. V. Kouznetsov, Tetrahedron, 2009, 65, 2721–2750 CAS.
- S. Kobayashi, H. Ishitani and S. Nagayama, Synthesis, 1995, 09, 1195–1202 Search PubMed.
- H.-Y. Noh, S.-W. Kim, S. I. Paek, H.-J. Ha, H. Yun and W. K. Lee, Tetrahedron, 2005, 61, 9281–9290 CAS.
- M. E. Squillacote and F. Liang, J. Org. Chem., 2005, 70, 6564–6573 CAS.
- C.-M. Wang, Z.-H. Liu, Y.-K. Chen, J.-M. Han, Y.-L. Chen, M.-M. Miao and H. Cao, Comput. Theor. Chem., 2013, 1017, 174–181 CAS.
- J. Hernández Muñoz, Synlett, 2017, 23, 1101–1102 Search PubMed.
- E. Ohgaki, J. Motoyoshiya, S. Narita, T. Kakurai, S. Hayashi and K. Hirakawa, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1990, 1, 3109–3112 Search PubMed.
- V. V. Kouznetsov, A. R. Romero Bohórquez, L. Astudillo Saavedra and R. Fierro Medina, Mol. Divers., 2006, 10, 29–37 CAS.
- L. S. Povarov, Russ. Chem. Rev., 1967, 36, 656 Search PubMed.
- D. Bello, R. Ramon and R. Lavilla, Curr. Org. Chem., 2010, 14, 332–356 CAS.
- I. Muthukrishnan, V. Sridharan and J. C. Menéndez, Chem. Rev., 2019, 119(8), 5057–5191 CAS.
- S. Hermitage, J. A. K. Howard, D. Jay, R. G. Pritchard, M. R. Probert and A. Whiting, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2004, 2, 2451–2460 CAS.
- R. Marques, J. O. S. Varejão, A. Sousa, S. Castañeda and S. A. Fernandes, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2019, 17, 2913–2922 Search PubMed.
- A. Jha, T.-Y. Chou, Z. Jaroudi, B. D. Ellis and T. S. Cameron, Beilstein J. Org. Chem., 2014, 10, 848–857 Search PubMed.
- L. R. Domingo, M. J. Aurell, J. A. Sáez and S. M. Mekelleche, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 25268–25278 CAS.
- J. I. Garcia, J. A. Mayoral and L. Salvatella, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2005, 1, 85–90 Search PubMed.
- http://www.molinspiration.com/services.
- http://www.organic-chemistry.org/prog/peo/.
- C. A. Lipinski, F. Lombardo, B. W. Dominy and P. J. Feeney, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 1997, 23, 3–25 CAS.
- P. Ertl, B. Rohde and P. Selzer, J. Med. Chem., 2000, 43, 3714–3717 CAS.
- https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/survivors/patients/side-effects-of-treatment.htm, accessed 4.16.2020.
- T. Sander, J. Freyss, M. Von Korff and C. Rufener, J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2015, 55, 460–473 CAS.
- S. Jain, V. Chandra, P. Kumar Jain, K. Pathak, D. Pathak and A. Vaidya, Arabian J. Chem., 2016, 4920–4946 Search PubMed.
- R. Musiol, Expert Opin. Drug Discovery, 2017, 12, 583–597 CAS.
- T. Mosmann, J. Immunol. Methods, 1983, 65, 55–63 CAS.
- D. Callacondo, A. Quispe, S. Lindo and A. Vaisberg, Rev. Peru. Med. Exp. Salud Publica, 2008, 25, 380–385 Search PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. CCDC 2039928. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/d0ra04555a |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |