Themed collection New Trends and Challenges in Surface Phenomena, Carbon Nanostructures and Helium Droplets

New trends and challenges in surface phenomena, carbon nanostructures and helium droplets – Festschrift for Giorgio Benedek
This themed collection includes a collection of articles on new trends and challenges in surface phenomena, carbon nanostructures and helium droplets.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 28103-28104
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP90196J
Giorgio Benedek: an extraordinary scientist and cultured gentleman
A Profile of Giorgio Benedek written by the Guest Editors of this Festschrift themed collection.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 28105-28108
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP90197H
Atom–surface scattering in the classical multiphonon regime
Many experiments that utilize beams of incident atoms colliding with surfaces as a probe of surface properties are carried out at large energies, high temperatures and with large mass atoms.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 16942-16972
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP01144A
Supraballs as spherical solid 3D superlattices of hydrophobic nanocrystals dispersed in water: nanoarchitectonics and properties
Nanoheaters: FCC solid spherical nanocrystal assemblies either dispersed in solution or internalized in tumor cells.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 14140-14149
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP00566B
On the fate of high-resolution electron energy loss spectroscopy (HREELS), a versatile probe to detect surface excitations: will the Phoenix rise again?
High-resolution electron energy loss spectroscopy is a powerful tool to investigate surface excitations (vibrations of chemisorbed atoms and molecules, phonons, plasmons). Here, a perspective on the status and the future perspectives of HREELS is presented.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 26061-26069
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP03804D
Variation of bending rigidity with material density: bilayer silica with nanoscale holes
Helium atom scattering experiments on a “holey” silica bilayer film reveal that the bending rigidity of the material, extracted from phonon dispersion curves, decreases with decreasing material density.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 17941-17945
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP01960D
Intercalation and reactions of CO under single layer graphene/Ni(111): the role of vacancies
We use synchrotron radiation-induced core level photoemission spectroscopy to investigate the influence of vacancies, produced by ion bombardment, on monolayer graphene/Ni(111) exposed to CO at pressures ranging from ultra-high vacuum up to near ambient (5.6 mbar) conditions.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 28486-28494
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP03441G
Interaction of imidazolium-based ionic liquids with supported phospholipid bilayers as model biomembranes
The cytotoxicity of ionic liquids (ILs) is receiving increasing attention due to their potential biological and environmental impact. We have used atomic force microscopy to investigate the interaction of ILs with supported phospholipid bilayers, as models of biomembranes.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 27328-27342
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP02866B
Observation of diffuse scattering in scanning helium microscopy
By studying well defined geometries (microspheres) in scanning helium microscopy (SHeM) the default scattering distribution for technological surfaces in SHeM is found to be diffuse and approximately cosine.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 26539-26546
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP01951E
Electron–phonon interaction and ultrafast photoemission from doped monolayer MoS2
We present results of combined density functional theory and many-body theory analysis of the effect of electron–phonon coupling on photoluminescence and ultrafast response of electron doped monolayer MoS2.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 25298-25306
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP02905G
A semiempirical potential for alkali halide diatoms with damped interactions I. Rittner potential
Damping functions are added to the T-Rittner potential of alkali halide diatoms, with the result that the potential has a realistic repulsive potential similar to isoelectronic rare gas dimers, but orders of magnitude deeper attractive wells.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 24823-24833
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP03405K
Nanostructured 3C-SiC on Si by a network of (111) platelets: a fully textured film generated by intrinsic growth anisotropy
Micron-wide, highly-oriented 3C-SiC platelets are obtained by stacking-fault-driven growth anisotropy.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 24487-24494
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP03250C
Enhanced elastic scattering of He2 and He3 from solids by multiple-edge diffraction
We report on a method of enhanced elastic and coherent reflection of 4He2 and 4He3 from a micro-structured solid surface under grazing incidence conditions.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 21593-21600
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP02641D
Effect of sodium chloride adsorption on the surface premelting of ice
We characterise the structure of the quasi-liquid layer at two low-index ice surfaces in the presence of sodium chloride (Na+/Cl−) ions by molecular dynamics simulations and discuss its effect on crystal growth and surface chemistry on ice.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 20932-20940
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP02277J
Time-dependent density functional theory calculations of electronic friction in non-homogeneous media
We assess the reliability of the local density friction approximation and show that, despite the strong approximations involved, it is able to provide a good estimate of the friction force suffered by an atomic particle at a metal surface.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 20239-20248
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP01972H
Quantum error correction with molecular spin qudits
Molecular multi-level spin qudits are very promising for quantum computing, embedding quantum error correction within single objects. We compare the performance of electronic/nuclear molecular qudits in the implementation of quantum error correction.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 20030-20039
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP01228F
Geometry of tellurene adsorbed on the Si(111)-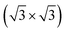 R30°-Sb surface from first principles calculations
R30°-Sb surface from first principles calculations
The 2D form of tellurium, named tellurene, is one of the latest discoveries in the family of 2D mono-elemental materials.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 18608-18614
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP01759H
Impact of the energy dispersion anisotropy on the plasmonic structure in a two-dimensional electron system
The effect of the band structure anisotropy (triangular, square, and hexagonal wrapping) on the electronic collective excitations (plasmons) in a two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) is studied in the framework of the random-phase approximation.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 17885-17894
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP02050E
Ordered assembly of non-planar vanadyl-tetraphenylporphyrins on ultra-thin iron oxide
Thanks to the ultrathin oxide layer, an ordered arrangement of flat-lying porphyrins with a protruding core is obtained on Fe(001).

