Photoinduced interfacial electron transfer from perovskite quantum dots to molecular acceptors for solar cells†
Abstract
Bandgap-engineered inorganic and hybrid halide perovskite (HP) films, nanocrystals, and quantum dots (PQDs) are promising for solar cells. Fluctuations of photoinduced electron transfer (PET) rates affect the interfacial charge separation efficiencies of such solar cells. Electron donor- or acceptor-doped perovskite samples help analyze PET and harvest photogenerated charge carriers efficiently. Therefore, PET in perovskite-based donor–acceptor (D–A) systems has received considerable attention. We analyzed the fluctuations of interfacial PET from MAPbBr3 or CsPbBr3 PQDs to classical electron acceptors such as 7,7,8,8-tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ) and 1,2,4,5-tetracyanobenzene (TCNB) at single-particle and ensemble levels. The significantly negative Gibbs free energy changes 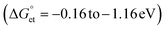 of PET estimated from the donor–acceptor redox potentials, the donor–acceptor sizes, and the solvent dielectric properties help us clarify the PET in the above D–A systems. The dynamic nature of PET is apparent from the decrease in photoluminescence (PL) lifetimes and PL photocounts of PQDs with an increase in the acceptor concentrations. Also, the acceptor radical anion spectrum helps us characterize the charge-separated states. Furthermore, the PL blinking time and PET rate fluctuations (108 to 107 s−1) provide us with single-molecule level information about interfacial PET in perovskites.
of PET estimated from the donor–acceptor redox potentials, the donor–acceptor sizes, and the solvent dielectric properties help us clarify the PET in the above D–A systems. The dynamic nature of PET is apparent from the decrease in photoluminescence (PL) lifetimes and PL photocounts of PQDs with an increase in the acceptor concentrations. Also, the acceptor radical anion spectrum helps us characterize the charge-separated states. Furthermore, the PL blinking time and PET rate fluctuations (108 to 107 s−1) provide us with single-molecule level information about interfacial PET in perovskites.

- This article is part of the themed collections: Halide Perovskite Optoelectronics and Quantum Dots: A Nanoscience Nobel Prize


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...