One-pot spatial engineering of multi-enzymes in metal–organic frameworks for enhanced cascade activity†
Wenqing
Fan
a,
Kang
Liang
 *ab and
Jieying
Liang
*a
*ab and
Jieying
Liang
*a
aSchool of Chemical Engineering, Australian Centre for NanoMedicine, The University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW 2052, Australia. E-mail: kang.liang@unsw.edu.au; jieying.liang@unsw.edu.au
bGraduate School of Biomedical Engineering, The University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW 2052, Australia
First published on 15th October 2024
Abstract
Enzyme encapsulation in metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) faces significant challenges, including restricted substrate diffusion, random enzyme distribution, and diminished catalytic performance, particularly in multi-enzyme systems. To address these issues, we propose a facile one-pot strategy to achieve spatial engineering of multiple enzymes in MOFs. Using the environmentally sustainable and cost-effective polymer, poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDADMAC), the surface charge of enzymes can be selectively modified. This modification allows enzymes with a negative surface charge to accelerate MOF nucleation, leading to their primary localization in the core, while enzymes with a positive surface charge slow the nucleation process, resulting in their exclusive placement in the outer shell. This structure enables effective compartmentalization, efficient intermediate transfer, prevention of cross-reactivity, and alteration of enzyme conformation. Consequently, this approach significantly enhances the cascade reaction activity and is effective even for incompatible enzymes, achieving a 1.69- to 14.85-fold improvement in catalytic efficiency compared to unmodified systems. Additionally, the resulting biocomposites exhibit robust catalytic performance under adverse environmental conditions and maintain their efficiency over multiple cycles, making them highly promising for diverse industrial and environmental applications.
Introduction
Enzymes, as biocatalysts, facilitate a wide range of biochemical reactions with remarkable efficiency and specificity under mild conditions.1 Their applications span across various fields, including pharmaceuticals, bioremediation, and the synthesis of biofuels and fine chemicals.2–7 Multi-enzyme cascade reactions, where multiple enzymes act sequentially on substrates to produce final products, offer enhanced reaction efficiency and specificity, making them highly effective for complex biochemical processes.8 These cascades can significantly amplify the benefits of single-enzyme reactions by increasing the yield and efficiency while minimizing side reactions, as they closely mimic natural metabolic pathways.9 The spatial positioning of enzymes within the reaction medium is crucial for multi-enzyme cascade reactions, as it ensures the efficient transfer of intermediates between enzymatic steps.10 However, achieving the close proximity of multiple enzymes without interference or cross-reactivity is challenging, especially when maintaining the high activity of each enzyme.11 Moreover, the industrial use of enzymes faces significant challenges, including their instability under harsh operational conditions, such as extreme temperatures, susceptibility to denaturation, and the high costs associated with production and purification.12–14 These issues, combined with low recovery rates and reduced reusability, often render enzymes less cost-effective for large-scale industrial applications.15 Therefore, there is a pressing need for a platform that can both stabilize enzymes and allow precise control over their spatial arrangement.To address the challenges mentioned above, metal–organic frameworks (MOFs)—coordination networks composed of organic ligands and metal nodes—offer a promising platform for enzyme immobilization due to their high surface areas, tunable structures, and high porosity.16,17 Among these, zeolitic imidazolate framework 8 (ZIF-8), constructed from zinc ions and imidazolate ligands, stands out for its exceptional structural and textural properties, making it an ideal candidate for biocatalysis applications.11,18 ZIF-8 can be engineered to facilitate selective substrate diffusion and protect enzymes from harsh environmental conditions.19,20 Traditional strategies for direct enzyme encapsulation within single-compartment MOFs, such as physical adsorption, covalent attachment, coprecipitation, and biomineralization, often result in random enzyme distribution, leading to reduced catalytic performance21–23 To overcome this, various methods have been developed to achieve more organized enzyme placement within MOFs, including stepwise encapsulation of enzymes through epitaxial shell-by-shell overgrowth,24 peptide-induced self-assembly,25 and post-filtration of different enzymes into MOF pores.26 However, these approaches are typically multi-step processes and often fail to achieve a precise spatial arrangement within a single MOF. The challenge remains to develop a more straightforward, one-step spatial engineering strategy that can position multiple enzymes in an organized structure, thereby simultaneously enhancing their cascade activity and stability. It has been reported that the surface properties of enzymes, such as functional groups (e.g., cysteine,27 carboxylate/phosphate groups,28 and histidine29) and surface charge, significantly influence their encapsulation within a MOF matrix. For example, modifying the enzyme surface with acetic anhydride increases its negative charge, which tends to concentrate Zn2+, thereby promoting rapid MOF nucleation. In contrast, an enzyme with a positive charge tends to exclude Zn2+, thereby slowing down the MOF nucleation process.30 This suggests that controlling enzyme surface properties could regulate the MOF nucleation and enzyme encapsulation process. However, to date, no research has explored the possibility of regulating the spatial distribution of different enzymes in one step by tailoring their surface properties.
In this work, poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDADMAC), a water-soluble, quaternary ammonium cationic polyelectrolyte, was used to modify enzymes. PDADMAC typically acts as a positively charged colloid in aqueous solutions31 and was used as a dispersant for enzymes. Thus, the positively charged PDADMAC readily coats the negatively charged enzyme surface through electrostatic interactions.32,33 A one-pot spatial engineering strategy was developed to position two different enzymes within an organized structure. By modifying the surface charge of one enzyme using PDADMAC, the naturally negatively charged enzyme was primarily localized in the core, while the surrounding shell contained only the positively charged PDADMAC-modified enzyme. This approach mimics a controlled hierarchical organization, akin to core-shelled compartmentalization, but within a single MOF construct (Scheme 1). Three enzyme models were employed: a compatible enzyme model using glucose oxidase/horseradish peroxidase (GOx/HRP) and two incompatible enzyme models using protease/GOx (Pro/GOx) and Pro/alcohol dehydrogenase (Pro/ADH). The results demonstrate that both compatible and incompatible multi-enzyme systems exhibited improved catalytic activity compared to unmodified counterparts, confirming that PDADMAC modification effectively stabilizes and organizes enzymes within a single MOF. Furthermore, these composites maintained high catalytic efficiency across multiple cycles and under environmental stress tests, including high temperatures, organic solvent exposure, and proteolytic degradation. This one-pot spatial engineering strategy for multi-enzyme encapsulation in MOFs shows great promise for enhancing cascade activity and stability, making these composites strong candidates for various industrial and environmental applications.
Results and discussion
Synthesis and characterization of multi-enzyme encapsulated MOFs
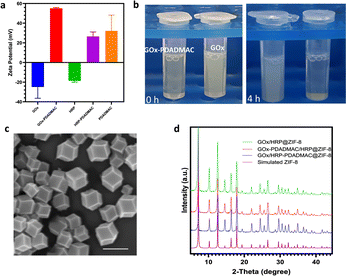
Glucose oxidase (GOx) and horseradish peroxidase (HRP) were employed as model enzymes for biocatalytic cascade reactions due to their widespread use in glucose detection,34 biosensors,6 and biofuel cells,7 where their sequential oxidation and reduction activities are crucial. The zeta potential of natural GOx increases as the GOx-to-PDADMAC ratio increases from 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.54 to 1
0.54 to 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5.81, with no further increase observed beyond this ratio (Fig. S1†). Therefore, a GOx-to-PDADMAC ratio of 1
5.81, with no further increase observed beyond this ratio (Fig. S1†). Therefore, a GOx-to-PDADMAC ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5.81 was selected for further study. The natural GOx exhibits a zeta potential of approximately −25 mV, which shifts to a positive value of 52 mV after modification with PDADMAC at this ratio (Fig. 1a), resulting in the modified enzyme, denoted as GOx-PDADMAC. It is observed that the negatively charged GOx facilitated a rapid MOF nucleation process, whereas the positively charged GOx-PDADMAC induces a relatively slower nucleation rate (Fig. 1b and S2†). Subsequently, both GOx and HRP were encapsulated within MOFs. The encapsulation process involved initially mixing the unmodified enzyme solutions with zinc nitrate hexahydrate, then adding the PDADMAC-modified enzyme solution, and finally incorporating 2-methylimidazole (HmIm), followed by continuous stirring for 4 hours to form the enzyme-ZIF-8 biocomposites. It is found that the addition of Zn ions alters the negative enzyme surface charge to around 0 mV, which does not induce electrostatic aggregation of the two different enzymes after the addition of a second positive PDADMAC-modified enzyme (Fig. S3†). GOx-PDADMAC and HRP were encapsulated within MOFs to produce GOx-PDADMAC/HRP@ZIF-8; conversely, GOx and PDADMAC-modified HRP (HRP-PDADMAC) were encapsulated to produce GOx/HRP-PDADMAC@ZIF-8. Unmodified GOx and HRP encapsulated in MOFs (GOx/HRP@ZIF-8) served as the control for comparison. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the enzyme-MOF composites show that the distinctive rhombic dodecahedral morphology of ZIF-8 was retained across all samples (Fig. 1c, S4, and S5†), indicating that the PDADMAC modification of either enzyme did not compromise the structural integrity of ZIF-8. X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns reveal that GOx-PDADMAC/HRP@ZIF-8, GOx/HRP-PDADMAC@ZIF-8, and GOx/HRP@ZIF-8 exhibit well-defined peaks characteristic of pure ZIF-8 (Fig. 1d and S6†), suggesting that neither the incorporation of enzymes nor the PDADMAC modification altered the crystalline structure of the ZIF-8 framework.
5.81 was selected for further study. The natural GOx exhibits a zeta potential of approximately −25 mV, which shifts to a positive value of 52 mV after modification with PDADMAC at this ratio (Fig. 1a), resulting in the modified enzyme, denoted as GOx-PDADMAC. It is observed that the negatively charged GOx facilitated a rapid MOF nucleation process, whereas the positively charged GOx-PDADMAC induces a relatively slower nucleation rate (Fig. 1b and S2†). Subsequently, both GOx and HRP were encapsulated within MOFs. The encapsulation process involved initially mixing the unmodified enzyme solutions with zinc nitrate hexahydrate, then adding the PDADMAC-modified enzyme solution, and finally incorporating 2-methylimidazole (HmIm), followed by continuous stirring for 4 hours to form the enzyme-ZIF-8 biocomposites. It is found that the addition of Zn ions alters the negative enzyme surface charge to around 0 mV, which does not induce electrostatic aggregation of the two different enzymes after the addition of a second positive PDADMAC-modified enzyme (Fig. S3†). GOx-PDADMAC and HRP were encapsulated within MOFs to produce GOx-PDADMAC/HRP@ZIF-8; conversely, GOx and PDADMAC-modified HRP (HRP-PDADMAC) were encapsulated to produce GOx/HRP-PDADMAC@ZIF-8. Unmodified GOx and HRP encapsulated in MOFs (GOx/HRP@ZIF-8) served as the control for comparison. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the enzyme-MOF composites show that the distinctive rhombic dodecahedral morphology of ZIF-8 was retained across all samples (Fig. 1c, S4, and S5†), indicating that the PDADMAC modification of either enzyme did not compromise the structural integrity of ZIF-8. X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns reveal that GOx-PDADMAC/HRP@ZIF-8, GOx/HRP-PDADMAC@ZIF-8, and GOx/HRP@ZIF-8 exhibit well-defined peaks characteristic of pure ZIF-8 (Fig. 1d and S6†), suggesting that neither the incorporation of enzymes nor the PDADMAC modification altered the crystalline structure of the ZIF-8 framework.
Performance of biocompatible multi-enzyme cascade upon encapsulation in MOFs
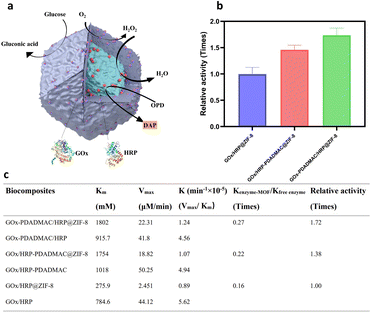
To investigate the catalytic performance of enzyme-MOF biocomposites, glucose and o-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride (OPD) were introduced into the enzyme-MOF suspension. Glucose is oxidized by oxygen, catalyzed by GOx, to produce gluconic acid and H2O2. HRP uses the H2O2 to oxidize OPD, forming 2,3-diaminophenazine (DAP) (Fig. 2a), which can be monitored using UV/vis spectroscopy at 420 nm. The results show that 6.8% of GOx and 40.4% of HRP are immobilized in GOx/HRP@ZIF-8. After PDADMAC modification, the encapsulation efficiency of GOx-PDADMAC and HRP changes slightly to 9.0% and 30.4%, respectively (Table S1†); the encapsulation efficiency of GOx and HRP-PDADMAC also changes slightly to 6% and 43.6%, respectively. Due to variations in enzyme encapsulation efficiency, it is crucial to normalize the enzyme amounts across different multi-enzyme MOFs. Previous studies often compared different multi-enzyme systems directly.24 To ensure accurate comparison, we used the natural enzymes as a benchmark after determining the enzyme loading efficiency in the MOF. Kinetic parameters were determined for the enzyme-MOF biocomposites and free enzymes using the Michaelis–Menten model. Significant differences in enzyme cascade performance were observed. Despite the lower cascade activity of all enzyme-MOF samples compared to free enzymes (Fig. S7†), because of the restricted substrate diffusion of the MOF,35,36 GOx/HRP-PDADMAC@ZIF-8, GOx-PDADMAC/HRP@ZIF-8 and GOx/HRP@ZIF-8 demonstrate activities that are only 0.22, 0.27, and 0.16 times that of the same amount of the free counterpart. Therefore, both PDADMAC-modified enzyme-MOF samples exhibit higher biocatalytic efficiency than the unmodified enzyme-MOF system. Specifically, GOx/HRP-PDADMAC and GOx-PDADMAC/HRP@ZIF-8 demonstrate 1.38 and 1.72 times higher activity than GOx/HRP@ZIF-8, respectively (Fig. 2b, c, and S7†). The effect of different pH conditions on the catalytic performance of enzyme-MOF biocomposites was further evaluated. The enzyme-MOF biocomposites exhibit optimal activity in a mild acidic environment (pH ≈ 5), while either increasing or decreasing the pH resulted in a reduction in their activity (Fig. S8†).Mechanism of enhanced multi-enzyme cascade activity
To elucidate the mechanism behind the enhanced catalytic performance, confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) was employed to visualize the spatial distribution of the enzymes. In GOx-PDADMAC/HRP@ZIF-8 (Fig. 3a and S9a†), the shell exclusively contains GOx-PDADMAC, with HRP primarily localized in the core. In contrast, GOx/HRP-PDADMAC@ZIF-8 exhibits a reversed distribution, with HRP-PDADMAC localized exclusively in the shell and GOx primarily concentrated in the core (Fig. S9b†). On the other hand, the unmodified GOx/HRP@ZIF-8 shows a more uniform enzyme distribution, though the biocomposites lack a regular shape. This irregularity is likely due to the small size of the enzyme-MOF particles and the limited resolution of the CLSM machine (Zeiss LSM 900). To further confirm the enzyme encapsulation process, the enzyme-MOF reactions were terminated at different times. It was found that 25.5% of HRP was encapsulated within one hour, while GOx-PDADMAC was slowly encapsulated in the MOF over four hours. Specifically, 3.7% of GOx-PDADMAC was encapsulated within the first hour, and an additional 3.5% was encapsulated between one and four hours (Fig. 3b). These observations confirm that the negatively charged enzyme promotes MOF nucleation, leading to its primary localization in the core. In contrast, PDADMAC-modified enzymes, due to their positive charge, are incorporated more slowly into the MOF. While some are found in the core, a shell forms that exclusively contains the PDADMAC-modified enzymes. To confirm that the enzymes were encapsulated within the MOFs and not merely adsorbed on the surface, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) was used to remove any physically adsorbed enzymes.37 The MOFs were dispersed in a 0.2 g SDS solution in 2 mL deionized water for 10 minutes to wash off adsorbed enzymes on the MOF surface. This was followed by three centrifugation/wash cycles in water. The results showed negligible enzyme activity loss for the GOx-PDADMAC/HRP@ZIF-8, indicating that these enzymes are encapsulated within the MOF. In contrast, all enzyme activity was lost for the GOx-PDADMAC-absorbed ZIF-8, suggesting that GOx-PDADMAC and HRP were indeed encapsulated within the MOF and not simply adsorbed on its surface (Fig. 3c). To rule out the possibility that PDADMAC alone enhances enzymatic activity, GOx was modified with varying amounts of PDADMAC, and no improvement in cascade reactions was observed (Fig. 3d and S10†). Furthermore, GOx-PDADMAC was encapsulated in ZIF-8, and its activity was comparable to that of unmodified GOx@ZIF-8 after normalizing the enzyme amounts (Fig. 3e and S11†). Control experiments with ZIF-8 and PDADMAC alone showed no enzymatic activity (Fig. 3e). Furthermore, PDADMAC was used to modify GOx and HRP separately, and then these modified enzymes were encapsulated within MOFs simultaneously, denoted as GOx-PDADMAC/HRP-PDADMAC@ZIF-8. The results showed that the activity of these encapsulated enzymes was 0.09 times that of the free enzymes after normalization of the enzyme amount, which is consistent with the findings of GOx/HRP@ZIF-8 (Fig. S12 and Table S1†). Therefore, these results confirm that PDADMAC itself does not enhance the intrinsic activity of the free enzymes, even when encapsulated within the MOF.To examine the tertiary structure of immobilized enzymes and uncover the structure–bioactivity relationship, we measured and compared the deconvoluted attenuated total reflectance-Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectra of GOx/HRP-PDADMAC@ZIF-8, GOx-PDADMAC/HRP@ZIF-8, GOx/HRP@ZIF-8, GOx/HRP, and GOx-PDADMAC/HRP (Fig. 3f, S13 and S14†). Enzymes show five peaks corresponding to α-helix, β-sheet, intermolecular β-sheet, β-turn, and random coil structures. Quantitative analysis reveals that the β-sheet and intermolecular β-sheet contents of enzymes increase with PDADMAC modification, indicating that PDADMAC enhances β-sheet formation, likely through electrostatic interactions, which shows that this interaction does not affect enzyme activity (Fig. 3d). Upon immobilization, the β-sheet content tends to increase, and the random coil content consistently decreases in GOx/HRP-PDADMAC@ZIF-8, GOx-PDADMAC/HRP@ZIF-8, and GOx/HRP@ZIF-8 compared to the free enzymes. This suggests that MOF immobilization reduces the disordered structure of the enzyme, promoting a more ordered and stable structure. However, the α-helix content of GOx-PDADMAC/HRP@ZIF-8 (26.13%) and GOx/HRP-PDADMAC@ZIF-8 (31.42%) is closer to that of the free enzymes (31.12%) compared to that of GOx/HRP@ZIF-8 (45.04%), which might contribute to the improved activity. Furthermore, the intermolecular β-sheet content of GOx-PDADMAC/HRP@ZIF-8 (7.01%) is also closer to that of the free enzymes (6.58%) compared to that of GOx/HRP-PDADMAC@ZIF-8 (24.11%), further contributing to the enhanced activity.
