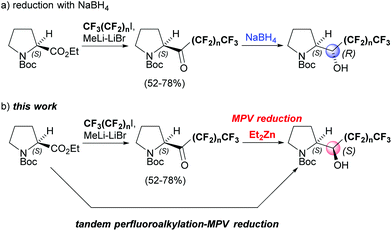
Asymmetric synthesis of (αS)-polyfluoroalkylated N-Boc-prolinols by the diethyl zinc-induced asymmetric Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley reduction of perfluoroalkyl N-Boc-pyrrolidyl ketones†
Kazumasa
Funabiki
*,
Hiroki
Iwata
,
Yosuke
Yano
,
Yasuhiro
Kubota
and
Masaki
Matsui
Department of Chemistry and Biomolecular Science, Faculty of Engineering, Gifu University, 1-1 Yanagido, Gifu 501-1193, Japan. E-mail: funabiki@gifu-u.ac.jp
First published on 11th February 2015
Abstract
The reduction of perfluoroalkyl N-Boc-pyrrolidyl ketones with diethyl zinc was investigated. As a result, asymmetric Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley reduction of perfluoroalkyl N-Boc-pyrrolidyl ketones proceeded smoothly with the use of 5 equiv. of diethyl zinc as a reducing agent in hexane at room temperature to give (αS)-polyfluoroalkylated N-Boc-prolinols in good yields (31–73%) with high diastereomer ratios (up to αR/αS = 7/93). The absolute configuration at the α-position of the major diastereomer is opposite to that obtained by the reduction of N-Boc-pyrrolidyl ketone with NaBH4 in ethanol. Furthermore, we also achieved the tandem perfluorobutylation-MPV reduction of N-Boc-proline ethyl ester to give (αS)-perfluorobutylated N-Boc-prolinol as a sole diastereomer in 45% yield.
Introduction
Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley (MPV) reduction is a classic reaction in organic synthesis. The MPV reduction of ketones normally requires metal alkoxides, e.g., alkali metal and aluminium alkoxides.1 Although there are a few successful examples of MPV reduction using diethyl zinc (Et2Zn),2 there have been no reports on stereoselective MPV reduction with Et2Zn.On the other hand, considerable attention has been focused on prolinol derivative-catalyzed asymmetric synthesis, since prolinol derivatives are some of the most important and versatile asymmetric organocatalysts in catalytic asymmetric reactions.3 Although α-trifluoromethylated aminoalcohols have been used as chiral ligands,4 a chiral auxiliary5 and organocatalysts,6 there have been few reports on asymmetric synthesis or the use of α-fluoroalkylated optically pure prolinol derivatives.7
Recently, we developed (αR)-polyfluoroalkylated prolinols based on the perfluoroalkyl-induced highly stereoselective reduction of perfluoroalkyl N-Boc-pyrrolidyl ketones with sodium borohydride (NaBH4) (a, Scheme 1).7a In this paper, we describe not only the complementary synthesis of (αS)-polyfluoroalkylated prolinols by the asymmetric MPV-type reduction of perfluoroalkyl N-Boc-pyrrolidyl ketones with Et2Zn, but also the one-pot asymmetric synthesis of (αS)-polyfluoroalkylated prolinols by the tandem perfluorobutylation-asymmetric MPV-type reduction8 of N-Boc proline ethyl ester (b, Scheme 1).
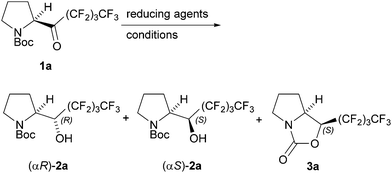
Results and discussion
As shown in Table 1, treatment of perfluorobutyl N-Boc-pyrrolidyl ketone (1a) with 5 equiv. of Et2Zn in hexane at 0 °C gave α-polyfluorobutylated prolinol 2a in 29% yield as a mixture of stereoisomers with an αR![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) αS ratio of 29
αS ratio of 29![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 71, together with recovery of the starting ketone 1a (54%) (entry 2).
71, together with recovery of the starting ketone 1a (54%) (entry 2).
