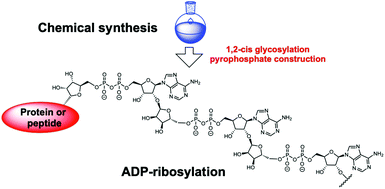
ADP-ribosylation is an important post-translational modification that plays a pivotal role in many cellular processes, including cell signaling, DNA repair, gene regulation and apoptosis. Although chemical synthesis of mono- or poly-ADP-ribosylated biomolecules is extremely difficult due to the challenges in regio- and stereoselective glycosylation, suitable protective group manipulations and pyrophosphate construction, synthetic procedures towards these bio-related targets have been reported in recent years. Chemically synthesized well-defined ADP-ribose derivatives serve as useful tools in biological experiments aimed to further elucidate native ADP-ribosylation. In this review, we will discuss the synthetic studies on mono-ADP-ribosylated proteins and oligo-ADP-ribose chains. Future possible synthetic targets and upcoming new methods for the synthesis of these molecules are also included.