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 17077-17087
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP05914A
Recognition of quinolone antibiotics by the multidrug efflux transporter MexB of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Putative binding modes (BMs) of quinolones to the bacterial efflux transporter MexB were identified. Multiple interaction patterns are possible, supporting the hypothesis that substrates oscillate between different BMs with similar affinity.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 16566-16575
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP00951J
Perturbation theory of scattering for grazing-incidence fast-atom diffraction
A classical analysis of grazing-incidence, fast atom diffraction (GIFAD) allows us to develop simple analytic results that connect observed phenomena directly to basic aspects of the potential, such as the lateral variation of the well-depth.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 15851-15859
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP01013E
Topology detection in cavity QED
We explore the physics of topological lattice models immersed in c-QED architectures for arbitrary coupling strength with the photon field, and investigate the use of the cavity transmission as a topology detector.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 15860-15870
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP01806C
Surface diffusion within the Caldeira–Leggett formalism
Intermediate scattering function for a light adsorbate considered to be distinguishable (black solid curve), boson (blue dashed curve) and fermion (red dotted curve).

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 15871-15890
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP01579J
Magnetic nature and hyperfine interactions of transition metal atoms adsorbed on ultrathin insulating films: a challenge for DFT
The magnetic ground state and hyperfine coupling parameters of first-row transition metal atoms adsorbed on metal-supported MgO ultrathin films are calculated using DFT. The methodological challenges and the role of the support are highlighted.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 15891-15903
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP01224C
Molecular hydrogen isotope separation by a graphdiyne membrane: a quantum-mechanical study
Quantum effects enable the separation of heavier hydrogen isotopes in their transport through graphdiyne.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 15840-15850
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP01044E
Phthalocyanine reactivity and interaction on the 6H-SiC(0001)-(3 × 3) surface investigated by core-level experiments and simulations
Core-level experiments require new adsorption models for phthalocyanine. Incorporation of Si adatoms into the molecules is energetically convenient.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 14937-14946
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP00750A
Water on porous, nitrogen-containing layered carbon materials: the performance of computational model chemistries
The performance of various computational model chemistries in predicting structural, thermodynamic and optical properties of water-covered carbon and nitrogen containing porous materials is investigated.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 14709-14726
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP00657J
Measuring surface phonons using molecular spin-echo
A new method to measure surface phonons with a molecular beam is presented.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 14198-14208
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP01372J
Thermal conduction and rectification phenomena in nanoporous silicon membranes
Non-equilibrium molecular dynamics simulations have been applied to study thermal transport properties, such as thermal conductivity and rectification, in nanoporous Si membranes.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 13625-13632
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP00775D
Steric hindrance in the on-surface synthesis of diethynyl-linked anthracene polymers
Steric hindrance effect in the formation of hybrid sp-sp2 carbon structures on Au(111) by on surface synthesis with anthracene-based precursors.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 13616-13624
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP00730D
Setting the limit for the lateral thermal expansion of layered crystals via helium atom scattering
Helium diffraction provides a direct method for measuring the surface thermal expansion of 2D materials.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 13229-13233
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP00758D
Delving into guest-free and He-filled sI and sII clathrate hydrates: a first-principles computational study
Computational first-principles investigations on structural properties and stability of He@sI and He@sII clathrate hydrate crystals.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 13119-13129
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP00701K
Temperature dependence in fast-atom diffraction at surfaces
We investigate the influence of the temperature in Fast Atom Diffraction at surfaces. The inelastic profiles broaden rapidly while the elastic one is constant but its intensity decreases with a Debye-Waller factor adapted to grazing incidences.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 12319-12328
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP00829G
Spectroscopic signatures of nonpolarons: the case of diamond
First-principles calculations of spectroscopy images showing polaronic signatures in intrinsic diamond produced by many-body electron–phonon interactions.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 12580-12591
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP01012G
Investigating the quasi-liquid layer on ice surfaces: a comparison of order parameters
The temperature dependence of the quasi-liquid layer on the surfaces of hexagonal and cubic ice is investigated with molecular dynamics simulations and a selection of different methods to discriminate the phase of molecules.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 12476-12487