| Entry | Reducing agents (equiv.) | Solvent | Conditions | Yield (%) | αR![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) αSa αSa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Determined by GC analysis. b Previous work. See ref. 7a. c Isolated yields of both diastereomers. | |||||
| 1b | NaBH4(3) | EtOH | rt, 7 h | 2a (78)c | >99![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) <1 <1 |
| 2 | Et2Zn (5) | Hexane | 0 °C, 24 h | 2a (29)c, 1a (54) | 29![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 71 71 |
| 3 | Et2Zn (5) | Hexane | rt, 24 h | 2a (73)c | 8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 92 92 |
| 4 | Et2Zn (2) | Hexane | rt, 24 h | 2a (41)c, 1a (46) | 8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 92 92 |
| 5 | i-Pr2Zn (5) | Hexane | rt, 24 h | 2a (74)c | 17![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 83 83 |
| 6 | Et2Zn (5) | Hexane | Reflux | 2a (57)c, 3a (13) | 14![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 86 86 |
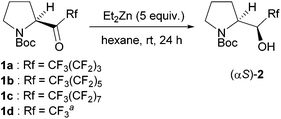
Interestingly, the absolute configuration at the α-position of the major diastereomer produced by MPV reduction is opposite to that obtained by the reduction of perfluorobutylated N-Boc-pyrrolidyl ketone 1a with NaBH4 in ethanol, as reported previously (entry 1).7a MPV reduction of the ketone 1a with Et2Zn at room temperature resulted in a large increase in the yield (73%) of prolinol 2a with a much better diastereomer ratio (αR/αS = 92/8) (entry 3). The diastereomers of 2a are separable by normal column chromatography with silica gel. However, two conformational isomers of (αS)-2a that arise from an amide moiety were observed by NMR spectroscopy. Employment of 2 equiv. of Et2Zn gave 2a in only 41% yield, together with the 46% recovery of the starting ketone 1a (entry 4). The use of diisopropyl zinc (i-Pr2Zn) in place of Et2Zn lowered the isomer ratio from 8/92 to 17/83 (entry 5). A higher reaction temperature gave both a lower diastereomer ratio (14/86) and a lower yield (57%), together with 1-perfluoroalkylated oxazolidinone 3a in 13% yield, which was produced via the cyclization of (αS)-2a (entry 6). Based on these results, the optimized reaction conditions are given in entry 2, which requires 5 equiv. of Et2Zn at room temperature.
Based on the screening of the reaction conditions in Table 1, other perfluoroalkyl N-Boc-pyrrolidyl ketones 1b,c,d carrying perfluorohexyl, perfluorooctyl, and trifluoromethyl groups were examined (Table 2). Perfluorohexylated and perfluorooctylated N-Boc-pyrrolidyl ketones 1b,c participated nicely in the MPV reduction with 5 equiv. of Et2Zn to give the corresponding α-polyfluorohexylated and perfluorooctylated prolinols 2b,c in 67–70% yields with αR/αS isomer ratios of 7–8/92–93. The reaction of trifluoromethylated N-Boc-pyrrolidyl ketone 1d containing ketone hydrate did not proceed smoothly to give the corresponding α-trifluoromethylated prolinol 2d in 31% yield as a mixture of stereoisomers with an αR![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) αS ratio of 8
αS ratio of 8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 92, together with recovery of the starting ketone 1a containing its hydrate (41%) (entry 4).
92, together with recovery of the starting ketone 1a containing its hydrate (41%) (entry 4).
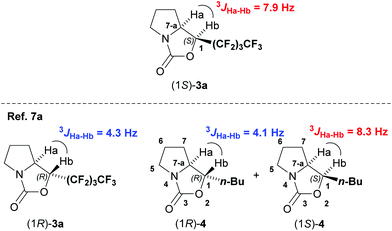
The stereochemistries at the α-position of α-perfluorobutylated prolinol (2a) produced by MPV reduction with Et2Zn could be confirmed to be S based on the vicinal coupling constant of the obtained 1-perfluorobutylated oxazolidinone 3a. The coupling constant between two protons at C-7-a and C1 of the obtained 1-perfluorobutylated oxazolidinone 3a was 7.9 Hz, which is similar to that previously reported for n-butylated oxazolidinone (1S)-4, as shown in Fig. 1.7a The stereochemical assignments for the other α-polyfluorobutylated prolinols 2b,c were made by comparison of the chemical shifts in 19F NMR with those of αR- and αS-2a.
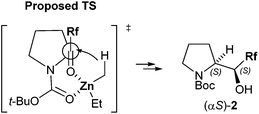
Based on the absolute stereochemistry at the α-carbon of (αS)-perfluorobutylated prolinol ((αS)-2a), a proposed transition state (TS) is shown in Fig. 2. A hydride transfers from an ethyl group of Et2Zn to perfluoroalkyl N-Boc-pyrrolidyl ketone 1 through a transition state (TS), where not only chelation between zinc metal and two oxygen atoms of two carbonyl groups of ketone and Boc groups 1 but also the steric repulsion between bulkier N-Boc-pyrrolidyl and ethyl groups are crucial.
