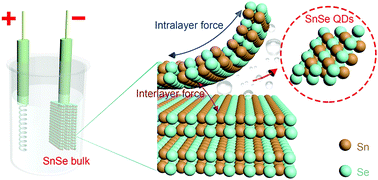
Tin selenide (SnSe) nanostructures hold great promise as an anode material in lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) due to their high storage capacity, rapid lithiation kinetics and long-term cycling stability. However, a scalable synthesis of SnSe nanostructures with a well-defined size remains a challenge in chemistry. Here, we report cathodic exfoliation of a bulk SnSe crystal for a high-yield (>90%) synthesis of sub-5 nm scale SnSe quantum dots (QDs). As-exfoliated SnSe QDs demonstrate a superior performance as the anode material for LIBs. Our results reveal that SnSe QDs not only accommodate the volume expansion/contraction during the reversible charging/discharging in LIBs but also increase the effective contact interface area between the nanostructured anode materials and electrolyte, leading to a high charging/discharging rate and superior cycling performance. Additionally, SnSe QD based LIBs exhibit a reversible capacity retention of 550 mA h g−1 and high coulombic efficiency approaching 100% after 1500 charging/discharging cycles at a current density of 0.5 A g−1.