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP00752E
Stabilization of phenanthrene anions in helium nanodroplets
Phenanthrene anions are stabilized in the ultracold environment of helium nanodroplets. Gentle shrinking of the helium matrix by collisions with helium gas makes the bare phenanthrene anion visible by high-resolution mass spectrometry.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 11662-11667
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP00991A
Electron–phonon coupling and superconductivity in a 2D Tl–Pb compound on Si(111)
A first principles investigation of the electron–phonon interaction and phonon-mediated pairing strength in a Si(111) supported single-layer Tl–Pb compound reveals strong variations with electronic surface bands and binding energy.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 10140-10146
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP00522K
UV resonance Raman spectroscopy of weakly hydrogen-bonded water in the liquid phase and on ice and snow surfaces
UV excitation selectively enhances Raman scattering from weakly hydrogen-bonded water molecules.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 10499-10505
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP01072K
Vibrational properties of graphdiynes as 2D carbon materials beyond graphene
Raman and IR spectra investigation of 2D carbon crystals belonging to the family of graphdiynes (GDYs) and having different structures is performed in this paper, focusing on how these spectra are affected by different topological features.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 10524-10536
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP00980C
Probing the presence and absence of metal-fullerene electron transfer reactions in helium nanodroplets by deflection measurements
Electrostatic deflection of a beam of helium nanodroplets containing fullerenes and metal atoms reveals whether these dopants are able to form charge-transfer complexes.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 10378-10383
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP00751G
Strain modulation in small molecule physisorption in two dimensions: LEED structure analysis and DFT modeling of the system 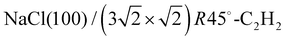
Surface structure analysis of the physisorption system NaCl(100)/Acetylene using quantitative low-energy electron diffraction (LEED) in combination with density functional theory (DFT).

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 9168-9175
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP05827D
Geometrical picture of the electron–electron correlation at the large-D limit
The correlation energy is bounded by an area law εcorr ≤ CΔ(area), which is a close resemblance of the area law conjecture of entanglement entropy.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 9298-9307
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP00438K
Surface electronic corrugation of a one-dimensional topological metal: Bi(114)
We present helium atom scattering measurements, normal to the steps of vicinal Bi(114), together with quantum mechanical scattering calculations. We thus obtain a representation of the surface electronic corrugation of the quasi one-dimensional metal.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 9146-9155
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP05284E
Surface dynamics on submonolayer Pb/Cu(001) surfaces
The interplay of the atomic structure and phonon spectra of various two-dimensional ordered phases forming during submonolayer (from 0.375 ML to ultimate 0.6 ML) Pb adsorption on a Cu(001) surface is investigated using embedded atom method interatomic interaction potentials.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 5164-5170
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP05705G
Helium structures around SF5+ and SF6+: novel intermolecular potential and mass spectrometry experiments
The structure of the He atoms around SF5+ and SF6+ is investigated both experimentally and theoretically.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022,24, 2004-2014
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP04725F
Bulk band structure of Sb2Te3 determined by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy
Rb atoms were deposited on an Sb2Te3 surface. Based on ARPES measurements performed on Rb-doped as well as clean Sb2Te3 surfaces it was found that the absolute valence band maximum of Sb2Te3 is likely to be found near the bulk Γ point.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 26401-26406
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP04031F
About this collection
This is a Festschrift issue, in honour of Professor Giorgio Benedek on the occasion of his 80th birthday.
Professor Benedek is a very well-known surface physicist, Emeritus Professor at the University of Milano-Bicocca and is still actively publishing today. He has contributed and is still contributing significantly to the study of surface phenomena, in particular to elementary surface vibrational excitations, atom-surface scattering, clusters grown on metal surfaces, chemical reactions at surfaces, electron-phonon interaction in topological insulators and semimetals, non-adiabatic effects, carbon nanostructures, graphene, helium droplets and quantum liquids, superfluidity, collective electronic excitations, covering experimental and theoretical aspects of all of these research lines. Giorgio has impressively remained at the forefront of many of these fields, and we are delighted to recognise his contributions with this Festschrift issue intended to cover the all low-dimensional systems and surface phenomena.
Guest Edited by: Marco Bernasconi (University of Milano-Bicocca), Ricardo Díez-Muiño (Centro de Física de Materiales and Donostia International Physics Center), Pedro M. Echenique (Donostia International Physics Center), Joseph R. Manson (Clemson University) Salvador Miret-Artés (Institute of Fundamental Physics) and J. Peter Toennies (University of Göttingen and MPI Institut für Dynamik und Selbstorganisation).