In conclusion, the enhanced cascade activity can be attributed to the compartmentalization of multiple enzymes, which reduces substrate inhibition and accelerates the reaction toward product formation within a confined space. When the first enzyme in the cascade is located in the shell, it facilitates a faster cascade reaction due to more efficient substrate transport. Glucose and oxygen molecules first migrate to the ZIF-8 shell, where GOx is located, and the generated H2O2 rapidly diffuses into the core, where HRP resides. The rapid formation of the substrate and intermediate concentration gradient drive the cascade reaction, leading to the efficient production of DAP. Additionally, the enzyme immobilization results in slight conformational changes, which may also contribute to improved activity.
Generalization of this strategy to incompatible multi-enzyme cascade reactions
Pro and GOx enzymes were selected to evaluate the generalization of one-pot spatial engineering strategy in an incompatible tandem biocatalytic reaction. Pro can induce the proteolysis of GOx while also catalyzing hydrolysis reactions.38 GOx can be used as an antibacterial agent in oral care products, given the abundance of proteolytic enzymes in the oral cavity.39 The H2O2 produced by GOx serves as an effective bactericide. However, it is crucial to compartmentalize GOx and Pro to prevent the proteolysis of GOx while allowing their cascade reaction. To achieve this, GOx and PDADMAC-modified Pro (Pro-PDADMAC) were encapsulated in MOFs to produce Pro-PDADMAC/GOx@ZIF-8, while Pro with PDADMAC-modified GOx (GOx-PDADMAC) was encapsulated to obtain Pro/GOx-PDADMAC@ZIF-8. Unmodified GOx and Pro encapsulated within MOFs (Pro/GOx@ZIF-8) served as a control sample. SEM images demonstrate the distinctive rhombic dodecahedral morphology of MOFs across all samples (Fig. S15†). XRD patterns for all samples exhibit well-defined peaks characteristic of pure ZIF-8, indicating high crystallinity and no significant differences in peak positions (Fig. S16†). Zeta potential analysis reveals that PDADMAC modification successfully alters the surface charge properties of Pro and GOx (Fig. S17†).A spectrophotometric assay was conducted to quantitatively evaluate the enzymatic activity of Pro and GOx encapsulated in MOFs. In this assay, 1,2,3,4-tetra-O-acetyl-beta-D-glucopyranose serves as the substrate for Pro, and 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) is used as the detection reagent. Pro hydrolyzes the glucopyranose substrate into glucose in a Tris buffer at pH 8.5, an environment optimal for Pro activity. Subsequently, GOx catalyzes the oxidation of glucose, leading to a color change in ABTS in the presence of HRP (Fig. 4a). Absorbance was recorded at 420 nm to measure the enzymatic activity, with results normalized based on enzyme encapsulation efficiency to ensure accurate comparisons (Table S1†). The free Pro/GOx system exhibits limited cascade activity without MOF immobilization due to the proteolysis of GOx by Pro (Fig. S18†). Pro/GOx-PDADMAC@ZIF-8, Pro-PDADMAC/GOx@ZIF-8, and Pro/GOx@ZIF-8 demonstrate activities that are 1.01, 1.14, and 0.68 times that of free Pro-GOx after normalization of their amount. Therefore, Pro-PDADMAC/GOx@ZIF-8 and Pro/GOx-PDADMAC@ZIF-8 demonstrate the highest relative activity, 1.69 and 1.50 times higher than that of Pro/GOx@ZIF-8 (Fig. 4b, S18 and Table S2†). CLSM images show the shell exclusively containing PDADMAC-modified enzymes, while unmodified enzymes were primarily found in the core (Fig. 4c and S19†). Notably, the enzyme that interacts first with the substrate, when positioned in the shell, exhibited enhanced activity. This spatial arrangement is particularly crucial for incompatible enzymes, as it allows for compartmentalization, efficient intermediate transfer, and prevention of cross-reactivity, thereby maintaining high catalytic efficiency.22
Pro and ADH are commonly utilized in bioconversion processes, which are pivotal for biofuel production, where the efficient conversion of biomass into fermentable sugars, followed by alcohol production, is essential.40,41 However, due to the incompatibility of Pro and ADH, compartmentalization of these enzymes is necessary to ensure optimal catalytic performance. ADH and PDADMAC-modified Pro (Pro-PDADMAC) were encapsulated in MOFs to create Pro-PDADMAC/ADH@ZIF-8, while Pro and ADH-PDADMAC were used to generate Pro/ADH-PDADMAC@ZIF-8. Unmodified ADH and Pro encapsulated within MOFs (Pro/ADH@ZIF-8) served as a control for comparison. Zeta potential analysis confirms that PDADMAC modification effectively alters the surface charge properties of both Pro and ADH (Fig. S20†). SEM analysis verifies that all samples retained the characteristic ZIF-8 morphology (Fig. S21†). XRD analyses further confirm that all samples preserved the crystallinity of ZIF-8 (Fig. S22†). A spectrophotometric assay was employed to quantitatively assess the cascade activity of Pro and ADH encapsulated in MOFs. The assay involves a coupling reaction where Pro first hydrolyzes L-norvaline ethyl ester to release L-norvaline, which ADH then utilizes in the presence of NAD+ to catalyze the conversion of NAD+ to NADH (Fig. 4d). This reaction was quantified by monitoring the increase in absorbance at 340 nm, reflecting the rate of NADH production and directly measuring the activity of both enzymes. The encapsulation efficiency of each MOF sample is detailed in Table S1.† Results show that Pro/ADH-PDADMAC@ZIF-8, Pro-PDADMAC/ADH@ZIF-8 and Pro/ADH@ZIF-8 demonstrate activities that are only 0.44, 3.99, and 0.27 times that of the free Pro-ADH after normalization of the same amount of enzyme. Therefore, Pro-PDADMAC/ADH@ZIF-8 exhibits the highest cascade activity, which is 14.85 times greater than that of Pro/ADH@ZIF-8 (Fig. 4e, S23 and Table S2†), while Pro/ADH-PDADMAC@ZIF-8 demonstrates only a 1.62-fold enhancement. In contrast, the free Pro/ADH system shows significantly reduced activity due to the proteolysis of ADH by Pro. CLSM images of Pro-PDADMAC/ADH@ZIF-8 and Pro/ADH-PDADMAC@ZIF-8 demonstrate a spatial distribution consistent with previous models (Fig. S24†). In the Pro-PDADMAC/ADH@ZIF-8 biocomposites, the substrate first enters the shell that exclusively contains Pro and induces the first step reaction, allowing intermediates to diffuse into the core where ADH further catalyzes the reaction in an organized manner. This spatial arrangement significantly improves incompatible multi-enzyme cascade activity.