Finally, the one-pot asymmetric synthesis of (αS)-perfluoroalkylated N-Boc-prolinol (αS)-2a through tandem perfluoroalkylation-MPV reduction of N-Boc proline ethyl ester was examined (Scheme 2). After N-Boc-proline ethyl ester was subjected to perfluorobutylation by the reaction of iodoperfluorobutane with a methyllithium–lithium bromide complex for 6 h at −78 °C, the resulting mixture was gradually warmed to room temperature overnight. Consequently, the one-pot tandem perfluorobutylation-MPV reduction successfully proceeded to give the (αS)-perfluorobutylated N-Boc-prolinol (αS)-2a as a sole diastereomer in 45% yield.
 | ||
| Scheme 2 One-pot tandem perfluoroalkylation-MPV reduction of N-Boc proline ethyl ester leading to (αS)-perfluoroalkylated N-Boc-prolinol 2a. | ||
Conclusions
In conclusion, we have developed an asymmetric Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley reduction of perfluoroalkyl N-Boc-pyrrolidyl ketones with the use of 5 equiv. of Et2Zn as a reducing agent to give (αS)-polyfluoroalkylated N-Boc-prolinols in good yields (31–73%) with high diastereomer ratios (up to αR/αS = 8/92). This method represents a complementary asymmetric synthesis of (αS)-polyfluoroalkylated N-Boc-prolinols, of which the absolute configuration of at the α-position of the major diastereomer is opposite to that obtained by the reduction of N-Boc-pyrrolidyl ketone with NaBH4 in ethanol. Furthermore, we have also achieved the tandem perfluorobutylation-MPV reduction of N-Boc-proline ethyl ester to give (αS)-perfluorobutylated N-Boc-prolinol (αS)-2a as a sole diastereomer in 45% yield.Acknowledgements
We thank Professor T. Konno of the Kyoto Institute of Technology for the HRMS measurements.Notes and references
- For selected reviews, see: (a) A. L. Wilds, Org. React., 1944, 2, 178 Search PubMed; (b) M. J. Palmer and M. Wills, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 1999, 10, 2045 CrossRef CAS; (c) K. Nishide and M. Node, Chirality, 2002, 14, 759 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) J. E. Jerome and R. H. Sergent, Chem. Ind., 2003, 89, 97 CAS.
- (a) S. Sasaki, T. Yamaguchi, H. Kubo, M. Kanai, A. Ishii and K. Higashiyama, Tetrahedron Lett., 2005, 46, 1497 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) K. Yearick and C. Wolf, Org. Lett., 2008, 10, 3915 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For recent reviews of the prolinol derivatives, see: (a) S. Meninno and A. Lattanzi, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 3821 RSC; (b) K. L. Jensen, G. Dickmeiss, H. Jiang, Ł. Albrecht and K. A. Jørgensen, Acc. Chem. Res., 2012, 45, 248 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) T. Katagiri, Y. Fujiwara, S. Takahashi, N. Ozaki and K. Uneyama, Chem. Commun., 2002, 986 RSC; (b) A. Harada, Y. Fujiwara and T. Katagiri, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 2008, 19, 1210 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) Y. Fujiwara, T. Katagiri and K. Uneyama, Tetrahedron Lett., 2003, 44, 6161 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Katagiri, N. Iguchi, T. Kawate, S. Takahashi and K. Uneyama, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 2006, 17, 1157 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) K. A. Wayman and T. Sammakia, Org. Lett., 2003, 5, 4105 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) G. T. Notte, T. Sammakia and P. J. Steel, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 13502 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) G. T. Notte and T. Sammakia, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 4230 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) H. Cui, Y. Li, C. Zheng, G. Zhao and S. Zhu, J. Fluorine Chem., 2008, 129, 45 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) X.-H. Xu, X.-L. Qiu and F.-L. Qing, Tetrahedron, 2008, 64, 7353 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) K. Funabiki, A. Shibata, K. Hatano and M. Matsui, J. Fluorine Chem., 2009, 130, 444 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) K. Funabiki, A. Shibata, H. Iwata, K. Hatano, Y. Kubota, K. Komura, M. Ebihara and M. Matsui, J. Org. Chem., 2008, 73, 4694 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) S. Goushi, K. Funabiki, M. Ohta, K. Hatano and M. Matsui, Tetrahedron, 2007, 63, 4061 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) G. Chaume, V. M.-C. Severen, S. Marinkovic and T. Brigaud, Org. Lett., 2006, 8, 6123 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) T. Taguchi, Y. Suda, M. Hamochi, Y. Fujino and Y. Iitaka, Chem. Lett., 1991, 20, 1425 CrossRef , and ref. 6f.
- For tandem perfluoroalkylation-MPV reduction of achiral esters, see: T. Yamazaki, T. Terajima and T. Kawasaki-Taskasuka, Tetrahedron, 2008, 64, 2419 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c5qo00008d |
| This journal is © the Partner Organisations 2015 |