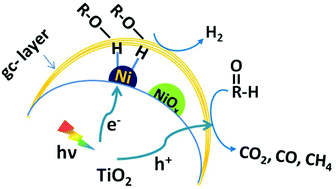
Hydrogen evolution from biomass via photocatalytic processes is possible but still challenging in the chemical industry. Herein, we report an enhanced photoreforming of biomass achieved by loading a graphitic carbon layer on TiO2/NiOx nanoparticles. Glucose and polyethylene glycol were used as renewable precursors to prepare a graphitic carbon layer on the NiOx nanoparticles. Enhanced hydrogen production yields of ∼270 μmol h−1 g−1 and ∼4000 μmol h−1 g−1 were obtained at room temperature and 80 °C, respectively, for photoreforming of a cellulose aqueous solution (∼2 wt%) over TiO2/NiOx@Cg. An interface between NiOx and the graphitic overlayer plays a key role in enhancing biomass photoreforming due to carbon modification for the nickel catalyst. This work demonstrates the feasibility of producing hydrogen directly from biomass by a single photocatalytic process, even over a non-precious metal co-catalyst with a fine-tuned structure of the carbon layer.