This one-pot spatial engineering approach achieves a comparable enhancement in multi-enzyme cascade activity (ranging from 1.69 to 14.85 times enhancement compared to the directly immobilized enzymes) to many established methods, which typically offer 1 to 16 times enhancement compared to the directly immobilized enzymes (Table S4†). Furthermore, unlike more complex strategies that involve multiple steps—such as epitaxial shell-by-shell overgrowth,24 peptide-induced self-assembly,25 and post-filtration of different enzymes into MOF pores26—this method provides a straightforward, one-step solution. It allows for the precise positioning of multiple enzymes within an organized structure, thereby improving the cascade activity. By fine-tuning the PDADMAC modification, this electrostatic strategy holds significant potential for broader application in other multi-enzyme systems, such as nanozyme–natural enzyme cascades for biofuel production,42 lignin degradation,43 or even more complex cascades involving three or four natural enzymes.44
Stability and recyclability of enzyme-MOF biocomposites
The resilience of the enzyme-MOF biocomposites under harsh conditions was evaluated (Fig. 5a). This includes assessing the thermal stability by incubating at 60 °C for one hour, chemical stability by exposing the composites to dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) for an hour, and resistance to enzymatic degradation by treating with protease for two hours. After these exposures, both GOx-PDADMAC/HRP@ZIF-8 and GOx/HRP@ZIF-8 retained substantial activity, while the free GOx/HRP system rapidly lost its activity (Fig. 5a and S25†). Similarly, Pro-PDADMAC@/GOxZIF-8 and Pro/GOx@ZIF-8 as well as Pro-PDADMAC/ADH@ZIF-8 and Pro/ADH@ZIF-8 maintained significant activity, whereas the free enzyme system became inactive quickly (Fig. 5a, S26 and S27†). The rapid inactivation of free enzymes is due to their susceptibility to denaturation and degradation under extreme conditions, which disrupts their structural integrity and active sites,45,46 whereas the MOF matrix protects the immobilized enzymes from such inactivating agents. In particular, the impact of various organic solvents, including methanol and acetone at different concentrations (1%, 5%, and 10%), as well as a combination of methanol, acetone, and DMSO, on the catalytic activity of the GOx-PDADMAC/HRP@ZIF-8 sample was further assessed. The enzyme-MOF biocomposites retained over 50% of their activity when exposed to solvent concentrations below 5% (Fig. S28†). However, at 10% solvent concentration, a more pronounced loss of activity was observed, indicating that excessive organic solvents can still reduce the stability and activity of the biocomposite. The thermal stability of GOx-PDADMAC/HRP@ZIF-8 was further evaluated across a range of temperatures (25 °C, 40 °C, 50 °C, 60 °C, and 70 °C). The biocomposite maintained excellent activity across different temperatures, with around 50% of its activity retained after exposure to 70 °C for one hour (Fig. S29†). Cycling stability was tested by monitoring the enzyme-MOF biocomposites' relative activity over five consecutive reuse cycles. Both GOx-PDADMAC/HRP@ZIF-8 and GOx/HRP@ZIF-8 retained more than 70% of their initial activity, while Pro-PDADMAC/ADH@ZIF-8 and Pro/ADH@ZIF-8 maintained more than 60% of their initial activity (Fig. 5b and S30†), making them highly promising for a wide range of industrial and environmental applications. The storage stability of the enzyme-MOF biocomposites was assessed by comparing the catalytic activity of GOx-PDADMAC/HRP@ZIF-8 and free GOx-PDADMAC/HRP after storage at 4 °C for 5 and 50 days. After 5 days, the MOF biocomposite showed negligible activity change, while the free enzyme slightly decreased. After 50 days, the MOF retained about 50% activity, while the free enzyme had no activity (Fig. S31†), indicating the excellent long-term storage stability of the developed enzyme-MOF biocatalysts.Experimental
Materials
Horseradish peroxidase (HRP), glucose oxidase (GOx), alkaline protease (Pro), Alcohol Dehydrogenase (ADH) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, zinc nitrate hexahydrate (99.0%), 2-methylimidazole (2-MeIm, 99.0%), poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) solution (PDADMAC), glucose, o-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride (OPD), 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS), 1,2,3,4-tetra-O-acetyl-beta-D-glucopyranose, L-norvaline ethyl ester hydrochloride (98.0%), cofactor NAD+, phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and Atto 633 NHS ester were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Australia). Alexa Fluor™ 488 NHS ester was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Australia). All other reagents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Australia) and used without further purification. Deionized (DI) water was used throughout this work.Characterization
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) measurements were conducted on an FEI Nova Nano SEM 230 under 10 kV acceleration voltage with a secondary electron detector. The samples were coated using Emitech K575x evaporative premium coater before imaging. The enzymes were tagged with fluorescent probes before encapsulation within the ZIF-8 particles for fluorescence testing. The zeta potential was recorded on the Malvern Zetasizer Nano Series. The crystallinity of biocatalytic ZIF-8 was analyzed using a PANalytical X-ray diffractometer. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was performed on a Bruker Alpha FTIR spectrometer. A fluorescent protein labeling method was used for quantitative analysis of the enzyme loading in the ZIF-8 samples using a CLARIO star microplate reader (BMG LABTECH Germany). Fluorescence images of the samples were captured using a Zeiss LSM 900.Synthesis of biocatalytic ZIF-8
Different enzyme solutions (HRP, GOx, Pro, ADH) (10 mg mL−1) were mixed with a PDADMAC solution (10 mg mL−1) in varying ratios (Table S1†). The synthesis process began with mixing 60 μL of untreated or PDADMAC-modified enzyme solution containing either HRP, GOx, Pro, or ADH at a concentration of 10 mg mL−1 with 363 μL of a zinc nitrate hexahydrate solution (13.5 mg mL−1). Then, 1452 μL of 2-MeIm (70.75 mg mL−1) was introduced, and the mixture was stirred continuously for 4 hours to promote the formation of ZIF-8 frameworks. After synthesis, the products were centrifuged at 6000 rpm for 5 minutes and washed three times with DI water to remove any remaining residues. The resultant nanoparticles were then resuspended in 300 μL of DI water for further analysis.Preparation of dye-labeled enzymes
To prepare dye-labeled enzymes, HRP and Pro were tagged with Atto 550 NHS ester, while GOx and ADH were labeled with Atto 633 NHS ester. After labeling, the mixtures were allowed to stand for 5 minutes to ensure thorough interaction between the dyes and the enzymes. Excess dyes were then removed using Zeba™ Dye and Biotin Removal Spin Columns, which cleared unreacted dyes and other residues via centrifugation at 1000 rcf for 2 minutes. The enzyme concentration was finally quantified to 10 mg mL−1.Loading efficiencies of enzymes in ZIF-8
To accurately calculate the loading efficiency of enzymes within ZIF-8, a specific protocol leveraging fluorescently labeled enzymes was employed. Initially, these labeled enzymes were used to replace regular or PDADMAC-treated enzymes during the synthesis of ZIF-8 materials. After synthesis, the ZIF-8 encapsulated enzymes were separated from residues by centrifugation and washed three times with water to remove any remaining residues. Following the washing steps, the enzyme-ZIF-8 was dissolved in a solution of NaCl and HCl (50 mM). This dissolution process releases the encapsulated enzymes, allowing for their quantification. The fluorescence spectra of these released enzymes were then recorded using a spectrophotometer. To determine the concentration of enzymes within the MOF, a standard curve was prepared using the same fluorescently labeled enzymes. The loading efficiency was then calculated using eqn (1): | (1) |
GOx and HRP cascade reaction
To assess the GOx and HRP activity, a spectrophotometric assay was conducted using a microplate reader with o-phenylenediamine (OPD) and glucose as substrates. In each well of a 96-well microplate, 120 μL of OPD solution (1 mg mL−1) and 100 μL of glucose solution (100 mg mL−1) were added to initiate the enzymatic reaction. Then, 10 μL of the enzyme-ZIF-8 sample was introduced to each well, ensuring thorough mixing to facilitate interaction with the substrates. The absorbance was detected at 420 nm. The enzymatic activity was quantified by calculating the rate constant, K, from the slope of the absorbance vs. time curve within this interval. The principle behind this assay is shown below: | (2) |
 | (3) |
GOx-PDADMAC/HRP@ZIF-8 was used to evaluate the effect of pH on the enzyme–MOF activity. The reaction was evaluated under different pH conditions: 2.33, 3.04, 5.32, 6.58, 7.00, 7.88, and 8.42.
GOx and Pro cascade reaction
To quantitatively evaluate the enzymatic activity of Pro and GOx encapsulated in MOFs, a detailed spectrophotometric assay was utilized. Initially, each well of a 96-well plate was prepared by adding 30 μL of ABTS (18 mM) solution, followed by 150 μL of 1,2,3,4-tetra-O-acetyl-beta-D-glucopyranose (6.6 mg mL−1 in Tris buffer with a pH of 8.5). To this mixture, 10 μL of the enzyme-ZIF-8 sample containing both Pro and GOx was added. The plate was then incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes, allowing the Pro to hydrolyze the glucopyranose substrate into glucose. Following this incubation period, 5 μL of HRP (1 mg mL−1) was introduced to each well. HRP catalyzes the reaction between the produced glucose and ABTS, resulting in a measurable color change.21 Absorbance was recorded at 420 nm for 15 minutes immediately after HRP addition, using a microplate reader. The enzymatic activity was determined by calculating the slope of the absorbance versus time curve. The principle behind this assay is shown below: | (4) |
 | (5) |
Pro and ADH cascade reaction
To assess the enzymatic activity of Pro and ADH within ZIF-8, a detailed spectrophotometric assay was conducted. In this assay, each well of a 96-well plate was prepared with 40 μL of Tris buffer (50 mM), followed by the addition of 110 μL of L-norvaline ethyl ester hydrochloride (50 mM) as the substrate for Pro. Subsequently, 30 μL of NAD+ (15 mM), essential for ADH activity, was added to each well. After introducing 10 μL of the enzyme-ZIF-8, the plate was incubated at room temperature. Absorbance at 340 nm, indicative of NADH formation, was monitored over 15 minutes using a microplate reader. The principle behind this assay is shown below: | (6) |
 | (7) |
To ensure an accurate comparison of enzymatic activity between enzyme-MOF and free enzyme samples in biocompatible and incompatible systems, normalization of the enzyme content across assays is crucial. Following the calculation of the enzyme concentration in the MOFs, based on the loading efficiency, it is necessary to adjust the concentration of the free enzyme solution to ensure that equal concentration can be used in the assays.
Calculation of enzyme kinetics
Enzyme kinetics were calculated using the formula:| A = ε × C × l | (8) |
 | (9) |
The concentration C of the reaction product was determined by measuring the absorbance and applying the formula. The change in concentration over time was used to calculate the reaction rate by determining the slope of the concentration vs. time curve.
The extinction coefficients (ε) used for calculating concentration include 16![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 700 M−1 cm−1 for DAP, 36
700 M−1 cm−1 for DAP, 36![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 M−1 cm−1 for oxidized ABTS, and 6220 M−1 cm−1 for NADH.
000 M−1 cm−1 for oxidized ABTS, and 6220 M−1 cm−1 for NADH.
Kinetic parameters Km and Vmax for both the enzyme-MOF and free enzyme were calculated by adjusting the substrate concentration and fitting the data to the Michaelis–Menten equation, using GraphPad Prism 10 software. The enzyme kinetic efficiency for the enzyme-MOF (K) was defined as the ratio Vmax/Km for the enzyme-MOF. The relative activity of each sample was calculated as Kenzyme–MOF/Kfreeenzyme.
Evaluation of operational stability of enzyme-MOF biocomposites
To evaluate the operational stability of enzyme-MOF biocomposites, a series of adverse conditions were employed to evaluate the protective capability of MOFs. The enzyme-MOF samples were exposed to DMSO, methanol, acetone, and their combinations to evaluate chemical stability. Protease was also used to study the protective role of the MOF against enzyme hydrolysis. Additionally, thermal stability was evaluated by incubating the samples at 25 °C, 40 °C, 50 °C, 60 °C, and 70 °C for one hour. These conditions were tested independently with a control group maintained under normal conditions. Following each treatment, the enzyme activity was measured spectrophotometrically using the same substrate and assay conditions, ensuring consistent comparison across all tests.For recyclability testing, the enzyme-MOF samples were repeatedly used in a standard reaction setup to assess their reusability. In this process, MOFs were mixed with reaction substrates and other solutions in 2 mL centrifuge tubes. The mixtures were then transferred using a syringe through centrifugal filters that containing the enzyme-MOF samples. The filtrate containing the reaction products was collected, while the enzyme-MOF remained in the reaction chamber of the filters. After each reaction cycle, excess reaction solution was washed off with DI water, and a new reaction mixture was introduced for the next cycle. This process was repeated multiple times, and the reaction solution was collected after each cycle to measure the enzymatic activity.
Conclusions
In conclusion, we developed a straightforward, one-step spatial engineering strategy that employs PDADMAC to selectively modify the surface charge of enzymes. Enzymes with a negative surface charge accelerate the MOF nucleation process, leading to their primary localization in the core, while enzymes with a positive surface charge slow down the nucleation process, resulting in a shell that exclusively contains positively charged enzymes. The cascade activities were improved by factors ranging from 1.69 to 14.85 for both compatible and incompatible enzyme systems. This enhancement is attributed to effective compartmentalization, efficient intermediate transfer, prevention of cross-reactivity among the cascade enzymes, as well as the altered enzyme conformation. Additionally, the developed enzyme-MOF biocatalytic systems exhibit superior stability against temperature variations, proteolysis, and exposure to organic solvents, along with excellent recyclability for sustained use. This one-pot spatial engineering approach simplifies the biocatalytic process by reducing the need for intermediate separation and purification steps, thereby streamlining the overall workflow and improving practicality for industrial applications.Data availability
The data supporting this article have been included as part of the ESI.†Author contributions
W. Fan performed the experiments and wrote the initial manuscript. K. Liang contributed to the project administration, conceptualization, writing – review and editing. J. Liang contributed to the characterization, analysis of the data, draft and project administration, conceptualization, writing – review and editing. All authors discussed and commented on the manuscript.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work received support from the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Investigator Grants project (2026262) (JL), the Australian Research Council (ARC) through grants DP210100422 (KL) and FT220100479 (KL), and the Scientia program at UNSW (KL). The authors acknowledge the facilities and the scientific and technical assistance of Microscopy Australia at the Electron Microscope Unit (EMU) within the Mark Wainwright Analytical Centre (MWAC) at UNSW Sydney.Notes and references
- Y. Weng, R. Chen, Y. Hui, D. Chen and C.-X. Zhao, Chem Bio Eng., 2024, 1, 99–112 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. T. Reetz, G. Qu and Z. Sun, Nat. Synth., 2024, 3, 19–32 CrossRef.
- S. Bhandari, D. K. Poudel, R. Marahatha, S. Dawadi, K. Khadayat, S. Phuyal, S. Shrestha, S. Gaire, K. Basnet and U. Khadka, J. Chem., 2021, 2021, 8849512 CrossRef.
- A. Wang, P. Sudarsanam, Y. Xu, H. Zhang, H. Li and S. Yang, Green Chem., 2020, 22, 2977–3012 RSC.
- M. P. Thompson, I. Peñafiel, S. C. Cosgrove and N. J. Turner, Org. Process Res. Dev., 2018, 23, 9–18 CrossRef.
- M. Khan and S.-Y. Park, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2015, 457, 281–288 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Chansaenpak, A. Kamkaew, S. Lisnund, P. Prachai, P. Ratwirunkit, T. Jingpho, V. Blay and P. Pinyou, Biosensors, 2021, 11, 16 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. M. Sperl and V. Sieber, ACS Catal., 2018, 8, 2385–2396 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Liang and K. Liang, Chem. Rec., 2020, 20, 1100–1116 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Liang and K. Liang, Nano Today, 2021, 40, 101256 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Wang, L. Yue and I. Willner, Nat. Catal., 2020, 3, 941–950 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Cao, X. Li and J. Ge, Trends Biotechnol., 2021, 39, 1173–1183 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Liu, P. Liu, S. Gao, Z. Wang, P. Luan, J. González-Sabín and Y. Jiang, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 420, 127659 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Liang, J. Ruan, B. Njegic, A. Rawal, J. Scott, J. Xu, C. Boyer and K. Liang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202303001 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Victorino da Silva Amatto, N. Gonsales da Rosa-Garzon, F. Antonio de Oliveira Simoes, F. Santiago, N. Pereira da Silva Leite, J. Raspante Martins and H. Cabral, Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem., 2022, 69, 389–409 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Huang, S. Zhang, Y. Tang, X. Zhang, Y. Bai and H. Pang, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2021, 449, 214216 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Yuan, L. Feng, K. Wang, J. Pang, M. Bosch, C. Lollar, Y. Sun, J. Qin, X. Yang and P. Zhang, Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1704303 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. Wang, R. He, L.-H. Xie, Z.-J. Lin, X. Zhang, J. Wang, H. Huang, Z. Zhang, K. S. Schanze and J. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 12478–12485 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Chen, Z. Yang, Y. Zhu and Y. Xia, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2, 16811–16831 RSC.
- Y. Du, X. Jia, L. Zhong, Y. Jiao, Z. Zhang, Z. Wang, Y. Feng, M. Bilal, J. Cui and S. Jia, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2022, 454, 214327 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Xu, G. Xiao, H. Li, Y. Shen, J. Zhang, T. Pan, X. Chen, B. Zheng, J. Wu and S. Li, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1802479 CrossRef.
- H. Liu, Y. Du, J. Gao, L. Zhou, Y. He, L. Ma, G. Liu, Z. Huang and Y. Jiang, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2019, 59, 42–51 CrossRef.
- J. Liang and K. Liang, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30, 2001648 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Man, C. Xu, X.-Y. Liu, D. Li, C.-K. Tsung, H. Pei, Y. Wan and L. Li, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13, 305 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Liang, F. Mazur, C. Tang, X. Ning, R. Chandrawati and K. Liang, Chem. Sci., 2019, 10, 7852–7858 RSC.
- D. Feng, T.-F. Liu, J. Su, M. Bosch, Z. Wei, W. Wan, D. Yuan, Y.-P. Chen, X. Wang and K. Wang, Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 5979 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. Chen, S. Huang, X. Kou, S. Wei, S. Huang, S. Jiang, J. Shen, F. Zhu and G. Ouyang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 1463–1467 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Gao, J. Hou, Z. Deng, T. Wang, S. Beyer, A. G. Buzanich, J. J. Richardson, A. Rawal, R. Seidel and M. Y. Zulkifli, Chem, 2019, 5, 1597–1608 CAS.
- H. Wang, L. Han, D. Zheng, M. Yang, Y. H. Andaloussi, P. Cheng, Z. Zhang, S. Ma, M. J. Zaworotko and Y. Feng, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 6263–6267 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Chen, X. Kou, S. Huang, L. Tong, Y. Shen, W. Zhu, F. Zhu and G. Ouyang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 2867–2874 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Eguílaz, R. Villalonga, L. Agüí, P. Yáñez-Sedeño and J. M. Pingarrón, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2011, 661, 171–178 CrossRef.
- X. Qin, H. Wang, X. Wang, Z. Miao, L. Chen, W. Zhao, M. Shan and Q. Chen, Sens. Actuators, B, 2010, 147, 593–598 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. L. Yao and K. K. Shiu, Electroanaly, 2008, 20, 1542–1548 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Song, K. Qu, C. Zhao, J. Ren and X. Qu, Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 2206–2210 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Liang, Q. Chen, J. Xue and K. Liang, Chem Catal., 2022, 2, 2515–2551 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Liang, M. Y. Bin Zulkifli, J. Yong, Z. Du, Z. Ao, A. Rawal, J. A. Scott, J. R. Harmer, J. Wang and K. Liang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 17865–17875 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. W. Fish, J. A. Reynolds and C. Tanford, J. Biol. Chem., 1970, 245, 5166–5168 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. M. Vriezema, P. M. Garcia, N. Sancho Oltra, N. S. Hatzakis, S. M. Kuiper, R. J. Nolte, A. E. Rowan and J. C. Van Hest, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2007, 46, 7378–7382 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. T. Pugliese, S. M. Pugliese and J. A. Ehrhard, US Pat., 9540631, 2017 Search PubMed.
- D. Chung, M. Cha, E. N. Snyder, J. G. Elkins, A. M. Guss and J. Westpheling, Biotechnol. Biofuels, 2015, 8, 1–13 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Rastogi and S. Shrivastava, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2017, 80, 330–340 CrossRef.
- L. Wang, W. Zhi, J. Wan, J. Han, C. Li and Y. Wang, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2019, 7, 3339–3348 CrossRef CAS.
- M. R. Ladole, P. B. Pokale, S. S. Patil, P. G. Belokar and A. B. Pandit, Bioresour. Technol., 2020, 317, 124035 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Dhakshinamoorthy, A. M. Asiri and H. Garcia, Dalton Trans., 2020, 49, 11059–11072 RSC.
- A. Santos, M. Oliveira and F. Maugeri, Bioresour. Technol., 2007, 98, 3142–3148 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. M. Daniel, M. Dines and H. H. Petach, Biochem. J., 1996, 317, 1–11 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4ta06211f |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |