Progresses in organocatalytic asymmetric dearomatization reactions of indole derivatives
Feng-Tao
Sheng†
,
Jing-Yi
Wang†
,
Wei
Tan
*,
Yu-Chen
Zhang
* and
Feng
Shi
 *
*
School of Chemistry and Materials Science, Jiangsu Normal University, Xuzhou, 221116, China. E-mail: fshi@jsnu.edu.cn; zhangyc@jsnu.edu.cn; wtan@jsnu.edu.cn; Web: http://www.x-mol.com/groups/Shi_Feng
First published on 13th October 2020
Abstract
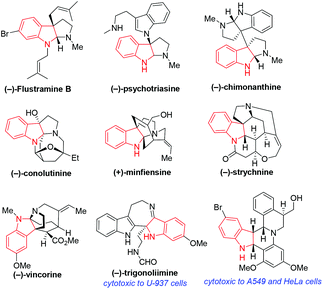
Chiral indole derivatives such as indolines and indolenines are important heterocyclic frameworks which constitute the core structures of many natural products and bioactive molecules. So, intensive attentions from chemists have been paid to the construction of such frameworks. Among different approaches, organocatalytic asymmetric dearomatization (organo-CADA) reactions of indole derivatives have become powerful methods toward this goal. Consequently, a variety of enantioenriched heterocyclic frameworks containing indoline, indolenine and the related cores have been constructed via organo-CADA reactions of indole derivatives, and a series of important natural products with structural complexity and enantiopurity have been synthesized based on these methodologies. This review summarizes the progresses in organo-CADA reactions of indole derivatives since 2004 and their applications in total synthesis of natural products, and gives some insights into challenging issues in this research field, which will enlighten the future development of this field.
1. Introduction
Chiral indole derivatives such as indolines and indolenines are important heterocyclic frameworks, which contain a tetra-substituted chiral center. Particularly, the framework of chiral indoline exists in a number of natural alkaloids and bioactive compounds (Fig. 1).1 Consequently, chemists have given intensive attention to the construction of chiral indoline-related frameworks.2,3In this context, catalytic asymmetric dearomatization (CADA) reactions4,5 have proven to be important methods for constructing chiral indoline-related frameworks. This is because CADA reactions are competent in transforming planar aromatic structures into stereoselective chiral frameworks. In particular, due to the advantages of asymmetric organocatalysis in synthesizing enantioenriched molecules with potential bioactivity,6,7 organocatalytic asymmetric dearomatization (organo-CADA) reactions of indole derivatives have become powerful methods for constructing optically pure indoline and indolenine frameworks.
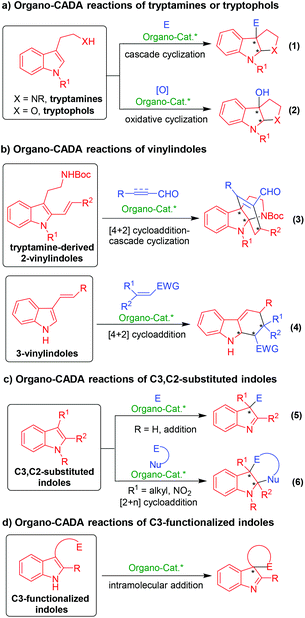
As summarized in Scheme 1, organo-CADA reactions of indole derivatives are classified into four categories based on different indole derivatives. This scheme summarizes the main characteristics and reaction types of the four kinds of indole derivatives in organo-CADA reactions.
The first type is organo-CADA reactions of tryptamines, tryptophols and their analogues (Scheme 1a), which can utilize the C3-nucleophilicity of the indole ring to attack electrophiles (E) and initiate a cascade cyclization, thus accomplishing the organo-CADA reactions (eqn (1)). In addition, in the presence of some oxidants, oxidative cascade cyclization would occur (eqn (2)). Clearly, the organo-CADA reactions of tryptamines or tryptophols provided an easy access to enantioenriched pyrroloindoline or furoindoline scaffolds, which are widely found in natural alkaloids.
The second type is vinylindole-involved organo-CADA reactions (Scheme 1b), which mainly include tryptamine-derived 2-vinylindoles (eqn (3)) and 3-vinylindoles (eqn (4)). Both of them acted as electron-rich dienes to undergo [4 + 2] cycloadditions with electronically poor alkenes or alkynes under organocatalysis, which constructed chiral indoline skeletons fusing a six-membered ring. More importantly, tryptamine-derived 2-vinylindoles can further undergo a cascade cyclization after the [4 + 2] cycloaddition due to the existence of the tryptamine functionality, thus constructing structurally complex bridged-cyclic pyrroloindoline frameworks (eqn (3)). This type of organo-CADA reactions provided important protocols for the total synthesis of related natural products.
The third type is organo-CADA reactions of C3- and/or C2-substituted indoles (Scheme 1c). In a very simple way, this class of indole derivatives can use their C3-nucleophilicity to attack electrophiles (E), thus realizing organo-CADA reactions and constructing indolenine scaffolds with optical purity (eqn (5)). If a nucleophilic site (Nu) is linked to the electrophiles, a [2 + n] cycloaddition could occur to construct chiral indoline-fused cyclic skeletons (eqn (6)).
The last type is organo-CADA reactions of C3-functionalized indoles which are incorporated with an electrophilic site (Scheme 1d). This class of indole derivatives utilized their C3-nucleophilicity to undergo intramolecular addition reaction with the inner electrophilic site, thus constructing enantioenriched spiro-indolenine frameworks.
Based on the organo-CADA reactions of these indole derivatives, a variety of enantioenriched heterocyclic frameworks containing the indoline and indolenine cores were constructed, and a series of important natural products with structural complexity and enantiopurity were synthesized based on these methodologies. Although CADA reactions have received great attention from the chemistry community,4,5 a summarization on the topic of organo-CADA reactions of indole derivatives has not appeared which requires a timely and systematic summary, thus enlightening the future development of this research field. For clarity, the organization of this review is based on the types of indole derivatives which are involved in organo-CADA reactions.
2. Organo-CADA reactions of tryptamines, tryptophols and their analogues
2.1 Organo-CADA reactions of tryptamines, tryptophols and their analogues with C,N-centered electrophiles
In 2004, MacMillan and coworkers utilized chiral imidazolidinone catalysts as competent amine-type organocatalysts to realize the first organo-CADA reaction of tryptamines and tryptophol (Scheme 2).8 In the presence of organocatalysts C1 or C2, tryptamines 1 underwent CADA reactions with α,β-unsaturated aldehydes 2 and 3, constructing pyrroloindoline architectures 4–5 in high yield and excellent stereoselectivities (Scheme 2a). Additionally, the organo-CADA reaction of tryptophol 6a with α,β-unsaturated aldehyde 3a could smoothly occur to construct a furanoindoline framework with good results (Scheme 2b). In the suggested reaction pathway and activation mode (Scheme 2c), α,β-unsaturated aldehydes 3 were activated by catalyst C2 to generate iminiums A, which were attacked by tryptamines 1 to undergo a Michael addition. Then, the generated intermediates B performed an intramolecular cyclization to give intermediates C. Finally, the hydrolysis of intermediates C gave rise to products 5 and released catalyst C2.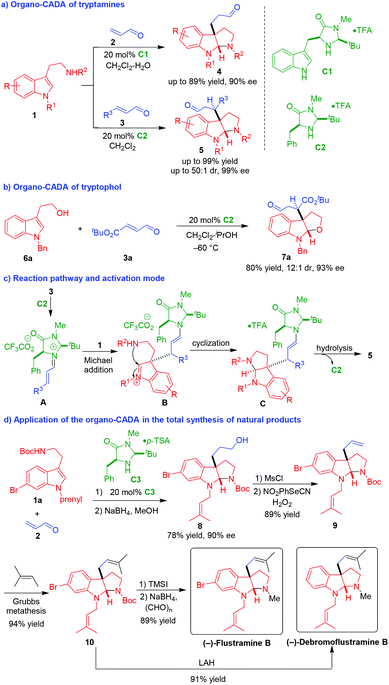 | ||
| Scheme 2 Organo-CADA reactions of tryptamines and tryptophol and their application in natural products synthesis by MacMillan and coworkers.8 | ||
More importantly, they realized the application of this organo-CADA reaction in the total synthesis of natural products (Scheme 2d). Namely, the CADA reaction of tryptamine 1a with α,β-unsaturated aldehyde 2 under the catalysis of chiral amine C3 generated the key compound 8 with a high enantioselectivity of 90% ee after reduction of the aldehyde group. Then, compound 8 was subjected to mesylation and elimination to give compound 9 bearing a terminal alkenyl group, which underwent a metathesis to generate compound 10 as a precursor of natural products. Finally, in the presence of lithium aluminum hydride (LAH), compound 10 underwent both carbamate reduction and dehalogenation to generate (−)-debromoflustramine B. Instead, the selective removal of the Boc-group from compound 10 followed by reductive N-methylation resulted in the generation of (−)-flustramine B. This seminal work explored the potential of organo-CADA reactions of tryptamines for the total synthesis of indoline-related natural alkaloids.
Chiral phosphoric acids (CPAs) have been recognized as a versatile organocatalysts in asymmetric catalysis for the enantioselective synthesis of nitrogenous and oxygeous heterocycles, especially enantioenriched indole derivatives.9 This is because the NH group in the indole moiety is easily activated by CPAs via hydrogen-bonding interactions.10 In 2012, You and coworkers utilized CPA (S)-C4 as a suitable organocatalyst to promote the CADA reaction of NH-unprotected tryptamines and tryptophol 11 with vinyl ketones 12 (Scheme 3a).11 Interestingly, this CADA reaction involved double Michael addition to vinyl ketones 12, which afforded N-alkylated pyrroloindolines 13 in overall high yields and moderate to good enantioselectivities.
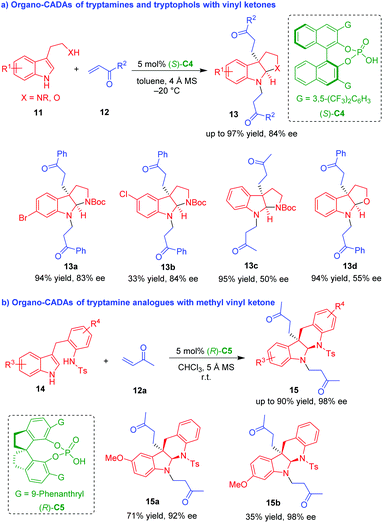 | ||
| Scheme 3 Organo-CADA reactions of tryptamines, tryptophol and analogues with vinyl ketones by You and coworkers.11,12 | ||
To expand the applicability of this strategy, in 2014, the same group devised tryptamine analogues 14 as competent substrates to undergo CADA reactions with methyl vinyl ketone (MVK) 12a in the presence of CPA (R)-C5, which constructed indolinoquinoline frameworks 15 in moderate to high yields and good enantioselectivities (Scheme 3b).12 Notably, both of the two approaches involved a cascade Michael addition/cyclization/N-Michael addition sequence, and the second N-Michael addition of in situ generated indoline to vinyl ketones should be ascribed to the strong nucleophilicity of the NH group in the structure of indoline.
Nearly at the same time, Antilla and coworker described CPA (R)-C6-promoted CADA reactions of tryptamines 16 with MVK 12a and diethyl diazene-1,2-dicarboxylates (DEAD) 17, respectively, which constructed enantioenriched pyrroloindoline frameworks 18 and 19 in good yields and high stereoselectivities (Scheme 4a).13 Notably, the authors performed NMR experiments to investigate the possible activation mode of CPA to substrates. In the reaction involving MVK 12a, they proposed that (R)-C6 simultaneously formed two hydrogen bonds with the indole NH group and the ester carbonyl group of tryptamines 16, and the amide NH group of tryptamines 16 formed another hydrogen bond with MVK 12a, thus controlling the enantioselectivity in the first step of Michael addition (Scheme 4b). The similarly activation mode was suggested for the reaction involving DEAD 17, and the difference is that (R)-C6 just formed one hydrogen bond with the ester carbonyl group of tryptamines 16 due to the existence of indole N-methyl group. More importantly, they applied the CADA reaction of tryptamines 16 with MVK 12a in the total synthesis of (−)-debromoflustramine B via a very concise synthetic route (Scheme 4c). Namely, the pyrroloindoline product 18a with 91% ee generated from CADA reaction was subjected to a Wittig olefination to give compound 20 with a retained enantioselectivity. Catalyzed by a Ru complex, the terminal olefin 20 isomerized into the internal alkene 21, which further underwent a reduction reaction to afford (−)-debromoflustramine B in an excellent yield.
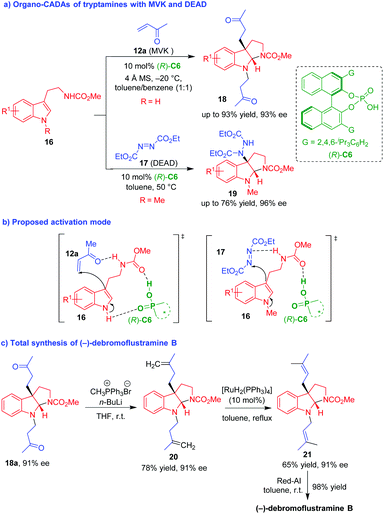 | ||
| Scheme 4 Organo-CADA reaction of tryptamines and its application in the total synthesis of (−)-debromoflustramine B by Antilla and coworker.13 | ||
In 2014, under the catalysis of chiral anion phase-transfer (CAPT), Toste and coworkers realized the CADA reaction of tryptamines 22 using aryldiazonium cations as a source of electrophilic nitrogen, which was in situ generated from aryldiazonium tetrafluoroborates 23 (Scheme 5).14 By this approach, a series of C3-diazenated pyrroloindolines 24 were synthesized in overall high yields and excellent enantioselectivities. The authors suggested that the interaction of CPA (R)-C7 with aryldiazonium tetrafluoroborates 23 provided a soluble chiral ion pair, which controlled the enantioselectivity in the step of nucleophilic addition of tryptamines 22 to aryldiazonium, thus generating an enantioenriched intermediate D to undergo the subsequent intramolecular cyclization to give products 24.
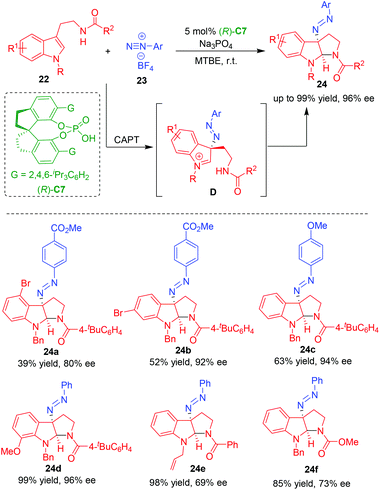 | ||
| Scheme 5 Organo-CADA reaction of tryptamines with aryldiazonium cations by Toste and coworkers.14 | ||
Shortly after, Liao, Deng and coworkers established the application of CAPT-enabled CADA reaction of tryptamine with aryldiazonium cation in the total synthesis of (−)-psychotriasine (Scheme 6).15 Initially, they developed the CAPT-enabled CADA reaction of tryptamine 25 with aryldiazonium cation 23a in the presence of (S)-C6, affording pyrroloindoline 26 bearing an azo group in a quantitative yield and a good enantioselectivity (Scheme 6a). The enantioselectivity of product 26 could be further improved to >96% ee after recrystallization. Then, compound 26 was utilized as a starting material for the total synthesis of (−)-psychotriasine (Scheme 6b). After protecting the NH group with Boc, the azo group of compound 26 was transformed into an amino group with the action of hydrazine hydrate and RANEY® Ni to generate an important intermediate compound 27. The Buchwald–Hartwig amination of 1,2-dibromobenzene with compound 27 afforded compound 28, which underwent Larock cyclization with alkyne 29 to give compound 30 bearing a newly generated tryptamine moiety. The subsequent removal of the N-Bz group of compound 30 and the re-protection of the free NH group with ClCO2Me gave rise to compound 31 bearing two N-CO2Me groups. Finally, the N-Boc group of compound 31 was removed with TFA and the two N-CO2Me groups were reduced into N-Me groups by Red-Al, leading to the total synthesis of (−)-psychotriasine.
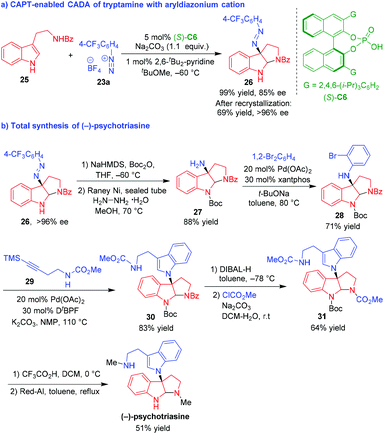 | ||
| Scheme 6 Application of organo-CADA reaction in the total synthesis of (−)-psychotriasine by Liao, Deng and coworkers.15 | ||
Under asymmetric catalysis, tryptophols always displayed the C3-nucleophilicity to undergo cascade addition–cyclization reactions with various electrophiles, thus realizing the CADA reactions. On the contrary, tryptophols rarely displayed the O-nucleophilicity in catalytic asymmetric reactions. In 2017, Shi and coworkers established catalyst-controlled chemo- and enantioselective CADA reaction of tryptophols 32 with isatin-derived imines 33 (Scheme 7).16 As illustrated in Scheme 7a, in the presence of chiral H-donor acidic catalyst such as CPA, tryptophols 32 displayed the C3-nucleophilicity to undergo CADA reaction with imines 33, affording dihydrofuroindoline derivatives 34 in high yields, excellent diastereo- and enantioselectivities. However, in the presence of chiral H-donor basic catalyst such as chiral squaramide-tertiary amine, tryptophols 32 displayed the O-nucleophilicity to undergo addition reaction with imines 33, generating 3-substituted 3-aminooxindoles 35 in good yields and high enantioselectivities. In the suggested activation mode of CADA reaction (Scheme 7b), CPA (S)-C6 simultaneously activated both tryptophols 32 and imines 33via hydrogen-bonding interactions, which facilitated an enantioselective C3-nucleophilic addition of tryptophols 32 to imines 33 to generate chiral intermediates E. The intermediates E rapidly underwent an intramolecular cyclization reaction to give dihydrofuroindoline products 34.
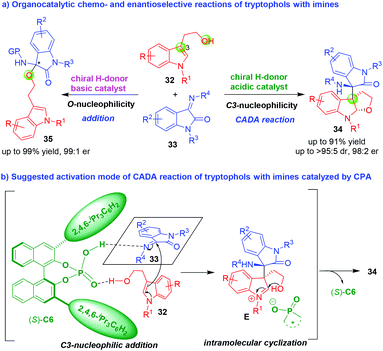 | ||
| Scheme 7 Organo-CADA reaction of tryptophols with isatin-derived imines by Shi and coworkers.16 | ||
Shortly after, the same group reported a CPA-enabled chemodivergent arylative CADA reaction of tryptophols 36 by using quinone imine ketals (QIKs) 37 as aryl group surrogates (Scheme 8a).17 By modulating the reaction conditions, two series of dihydrofuroindoline products 38 and 39 could be generated in a chemoselective manner with generally high yields, and excellent diastereo- and enantioselectivities. The investigation on the possible reaction pathway (Scheme 8b) revealed that product 39a was initially generated after stirring 36a and 37a for just one minute. However, product 39a was rapidly transformed into N-aryl-substituted product 38a in the reaction mixture. To make the reaction stop at the stage of forming 39, the authors utilized the operation of slowly adding QIK 37 to an excess amount of tryptophols 36 by a syringe pump (Scheme 8a, left). Based on the experimental results, the authors suggested a possible reaction pathway and activation mode of CPA (S)-C5 to the two substrates (Scheme 8c). The two substrates of 36 and 37 were simultaneously activated by (S)-C5, thus facilitating an enantioselective 1,4-addition between them to generate chiral intermediates F, which promptly underwent alcohol elimination to give intermediates G. The subsequent intramolecular cyclization of intermediates G gave rise to N-unprotected dihydrofuroindoline products 39. If there were excess amount of QIK 37 in the reaction system, products 39 would perform N-arylation reaction with QIKs 37 to afford N-aryl-protected dihydrofuroindoline products 38.
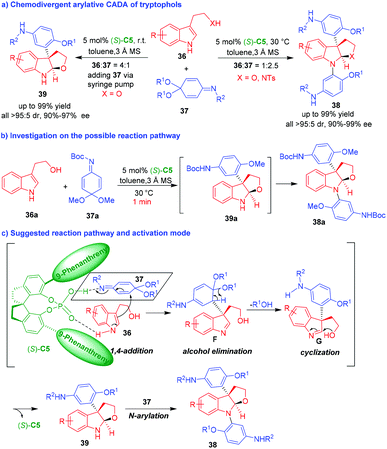 | ||
| Scheme 8 Organo-CADA reactions of tryptophols with QIKs by Shi and coworkers.17 | ||
In 2020, Shin and coworkers reported a CADA reaction of tryptamine analogues 14 by using allenamides 40 as suitable electrophilic precursors in the presence of CPA (S)-C8, which constructed indoloquinolone scaffolds in moderate to good yields and generally high enantioselectivities (Scheme 9).18 Based on the control experiments, it was discovered that the two NH groups in tryptamine analogues 14 are crucial for controlling the enantioselectivity. So, they proposed that the P![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group of CPA should simultaneously form two hydrogen bonds with both of the two NH groups. But there are two possible activation modes of CPA on allenamides 40. The first one is the ion-paring interaction between the anion of CPA and the α,β-unsaturated iminium ion in situ generated by the protonation of allenamides 40 (activation mode A), while the second one is the covalent interaction generated from the addition reaction of CPA anion to the α,β-unsaturated iminium (activation mode B). The authors believed that activation mode B was more favorable than activation mode A based on a previously reported DFT calculation.19
O group of CPA should simultaneously form two hydrogen bonds with both of the two NH groups. But there are two possible activation modes of CPA on allenamides 40. The first one is the ion-paring interaction between the anion of CPA and the α,β-unsaturated iminium ion in situ generated by the protonation of allenamides 40 (activation mode A), while the second one is the covalent interaction generated from the addition reaction of CPA anion to the α,β-unsaturated iminium (activation mode B). The authors believed that activation mode B was more favorable than activation mode A based on a previously reported DFT calculation.19
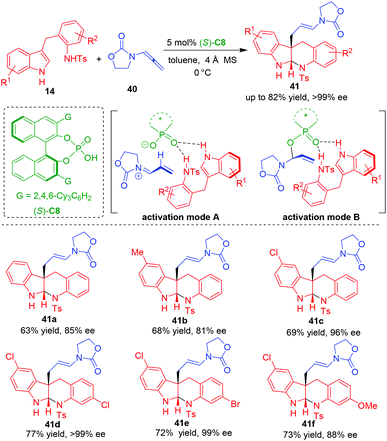 | ||
| Scheme 9 Organo-CADA reaction of tryptamine analogues with allenamides by Shin and coworkers.18 | ||
2.2 Organo-CADA reactions of tryptamines, tryptophols and their analogues with halogen-centered electrophiles
Although organo-CADA reactions of tryptamines or tryptophols with C,N-centered electrophiles have developed rapidly, halogen-centered electrophiles were not employed to such reactions until 2011. In that year, Gouverneur and coworkers established the first organo-CADA reaction of tryptamines or tryptophols 42 with a fluorinating reagent (NFSI) in the presence of catalytic amount of hydroquinine 1,4-phthalazinediyl diether [(DHQ)2PHAL] C9, which afforded fluorinated pyrroloindolines or furoindolines 43 in moderate to good yields and acceptable enantioselectivities (Scheme 10a).20 Furthermore, indole derivative 44 could undergo organocatalytic asymmetric dearomative difluorocyclization under the same reaction conditions, offering product 45 in a moderate enantioselectivity (Scheme 10b).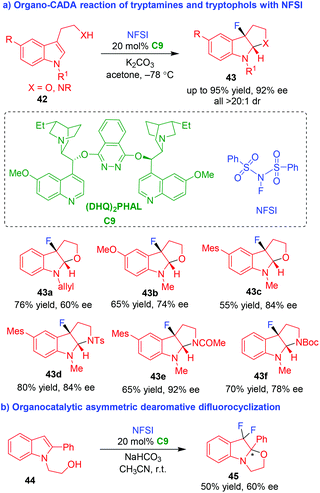 | ||
| Scheme 10 Organo-CADA reaction of tryptamines or tryptophols with a fluorinating reagent by Gouverneur and coworkers.20 | ||
Apart from catalytic asymmetric fluorination, catalytic asymmetric selenofunctionalization is also an important transformation. In 2013, the first organocatalytic asymmetric selenofunctionalization of tryptamines was realized by Gong and coworkers in the presence of CPA, which constructed C3-selenyl-substituted pyrroloindoline frameworks in high yields (up to 85%) and good enantioselectivities (up to 89% ee).21
In 2014, You's group established organo-CADA reactions of tryptamines and their analogues with brominating or chlorinating reagents, thus realizing the bromocyclization and chlorocyclization of tryptamine derivatives (Scheme 11).22,23 In the presence of chiral amine catalyst C9 and L-(−)-camphorsulfonic acid (CSA), tryptamines 46 underwent CADA reaction with N-bromoacetamide (NBAc), giving rise to C3-bromo-substituted pyrroloindolines 47 in high yields and moderate enantioselectivities (Scheme 11a).22 The CADA reaction of tryptamine analogues 48 was realized by using DCDMH as a chlorination reagent under the catalysis of (DHQD)2PHAL C10, which constructed enantioenriched oxazinoindoline scaffolds 49 in high yields and excellent enantioselectivities (Scheme 11b).23
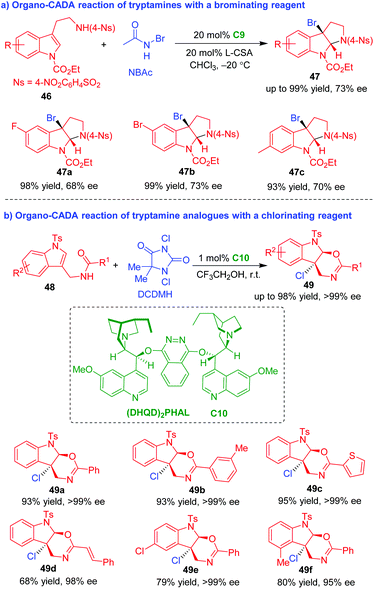 | ||
| Scheme 11 Organo-CADA reactions of tryptamines and analogues with brominating or chlorinating reagents by You and coworkers.22,23 | ||
Among different halogenating dearomative cyclizations of indole derivatives, catalytic asymmetric bromocyclization is highly valuable because the C–Br bond is easier to cleavage, thus ensuring useful transformations. To this end, Ma, Xie, Lai and coworkers successfully devised organo-CADA bromocyclizations of tryptamines and tryptophols and realized their application in total synthesis of natural alkaloids (Scheme 12).24–26 In 2013, they developed catalytic asymmetric dearomative bromocyclization of tryptamines 50 in the presence of CPA (R)-C11 by using bromine salt 51 as a brominating reagent, providing an easy access to optically pure brominated pyrroloindolines 52 in high yields and excellent enantioselectivities (Scheme 12a).24
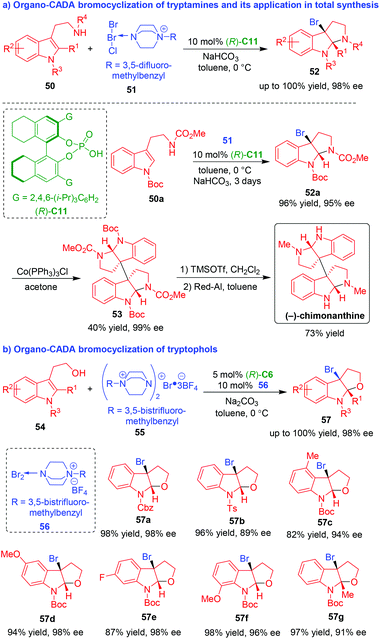 | ||
| Scheme 12 Organo-CADA bromocyclizations of tryptamines and tryptophols by Ma, Xie, Lai and coworkers.24–26 | ||
More importantly, this methodology was applied in the brief, enantioselective synthesis of natural alkaloid (−)-chimonanthine. In brief, the CADA reaction of tryptamine 50a with 51 afforded brominated product 52a with optical purity, which underwent a homodimerization in the presence of Co(PPh3)3Cl to generate bispyrroloindoline 53. Finally, the removal of N-Boc group with TMSOTf and the reduction of N-CO2Me group with Red-Al accomplished the total synthesis of (−)-chimonanthine. Furthermore, the methodology of organocatalytic asymmetric dearomative bromocyclization of tryptamine was also employed for the first enantioselective total synthesis of (−)-conolutinine in ten steps.25
Soon after, the same group developed catalytic asymmetric dearomative bromocyclization of tryptophols 54 in the presence of CPA (R)-C6 by using bromine salt 55 as a brominating reagent. Interestingly, they discovered that the addition of catalytic amount of DABCO-derived bromine salt 56 increased the enantioselectivity of the product (Scheme 12b).26 By this protocol, a series of 3-bromofuroindolines 57 were synthesized in high yields and excellent enantioselectivities.
Although chiral amine-catalyzed asymmetric dearomative fluorocyclizations of tryptamines and tryptophols have been established in 2011 by Gouverneur and coworkers,20 highly enantioselective fluorocyclizations of tryptamines and tryptophols are still highly desired. To achieve this goal, in 2017 and 2018, based on the strategy of asymmetric fluorination using anionic chiral phase-transfer catalyst,27 You and coworkers successfully devised CPA (S)-C12 catalyzed asymmetric dearomative fluorocyclizations of NH-unprotected tryptamines 58 and tryptophols 60 by using Selectfluor® as a fluorating reagent (Scheme 13),28,29 which afforded C3-fluoropyrroloindolines 59 and C3-fluorofuroindolines 61, respectively, in a highly enantioselective manner. Notably, the authors performed control experiments to investigate the reaction mechanism. In organo-CADA fluorocyclization of tryptamines 58 (Scheme 13a),28 they discovered there was a significant background reaction in the absence of CPA (S)-C12 or proton sponge. Additionally, it was revealed that the addition of HBF4 accelerated the reaction, while the addition of proton sponge would slow down the reaction. Therefore, they deduced that the role of proton sponge was to neutralize HBF4 released in situ from Selectfluor®, thus inhibiting the background reaction. In organo-CADA fluorocyclization of tryptophols 60 (Scheme 13b),29 they investigated the role of 4-fluorophenyl boronic acid by treating tryptophol 60a with boronic acid together, and the reaction generated boronic ester 62a which was detected by in situ NMR, 13C NMR and HRMS. Moreover, the reaction of boronic ester 62a with Selectfluor® in the presence of (S)-C12 could give rise to product 61a in similar results with those under standard conditions, thus confirming boronic ester 62a was a key intermediate for the fluorocyclization reaction.
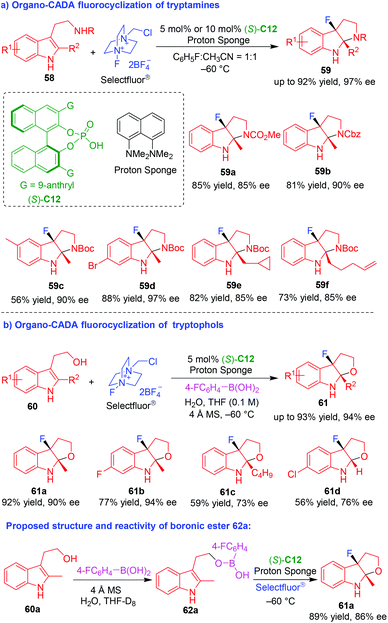 | ||
| Scheme 13 Organo-CADA fluorocyclizations of tryptamines and tryptophols by You and coworkers.28,29 | ||
In 2020, Hamashima and coworkers utilized chiral dicarboxylic acid C13 as a precatalyst in the organo-CADA fluorocyclization of tryptamine analogues 63 by using Selectfluor® as a fluorating reagent (Scheme 14).30 The utilization of the catalytic system is based on the consideration that the dicarboxylate ion of C13 could act as a chiral anionic phase-transfer catalyst to bring Selectfluor® into the organic phase, thus controlling the reactivity and enantioselectivity of the dearomative fluorocyclization. By this reaction, a series of C3-fluoropyrroloindoline derivatives 64 were generated in good yields and high enantioselectivities. Furthermore, the authors discovered that the addition of a small amount of water played an important role in the reaction, which might facilitate the formation of C13 anion and mediate the hydrogen-bonding interaction between the catalyst and the anion of substrates 63.
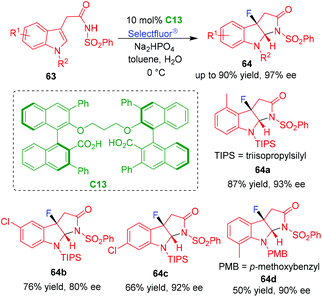 | ||
| Scheme 14 Organo-CADA fluorocyclization of tryptamine analogues by Hamashima and coworkers.30 | ||
2.3 Organo-CADA reactions of tryptamines, tryptophols and their analogues with O-centered reagents
Compared to well-developed organo-CADA reactions of tryptamines, tryptophols and their analogues with C-, N-, halogen-centered electrophiles, such reactions with O-centered reagents are rather underdeveloped, which might be ascribed to the formidable challenge in controlling the chemoselectivity and enantioselectivity of catalytic asymmetric indole oxidation. This challenge was firstly confronted in 2011 by Miller, Movassaghi and coworkers (Scheme 15).31 In that year, they reported a highly chemo- and enantioselective CADA oxidation of tryptamine analogues 65 by using hydrogen peroxide as an oxidant and peptide C14 as a chiral organocatalyst, delivering 3-hydroxy-indolenines 66 in good yields and moderate to high enantioselectivities (Scheme 15a). It was suggested that products 66 might be derived from the intermediate indole oxides H. Moreover, enantioenriched hydroxy-indolenine 66e could be utilized in stereospecific rearrangements to give 2-oxindole 67 with a retained enantiopurity (Scheme 15b).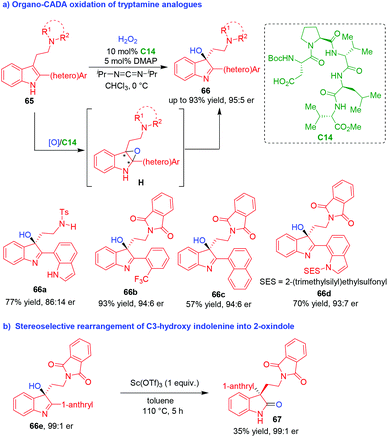 | ||
| Scheme 15 Organo-CADA oxidation of tryptamine analogues by Miller, Movassaghi and coworkers.31 | ||
Later, Movassaghi and coworkers established the total synthesis of (−)-trigonoliimines A–C on the basis of asymmetric dearomative oxidation of bis-tryptamines in the presence of equivalent chiral oxidant,32,33 and they investigated the anticancer activities of these compounds.33
Organo-CADA reactions of indole derivatives scarcely involved the generation of radical intermediates in spite of the fact that the catalytic asymmetric radical chemistry has become an emerging area.34 Therefore, the development of radical-involved CADA reactions is highly valuable and the control of the enantioselectivity in such reactions remains a great challenge. In 2018, Knowles and coworkers established an organo-CADA oxidation of tryptamines via noncovalent stabilization of indole radical cations and realized the application of this methodology to the synthesis of several natural alkaloids (Scheme 16).35 In the presence of a photocatalyst and chiral phosphate base (S)-C15, tryptamines 68 underwent a catalytic asymmetric dearomative proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET) reaction with TEMPO˙ radical, affording alkoxyamine-substituted pyrroloindolines 69 in good yields and high enantioselectivities (Scheme 16a). In this reaction, an oxidative PCET process provided an ionic hydrogen-bonded intermediate I between the radical cation of tryptamine 69 and the CPA anion of (S)-C15. Then, TEMPO˙ radical rapidly captured the radical cation of tryptamine and generated intermediate J in an enantioselective manner due to the ion-paring interaction and the hydrogen-bonding interaction of CPA anion. The subsequent intramolecular cyclization of intermediate J generated product 69 and released the CPA catalyst.
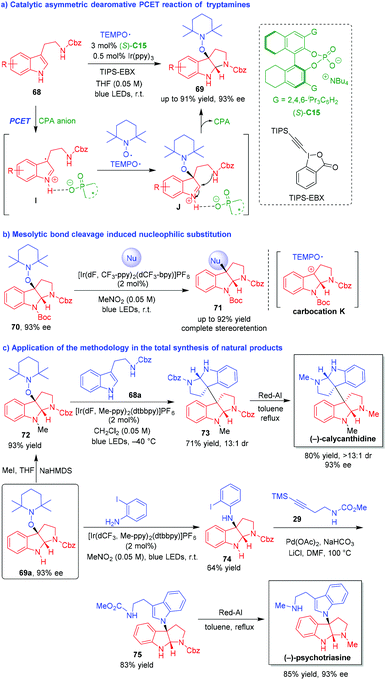 | ||
| Scheme 16 Organo-CADA oxidation of tryptamines with TEMPO˙ radical by Knowles and coworkers.35 | ||
Furthermore, enantioenriched alkoxyamine-substituted pyrroloindolines 70 could undergo single-electron oxidation/mesolytic cleavage sequence to give transient carbocation intermediates K, which were readily attacked by a wide range of nucleophiles to give C3-nucleophile-substituted pyrroloindolines 71 in high yields with complete stereoretention (Scheme 16b).
More importantly, starting form alkoxyamine-substituted pyrroloindoline 69a with 93% ee, the authors successfully accomplished the total synthesis of (−)-calycanthidine, (−)-psychotriasine and (−)-chimonanthine with very concise synthetic routes. As illustrated in Scheme 16c, N-methylation of 69a afforded pyrroloindoline 72, which was subjected to nucleophilic substitution with tryptamine 68avia the process of single-electron oxidation/mesolytic cleavage, accompanying by the dearomative intramolecular cyclization of 68a to generate compound 73. Then, the reduction of the two Cbz groups in compound 73 by Red-Al led to the production of (−)-calycanthidine with complete enantioretention. The synthetic route for (−)-psychotriasine also involved a nucleophilic substitution of 69a by using ortho-iodoaniline as a nucleophile, and the reaction offered N-aryl pyrroloindoline 74 as a suitable substrate to undergo Larock annulation with alkyne 29, thus generating the core structure 75 of the target natural product. Finally, the reduction of the N-ester groups in compound 75 resulted in the production of (−)-psychotriasine with a maintained enantioselectivity of 93% ee. This work not only contributed greatly to the research field of organo-CADA reactions of indole derivatives, but also provided a powerful method for enantioselective total synthesis of related natural alkaloids.
Nearly at the same time, Xia and coworkers also reported an organo-CADA oxidation of tryptamines 76via a radical process (Scheme 17).36 Different with the strategy of Knowles,35 the authors discovered that visible light could directly excite TEMPO and tryptamines 76 could convert into tryptamine radicals via a hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) process without the photocatalyst of iridium. Catalyzed by CPA (R)-C11, the asymmetric dearomative HAT reaction of tryptamines 76 with TEMPO˙ radical smoothly afforded TEMPO-substituted pyrroloindolines 77 in high yields and excellent enantioselectivities (Scheme 17a). Notably, this methodology could be applicable in the total synthesis of natural product (−)-verrupyrroloindoline in five steps (Scheme 17b). Compound 77a with 98% ee could conveniently transform into compound 78via deprotection of N-Cbz group and Michael addition with alkynyl ester. The condensation of compound 78 with acetaldehyde, followed by an intramolecular cyclization, afforded compound 79 bearing the core structure of natural product. At last, the removal of TEMP group under a reductive condition gave rise to (−)-verrupyrroloindoline without the erosion of the enantioselectivity.
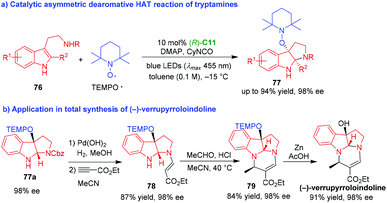 | ||
| Scheme 17 Organo-CADA oxidation of tryptamines with TEMPO˙ radical by Xia and coworkers.36 | ||
The C3-nucleophilicity is a common reactivity of indole derivatives, but the C3-electrophilicity is a “new world” of indole chemistry,37 which has rarely been disclosed.38 In 2019, You, Zhang and coworkers established an innovative organo-CADA oxidation of tryptamines, tryptophols and their analogues 80via an umpolung strategy (Scheme 18).39 In this reaction, indole derivatives 80 displayed C3-electrophilicity to react with N-hydroxycarbamate 81 as nucleophiles in the presence of a photocatalyst and CPA (R)-C16, offering a variety of C3-oxyamine-subsituted indoline derivatives 82 in high yields and good enantioselectivities (Scheme 18a).
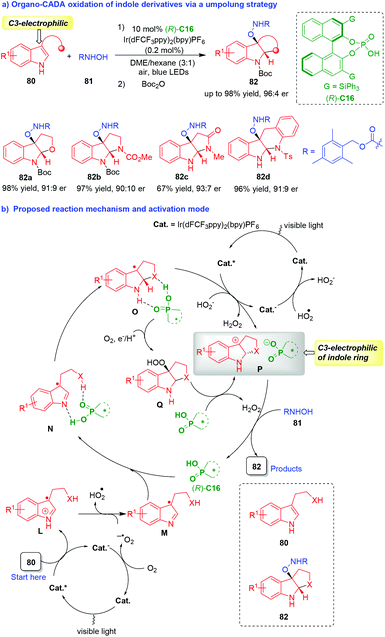 | ||
| Scheme 18 Organo-CADA oxidation of tryptamines, tryptophols and their analogues via an umpolung strategy by You, Zhang and coworkers.39 | ||
In the proposed reaction mechanism and activation mode (Scheme 18b), two sequential single-electron-transfer (SET) oxidation of indole derivatives 80 were involved under the dual catalysis of photocatalyst (Cat.) and CPA (R)-C16, which inverted the reactivity of indole derivatives 80 from C3-nucleophilic to C3-electrophilic. In brief, the first SET oxidation of substrates 80 generated the radical cations L, which were deprotonated to give radicals M. Then, with the aid of CPA (R)-C16, radicals M underwent the sequence of cyclization/second SET oxidation via the formation of intermediates N and O to give carbocations P as key intermediates. In the structure of carbocations P, the C3-position of the indole ring had a positive charge, thus displaying C3-electrophilicity. Additionally, there was an electrostatic interaction between the tertiary pyrroloindoline carbocations P and the CPA anion, which played an important role in controlling the enantioselectivity of the subsequent nucleophilic addition of N-hydroxycarbamates 81 to carbocations P, leading to the generation of enantioenriched products 82 and the completion of the catalytic cycle. It should be noted that an alternative reaction pathway from intermediates O to carbocations Pvia the formation of intermediates Q could not be fully excluded. This work has not only provided a robust method for the synthesis of enantioenriched C3-oxyamine-subsituted indoline derivatives, but also offered an umpolung strategy for designing organo-CADA reactions of indole derivatives, which will greatly advance the development of CADA reactions and indole chemistry.
3. Organo-CADA reactions of vinylindoles
Vinylindoles are versatile building blocks in cycloadditions.40 Among them, tryptamine-derived vinylindoles are competent substrates for cascade reactions due to the existence of both tryptamine and vinylindole moieties. In 2009, MacMillan and coworkers designed an innovative organo-CADA reaction of tryptamine-derived vinylindole 83 with propynal 84 in the presence of chiral amine catalyst C17, which constructed a bridged tetracyclic carbazole framework 85 in a high yield and excellent enantioselectivity (Scheme 19a).41 This cascade reaction started with C17-catalyzed asymmetric [4 + 2] cycloaddition of vinylindole 83 and propynal 84 to give a chiral intermediate R, which rapidly isomerized into intermediate S bearing an iminium group. Then, by making avail of the tryptamine functionality, an intramolecular cyclization of intermediate S occurred to give the tetracyclic pyrroloindoline structure, which transformed to final product 85via hydrolysis to release C17 and reduction of the formyl group.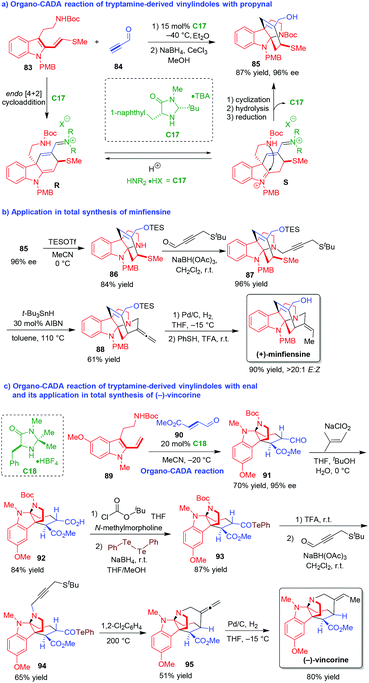 | ||
| Scheme 19 Organo-CADA reaction of tryptamine-derived vinylindoles with propynal or enal and its application in natural products synthesis by MacMillan and coworkers.41,42 | ||
More importantly, this methodology could be successfully used for the asymmetric total synthesis of natural product (+)-minfiensine in a rather concise way (Scheme 19b).41 Compound 85 with 96% ee was subjected to simultaneous deprotection of N-Boc group and protection of the OH group with TESOTf, which afforded compound 86 in 84% yield. Then, compound 86 underwent a reductive amination with 4-(tert-butylthio)but-2-ynal to generate N-alkynyl-substituted compound 87, which further underwent intramolecular alkyne radical cyclization to give compound 88 bearing an allene group. Finally, the hydrogenation of the allene group in compound 88 occurred in a highly (E/Z)-selective manner, and the deprotection of the OTES group accomplished the total synthesis of (+)-minfiensine.
Furthermore, the same group also developed an organo-CADA reaction of tryptamine-derived vinylindole 89 with enal 90, and realized its application in the total synthesis of (−)-vincorine (Scheme 19c).42 Similarly, the CADA reaction of vinylindole 89 with enal 90 in the presence of chiral amine catalyst C18 involved the cascade sequence of asymmetric [4 + 2] cycloaddition and intramolecular cyclization, which offered tetracyclic pyrroloindoline 91 in 70% yield and 95% ee. Then, the oxidation of the formic group in compound 91 led to the generation of carboxylic acid 92, which was converted into telluride 93via a sequence involving the generation of a mixed anhydride followed by the reaction with 1,2-diphenylditellane. In the next step, the deprotection of N-Boc group with TFA gave NH group, which underwent N-alkylation with 2-butynal-4-tert-butyl sulfide via reductive amination to give compound 94 as an alkyl radical precursor. Under a high temperature (200 °C), compound 94 underwent an intramolecular radical cyclization of the acyl telluride with the thermally initiated alkyl radical, offering the allene compound 95. Finally, the selective hydrogenation of the allene functionality in compound 95 resulted in the synthesis of (−)-vincorine as a single (E/Z)-isomer.
In 2011, MacMillan and coworkers further demonstrated the art of synthesis via the combination of organocascade catalysis with collective natural product synthesis, which provided a robust method for the total synthesis of a series of natural alkaloids from a common intermediate (Scheme 20).43,44 The key reaction was an organo-CADA cascade reaction of tryptamine-derived vinylindole 96 with propynal 84 in the presence of chiral amine catalyst ent-C17, which generated enantioenriched tetracyclic spiroindoline 97 as a common intermediate for versatile synthesis of natural products (Scheme 20a).43
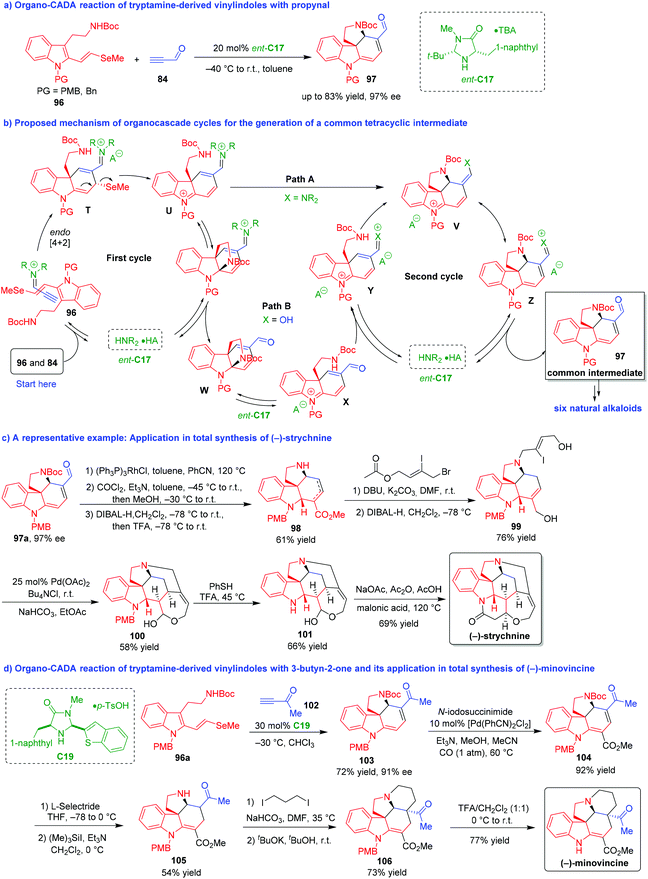 | ||
| Scheme 20 Organo-CADA reaction of tryptamine-derived vinylindoles with propynal or 3-butyn-2-one and its application in natural products synthesis by MacMillan and coworkers.43,44 | ||
In the proposed mechanism for the generation of spiroindoline 97 (Scheme 20b), propynal 84 was activated by ent-C17 to generate an iminium intermediate, which underwent a stereoselective [4 + 2] cycloaddition with vinylindole 96 to give intermediate T. Then, intermediate T transformed into unsaturated iminium Uvia β-elimination of methyl selenide. In the next transformation of intermediate U to tetracyclic intermediate V, there were two possible pathways A and B. In pathway A, intermediate U directly underwent an intramolecular conjugate addition to generate intermediate V. In pathway B, intermediate U underwent another type of intramolecular cyclization at the indole C2-position to give bridged intermediate W after hydrolysis. In the presence of Brønsted acid (involved in ent-C17), intermediate W could undergo the sequence of ring-opening/conjugate addition via intermediates X and Y to give intermediate V. Finally, intermediate V isomerized into intermediate Z, which led to the generation of product 97 as a common structure for the total synthesis.
Based on this key reaction and the formation of the common intermediate 97, the authors accomplished asymmetric total syntheses of six natural alkaloids including strychnine, aspidospermidine, vincadifformine, akuammicine, kopsanone and kopsinine. Herein, the total synthesis of (−)-strychnine was selected as a representative example to demonstrate the power of this methodology (Scheme 20c).43 The common intermediate 97a with 97% ee was subjected to deformylation by using Wilkinson's catalyst [(Ph3P)3RhCl] and a subsequent introduction of a carbomethoxy group via the reaction with phosgene and methanol. The subsequent reduction with DIBAL-H afforded unsaturated ester 98 as a mixture of alkene isomers in 61% total yield for the three steps. Then, compound 98 underwent allylation with substituted allyl bromide and simultaneous alkene isomerization, followed by the reduction of both ester functionalities in the presence of DIBAL-H. The resulted compound 99 performed Jeffery–Heck cyclization/lactol formation to generate compound 100, which further underwent deprotection of N-PMB group to give Wieland–Gumlich aldehyde 101. Finally, an intramolecular cyclization of compound 101 occurred in the presence of malonic acid, acetic anhydride and sodium acetate to complete the total synthesis of (−)-strychnine.
Two years later, the same group expanded the strategy of organocatalytic asymmetric [4 + 2] cycloaddition/β-elimination/conjugate addition cascade to the total synthesis of (−)-minovincine (Scheme 20d).44 The key step was also an organo-CADA cascade reaction of tryptamine-derived vinylindole 96a with 3-butyn-2-one 102 in the presence of chiral amine catalyst C19, leading to the generation of tetracyclic spiroindoline 103 with 91% ee as a key intermediate compound for the total synthesis. Under the catalysis of palladium complex, spiroindoline 103 underwent carbomethoxylation to give compound 104, which was subjected to a regioselective 1,4-conjugate reduction and N-Boc removal to generate compound 105. Then, compound 105 performed N-alkylation with 1,3-diiodopropane and intramolecular cyclization with the help of potassium tert-butoxide, thus producing compound 106 as a single diastereomer. The final deprotection of N-PMB group in compound 106 led to the total synthesis of (−)-minovincine.
3-Vinylindoles can act as electron-rich dienes in Diels–Alder reactions.40 In 2009, Ricci, Bernardi and coworkers established the first organocatalytic asymmetric Diels–Alder reaction of 3-vinylindoles 107 with electronically poor dienophiles such as maleimides 108 and quinones 109 in the presence of bifunctional thiourea-tertiary amine C20 (Scheme 21).45 Very interestingly, this organocatalytic asymmetric [4 + 2] cycloaddition gave rise to dearomative products 110 in high yields and excellent enantioselectivities, and the newly formed carbon–carbon double bond did not isomerize into aromatic indole ring. In the suggested transition state, thiourea-tertiary amine catalyst C20 simultaneously activated both 3-vinylindole 107a and N-phenylmaleimide 108avia forming multiple hydrogen bonds, thus controlling the diastereo- and enantioselectivity of the [4 + 2] cycloaddition.
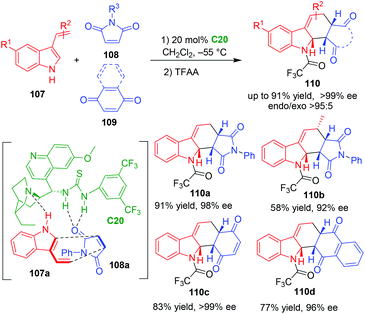 | ||
| Scheme 21 Organo-CADA [4 + 2] cycloaddition of 3-vinylindoles with dienophiles by Ricci, Bernardi and coworkers.45 | ||
In 2011, Barbas and coworkers utilized C2-symmetric bisthiourea C21 as a suitable organocatalyst to enable CADA [4 + 2] cycloaddition of 3-vinylindoles 107 with methyleneindolinones 111, constructing carbazolespirooxindole frameworks 112 in high yields, excellent diastereo- and enantioselectivities (Scheme 22).46 Notably, this reaction has a wide substrate scope, and a variety of substituted 3-vinylindoles 107 could serve as competent substrates, which provided a practical method for the synthesis of spirooxindoles with potential bioactivities. Moreover, the chiral catalyst and solvent could be recycled. The authors also suggested a hydrogen-bonding interaction between the catalyst and the substrates.
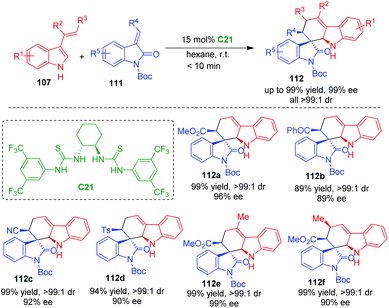 | ||
| Scheme 22 Organo-CADA [4 + 2] cycloaddition of 3-vinylindoles with methyleneindolinones by Barbas and coworkers.46 | ||
In 2013, Enders and coworkers reported an organo-CADA cascade reaction of 3-vinylindoles 107 with α,β-unsaturated aldehydes 3 in the presence of proline-derived catalyst C22, which constructed tetracyclic pyridocarbazole scaffolds 113 in good yields and excellent stereoselectivities (Scheme 23).47 This reaction occurred via iminium–iminium–enamine activation sequence. Namely, the first step was asymmetric Diels–Alder reaction of 3-vinylindoles 107 with vinyl iminiums A′ generated in situ from α,β-unsaturated aldehydes 3 and C22, resulting in the formation of tetrahydrocarbazole intermediates B′. Then, another molecule of aldehydes 3 was activated by C22 to yield vinyl iminiums A′, which underwent aza-Michael addition with intermediates B′ to give intermediates C′. Due to the enamine activation mode, the intermediates C′ underwent an intramolecular aldol condensation to generate the final products 113.
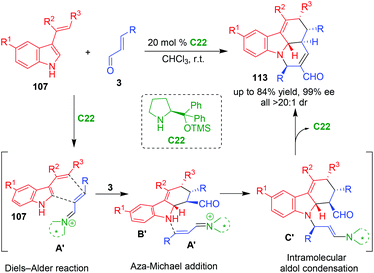 | ||
| Scheme 23 Organo-CADA cascade reaction of 3-vinylindoles with α,β-unsaturated aldehydes by Enders and coworkers.47 | ||
In 2019, Guo and coworkers expanded the electronically poor dienophiles to nitroolefins 114, and established an organo-CADA [4 + 2] cycloaddition of 3-vinylindoles 107 with nitroolefins 114 in the presence of chiral thiourea-tertiary amine catalyst C23, delivering tetrahydrocarbazole derivatives 115 in moderate to good yields and excellent enantioselectivities (Scheme 24).48 In addition, the authors performed theoretical calculations to investigate the possible activation mode of C23 to the substrates. It was revealed that C23 was more likely to utilize its carbonyl group, rather than the tertiary amine group, in forming a hydrogen bond with the indole NH group, thus activating 3-vinylindoles 107 to participate in the reaction.
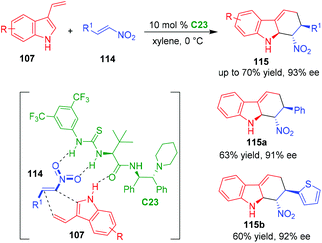 | ||
| Scheme 24 Organo-CADA [4 + 2] cycloaddition of 3-vinylindoles with nitroolefins by Guo and coworkers.48 | ||
Apart from 3-vinylindoles, Shi and coworkers reported that 3-methyl-2-vinylindoles 116 could also underwent organo-CADA reaction with quinone monoimides 117 under the catalysis of CPA (R)-C6, which generated indolenines 118 bearing a quaternary stereogenic center in high yields and excellent enantioselectivities (Scheme 25).49 Very interesting, in this reaction, the reactivity of 3-methyl-2-vinylindoles 116 was switched from C2′-nucleophilicity to indole C3-nucleophilicity, which was different from previously reported [2 + n] cycloadditions of 3-methyl-2-vinylindoles,50 thus enabling the CADA reaction with quinone monoimides 117 in a chemospecific fashion. In the suggested activation mode, (R)-C6 simultaneously formed two hydrogen bonds with the NH group of 116 and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N group of 117, thus activating both of the substrates to undergo an enantioselective indole C3-nucleophilic addition. The generated intermediates D′ rapidly underwent an isomerization to give final products 118.
N group of 117, thus activating both of the substrates to undergo an enantioselective indole C3-nucleophilic addition. The generated intermediates D′ rapidly underwent an isomerization to give final products 118.
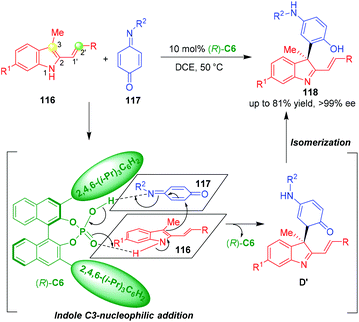 | ||
| Scheme 25 Organo-CADA reaction of 3-methyl-2-vinylindoles with quinone monoimides by Shi and coworkers.49 | ||
4. Organo-CADA reactions of C3,C2-substituted indoles
4.1 Organo-CADA cycloadditions of C3,C2-substituted indoles
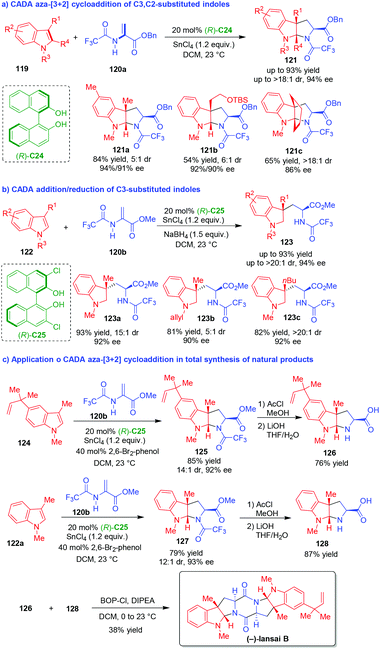 | ||
| Scheme 26 CADA reactions of C3,C2-substituted indoles and the application in total synthesis of natural products by Reisman and coworkers.51–53 | ||
More importantly, this methodology was conveniently used in the total synthesis of natural alkaloids including (−)-lansai B, (+)-nocardioazines A and B.53 As exemplified by the synthesis of (−)-lansai B (Scheme 26c), the CADA aza-[3 + 2] cycloaddition of C3-substituted indole 124 with 2-amidoacrylate 120b afforded pyrroloindoline 125 in a high yield, good diastereoselectivity and excellent enantioselectivity. The subsequent cleavage of the TFA group in compound 125, followed by hydrolysis of the methyl ester with LiOH, led to the generation of compound 126. Accordingly, compound 122a underwent similar transformations to give compound 128via the formation of 127. Finally, the condensation of compounds 126 and 128 with BOPCl accomplished the total synthesis of (−)-lansai B.
In 2018, Tan and coworkers established an organo-CADA aza-[3 + 2] cycloaddition of C3,C2-substituted indoles 129 with azonaphthalenes 130 under the catalysis of CPA (R)-C12, which constructed enantioenriched pyrroloindole skeletons 131 bearing two contiguous quaternary stereogenic centers in high yields and excellent stereoselectivities (Scheme 27a).54 It's worth-noting that the azo group in substrates 130 played an important role as a directing and activating group in this reaction. Additionally, the different R1 an R2 groups of C3,C2-substituted indoles 129 were crucial to control the chemoselectivity of the reaction because axially chiral arylindole frameworks were constructed instead of the pyrroloindole skeletons in other cases. In the suggested reaction pathway and activation mode (Scheme 27b), CPA (R)-C12 acted as a bifunctional catalyst to form two hydrogen bonds with both substrates, thus facilitating an enantioselective 1,4-addition between them to generate intermediates E′, which underwent an rearomatization of the phenyl ring and a subsequent intramolecular cyclization to complete the aza-[3 + 2] cycloaddition.
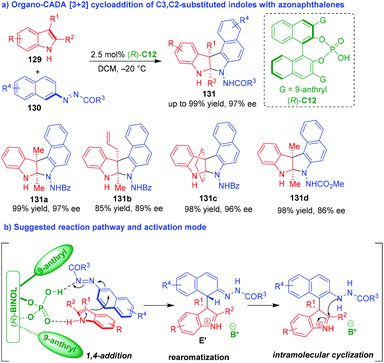 | ||
| Scheme 27 Organo-CADA aza-[3 + 2] cycloaddition of C3,C2-substituted indoles with azonaphthalenes by Tan and coworkers.54 | ||
Very recently, Lu and coworkers discovered azoalkenes 132 could act as suitable carbon–carbon–nitrogen (CCN) building blocks in organo-CADA aza-[3 + 2] cycloadditions with C3,C2-substituted indoles 129 in the presence of CPA (R)-C6 owing to the hydrazine-enamine tautomerization of azoalkenes 132, which delivered optically pure pyrroloindolines 133 in excellent yields and perfect enantioselectivities (Scheme 28a).55 The activation mode of CPA (R)-C6 to the substrates was still a dual activation mode via hydrogen-bonding interactions (Scheme 28b), which promoted the enantioselective reaction sequence of 1,4-addition/tautomerization/intramolecular cyclization to obtain enantioenriched pyrroloindolines 133.
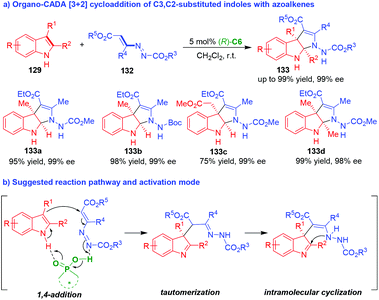 | ||
| Scheme 28 Organo-CADA aza-[3 + 2] cycloaddition of C3,C2-substituted indoles with azoalkenes by Lu and coworkers.55 | ||
Compared with rapidly developed organo-CADA aza-[3 + 2] cycloaddition of C3,C2-substituted indoles, the corresponding oxa-[3 + 2] cycloadditions are rather underdeveloped, which might be ascribed to the lack of suitable oxygen-containing three-atom building blocks. In 2014, Zhang and coworkers discovered that quinone monoimines 117 could act as competent oxygen-containing three-atom building blocks in CPA (R)-C6-catalyzed dearomative oxa-[3 + 2] cycloadditions of C3,C2-substituted indoles 129, constructing benzofuroindoline frameworks 134 in moderate to good yields and excellent enantioselectivities (Scheme 29a).56 In the suggested reaction pathway, (R)-C6 simultaneously activated both 129 and 117via hydrogen-bonding interactions, thus promoting an enantioselective 1,4-addition between them to give intermediates F′, which rapidly underwent aromatization to generate intermediates G′. At last, the intramolecular cyclization of intermediates G′ gave rise to benzofuroindolines 134.
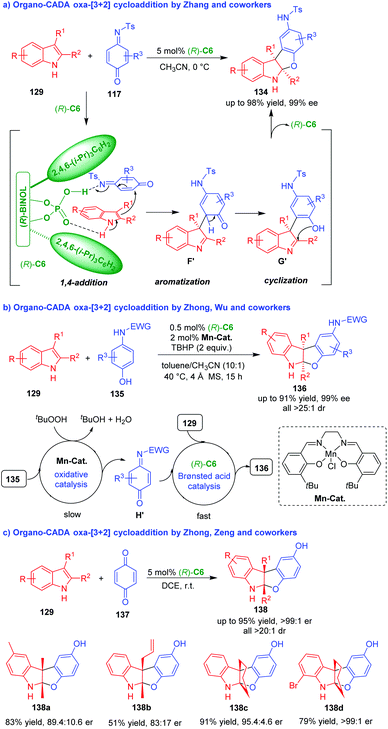 | ||
| Scheme 29 Organo-CADA oxa-[3 + 2] cycloaddition of C3,C2-substituted indoles with quinone derivatives.56–58 | ||
In 2019, Zhong, Wu and coworkers employed the strategy of Mn(III)/Brønsted acid relay catalysis in the asymmetric dearomative oxa-[3 + 2] cycloaddition of C3,C2-substituted indoles 129 with aminophenols 135 in the presence of Mn-complex and CPA (R)-C6 by using TBHP as an oxidant, which offered benzofuroindolines 136 in good yields and high stereoselectivities (Scheme 29b).57 There are two catalytic cycles in the reaction process. One is oxidative catalysis of Mn-catalyst to convert aminophenols 135 into quinone monoamine intermediates H′, which is a slow step. Another is chiral Brønsted acid catalysis of (R)-C6 to facilitate the [3 + 2] cycloadditions of C3,C2-substituted indoles 129 with intermediates H′, which is a fast step. So, different from Zhang's method,56 this synthetic method could directly utilize aminophenols 135 as starting substrates, which is atom-economy and step-economy.
Nearly at the same time, Zhong, Zeng and coworkers employed 1,4-quinone 137 as a suitable oxygen-containing three-atom building blocks in (R)-C6-catalyzed dearomative oxa-[3 + 2] cycloaddition of C3,C2-substituted indoles 129 under mild reaction conditions (Scheme 29c).58 This approach also constructed benzofuroindolines 138 in moderate to good yields, excellent diastereoselectivities and considerable enantioselectivities.
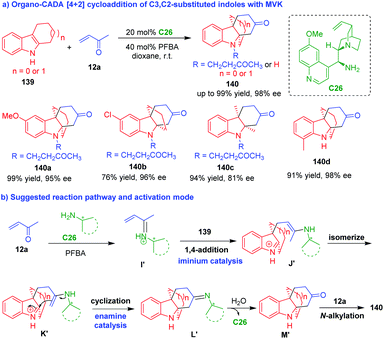 | ||
| Scheme 30 Organo-CADA [4 + 2] cycloaddition of C3,C2-substituted indoles with MVK by You and coworkers.59 | ||
The Povarov reaction is an inverse electron-demand aza-Diels–Alder reaction between electron-rich dienophiles with in situ generated aldimines, but indoles were scarcely used as dienophiles in such reactions. In 2013, Sun, Zhu and coworkers innovatively utilized a three-component Povarov reaction to realize an organo-CADA reaction of indoles (Scheme 31a). In this reaction, indoles 141 were employed as the dienophiles, and well-designed aromatic aldehydes 142 bearing an oxetane moiety were employed as reaction partners for generating aldimines with anilines 143 in the presence of CPA (R)-C7. The oxetane moiety in substrates 142 was discovered to be a superb directing group which played a crucial role in controlling both the reactivity and the enantioselectivity of the three-component Povarov reaction. Based on this design, a series of polycyclic molecules 144 with structural complexity were synthesized in overall high yields and good stereoselectivities. In addition, the evaluation of the bioactivity of some products discovered products 144d–144f were cytotoxic to human lung carcinoma (A549) and human cervical carcinoma (HeLa) cells with IC50 ranging from 15.0 to 27.5 μM (Scheme 31b). This three-component CADA [4 + 2] cycloaddition was suggested to occur in a stepwise manner (Scheme 31c). Namely, the condensation of aldehydes 142 with anilines 143 generated aldimines N′, which underwent a stepwise [4 + 2] cycloaddition with indoles 141 under the activation of (R)-C7. Notably, it is suggested that the oxetane moiety might serve as a hydrogen-bonding acceptor to form a hydrogen bond with (R)-C7 in the reaction process, thus controlling the reactivity and the enantioselectivity of the reaction.
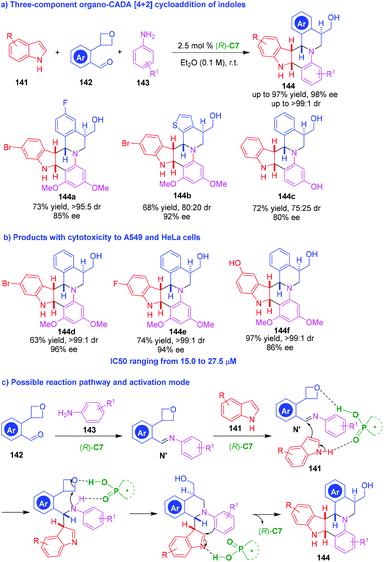 | ||
| Scheme 31 Three-component organo-CADA [4 + 2] cycloaddition of indoles by Sun, Zhu and coworkers.60 | ||
Normally, C3,C2-substituted indoles act as two-carbon (2C) building blocks in [2 + n] cycloaddition. In 2013, Wu and coworkers utilized C3,C2-substituted indoles 145 with a unique structure as three-carbon (3C) building blocks in formal [3 + 3] cycloaddition (Scheme 32a).61 In this organo-CADA formal [3 + 3] cycloaddition, acrolein 2 was utilized as another 3C reaction partner, and the reaction in the presence of chiral primary amine catalyst C26 smoothly afforded tricyclic hydrocarbazoles 146 in high yields and excellent enantioselectivities. This reaction occurred via a cascade sequence of 1,4-addition/isomerization/intramolecular cyclization/dehydration, which was enabled by chiral iminium catalysis.
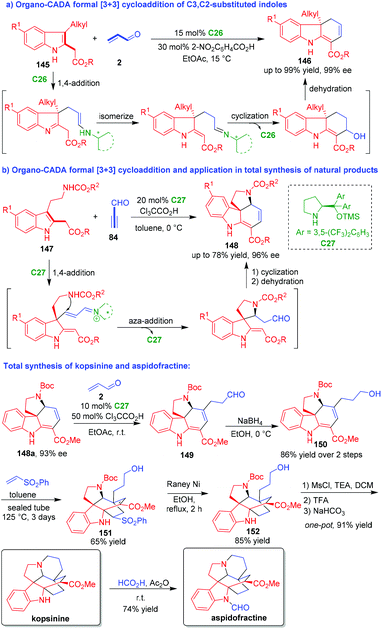 | ||
| Scheme 32 Organo-CADA formal [3 + 3] cycloadditions of C3,C2-substituted indoles by Wu and coworkers.61–63 | ||
Shortly after, the same group developed another organo-CADA formal [3 + 3] cycloaddition and realized its application in total synthesis of natural products (Scheme 32b).62 They utilized tryptamine-derived C3,C2-substituted indoles 147 as 3C building blocks to react with propynal 84 in the presence of chiral amine catalyst C27, which constructed tetracyclic frameworks 148 in moderate yields and high enantioselectivities via a cascade process. More importantly, they employed this methodology in the total synthesis of kopsinine and aspidofractine. The Michael addition of 148a with 93% ee to acrolein 2 in the presence of C27 afforded aldehyde 149, which was reduced into alcohol 150. Then, the Diels–Alder reaction of compound 150 with vinyl phenylsulfone generated bridged pentacyclic compound 151. The sulfone moiety of compound 151 was removed by the action of RANEY® Ni to give compound 152. Subsequently, compound 152 was subjected to the mesylation of the OH group and the removal of the N-Boc group, thus facilitating an intramolecular cyclization to accomplish the synthesis of kopsinine. Finally, the N-formylation of kopsinine gave rise to another natural product, aspidofractine.
Additionally, they extended this methodology to organo-CADA formal [3 + 3] cycloadditions of tryptamine-derived 2-vinylindoles with propynal under the catalysis of chiral imidazolidinone catalyst, which also constructed tetracyclic frameworks similar to 148.63
4.2 Organo-CADA additions of C3,C2-substituted indoles
Organo-CADA addition of C3,C2-substituted indoles with electrophiles is the most convenient method for the synthesis of enantioenriched indolenines. So, chemists have employed different electrophiles to react with C3,C2-substituted indoles under organocatalysis. In 2014, Shi and coworkers established two organocatalytic asymmetric arylative dearomatizations of C3,C2-substituted indoles 129 with quinone imine ketals (QIKs) 37 under the catalysis of CPA (R)-C6, which synthesized two series of optically pure indolenines 153 and 155 in high yields and excellent stereoselectivities (Scheme 33a).64 The two CADA reactions occurred via a tandem process. As illustrated in Scheme 33b, (R)-C6 activated both substrates 129 and 37 at the same time via forming hydrogen bonds, which facilitated an enantioselective 1,4-addition between them to give intermediates O′. Then, intermediates O′ rapidly underwent alcohol elimination to accomplish the first CADA reaction and generate indolenines 153. In the second CADA reaction, the addition of Hantzsch ester (HEH) 154a led to a stereoselective transfer hydrogenation between HEH 154a and indolenines 153 by the activation of CPA (R)-C6, thus affording indolines 155 in excellent enantio- and diastereoselectivities.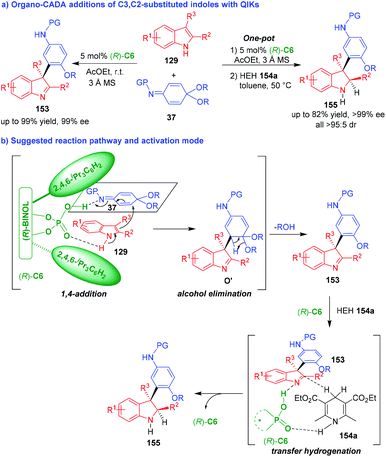 | ||
| Scheme 33 Organo-CADA addition of C3,C2-substituted indoles with QIKs by Shi and coworkers.64 | ||
Nearly at the same time, Bandini and coworkers utilized allenamides 156 as competent electrophiles to perform organo-CADA addition with C3,C2-substituted indoles 129 in the presence of (S)-C28, which generated a series of indolenines 157 in moderate to good yields and high enantioselectivities (Scheme 34a).65 In addition, they also established a cascade sequence of dearomatization/hydrogen transfer by adding HEH 154b to the reaction system under the catalysis of (R)-C6, which delivered indolines 158 in moderate yields and good stereoselectivities. The authors suggested two possible activation modes (Scheme 34b). One is noncovalent activation of CPA to allenamides via forming a hydrogen bond; another is covalent activation of CPA to allenamides via forming a covalent bond. To find out the more possible activation mode, Bandini, Miscione and coworkers carried out density functional theory (DFT) calculations and ESI-MS analysis to investigate the reaction mechanism, and it was discovered that allenamides formed adducts with CPA through a proton transfer and generated a covalent bond at the beginning of the reaction.19
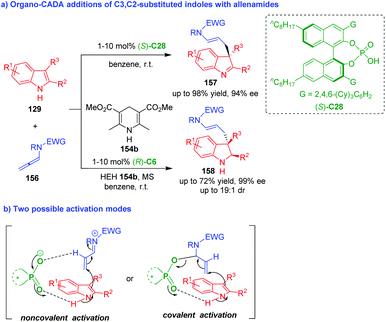 | ||
| Scheme 34 Organo-CADA addition of C3,C2-substituted indoles with allenamides by Bandini and coworkers.65 | ||
In 2014, Wu and coworkers realized an organo-CADA addition of indoloazepines 159 by using propargyl aldehydes or ketone 160 as electrophiles in the presence of the MacMillan's catalyst C29, affording C3-alkenyl-substituted indolinoazepines 161 in generally good yields and high enantioselectivities (Scheme 35).66 Notably, apart from propargyl aldehydes, propargyl ketone could also participate in the reaction to give product 161f in a high enantioselectivity albeit with a low yield. In the suggested activation mode, propargyl aldehydes or ketone 160 were activated by catalyst C29 to generate chiral alkynyl iminium intermediates, which were readily attacked by indoloazepines 159 from the terminal position of the alkynyl group, thus initiating the CADA addition.
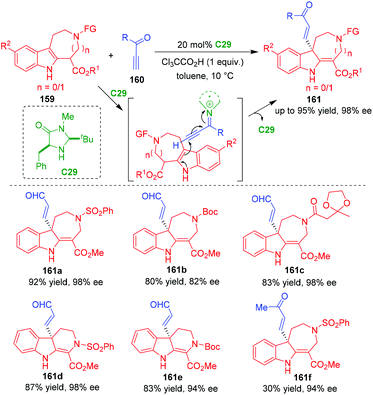 | ||
| Scheme 35 Organo-CADA addition of indoloazepines with propargyl aldehydes or ketone by Wu and coworkers.66 | ||
Recently, Wang, Sun and coworkers employed β,γ-alkynyl-α-imino esters 162 as electrophiles to react with C3,C2-substituted indoles 129 in the presence of CPA (S)-C30, thus realizing an organo-CADA addition of C3,C2-substituted indoles (Scheme 36).67 More importantly, this dearomative reaction occurred with a selectivity of γ-addition, thus generating products 163 bearing a quaternary stereogenic center with central chirality and a moiety of tetrasubstituted α-aminoallenoate with axial chirality. In fact, the simultaneous construction of two elements of chirality has become a hot topic in catalytic asymmetric synthesis.68,69 So, this approach has not only contributed to the research field of CADA, but also added a good example for simultaneously controlling two different elements of stereogenicity. Moreover, the authors performed DFT calculations to investigate the possible activation mode. They discovered that CPA still acted as a bifunctional catalyst to activate both of the two substrates via hydrogen-bonding interactions, thus promoting the addition of 129 to the γ-position of 162 and controlling the stereoselectivity via steric effect and π–π interaction between the catalyst and the substrates.
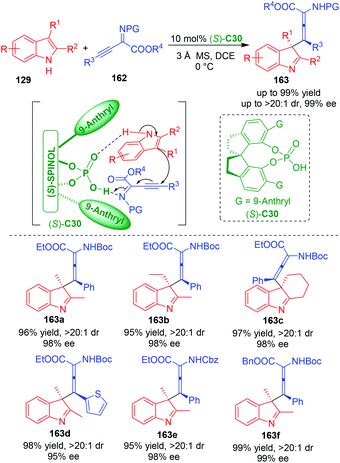 | ||
| Scheme 36 Organo-CADA addition of C3,C2-substituted indoles with β,γ-alkynyl-α-imino esters by Wang, Sun and coworkers.67 | ||
4.3 Organo-CADA reductions and oxidations of C3,C2-substituted indoles
In 2011, Chen, Sun and coworkers realized an organo-CADA reduction of C3,C2-substituted indoles 164 by trichlorosilane in the presence of chiral Lewis base C31 or C32, which afforded enantioenriched indolines 165 in high yields, good enantioselectivities and exclusive diastereoselectivity (Scheme 37a).70 This reaction took advantage of the combined catalysis of an achiral Brønsted acid (B–H) and a chiral Lewis base (L–B*). Namely, the C3-protonation of indoles 164 in the presence of B–H (in situ generated from water and trichlorosilane) would give rise to electrophilic indolenium ions. The indolenium intermediates could be attacked by HSiCl3 assisted by L–B*, which was followed by a hydrogen transfer to give final products 165. This reaction opened a new avenue for direct CADA reduction of indoles under organocatalysis.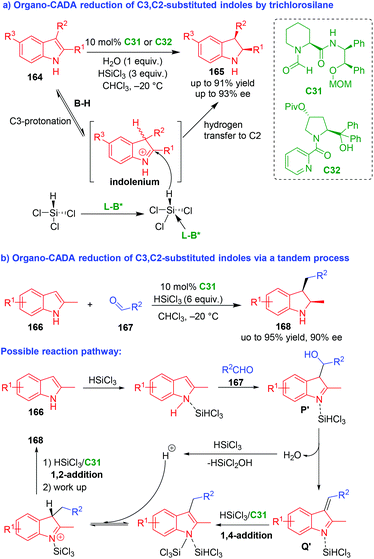 | ||
| Scheme 37 Organo-CADA reduction of C3,C2-substituted indoles by Chen, Sun, Wang and coworkers.70,71 | ||
Three years later, Sun, Wang and coworkers expanded the application of this strategy to organo-CADA reduction of C3,C2-substituted indoles via a tandem process (Scheme 37b).71 In detail, the three-component reaction of 2-methylindole 166, aldehydes 167 and trichlorosilane in the presence of chiral Lewis base C31 offered 2-methyl-3-alkylindolines 168 in high yields and good stereoselectivities. In the possible reaction pathway, 2-methylindole 166 was activated by trichlorosilane and underwent an addition reaction with aldehydes 167 to form 3-indolylmethanol analogous P′, which were readily transformed into vinyl imine intermediates Q′ after dehydration. Subsequently, in the presence of C31, intermediates Q′ underwent tandem process of 1,4-addition/1,2-addition with trichlorosilane to give products 168 after work up.
In 2020, Song, Yu and coworkers established an organo-CADA reduction of C2-substituted indoles 169 in the presence of catecholborane 170, water and CPA (S)-C33, which generated C2-substituted indolines 171 in moderate to good yields and high enantioselectivities (Scheme 38).72 In this reaction, the authors suggested that a new chiral B–H was generated in situ from CPA boron complex and water, whose acidity is higher than TsOH estimated by DFT calculations. Additionally, they performed DFT calculations on the possible reaction pathways and activation mode of the new chiral B–H on the substrate. In the key transition state leading to the generation of the chiral center, it is suggested that the new chiral B–H formed a hydrogen-bonding interaction with the NH group of the iminium intermediate, thus facilitating an enantioselective hydrogen transfer to give optically pure product. Moreover, several C2-alkyl-substituted indoles 169 could also undergo the organo-CADA reduction in the presence of CPA (S)-C8, which gave rise to indolines 171e–171g bearing bulky C2-substituents in moderate yields and considerable enantioselectivities.
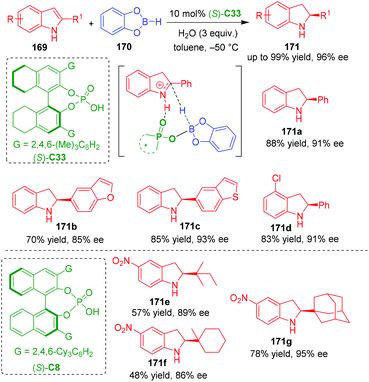 | ||
| Scheme 38 Organo-CADA reduction of C2-substituted indoles by Song, Yu and coworkers.72 | ||
In contrast to reduction reactions, catalytic asymmetric oxidation of indole derivatives is also a method for realizing the CADA reactions. In 2018, Jiang, Zhao and coworkers established an organo-CADA reaction of C3,C2-substituted indoles 172via a cascade reaction involving aerobic oxidation and semipinacol rearrangement under visible-light-driven cooperative catalysis of CPA (S)-C34 and organophotoredox catalyst DPZ (dicyanopyrazine-derived chromophore),73 which was developed by their group.74 By this approach, chiral oxindole derivatives 173 were obtained in high yields and moderate to good enantioselectivities (Scheme 39). Based on the control experiments, the authors suggested that the first step of aerobic oxidation would generate a chiral intermediate of 3-hydroxy indolenine R′, which acted as a chiral promoter for the second step of semipinacol rearrangement.
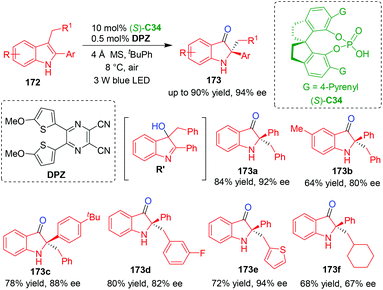 | ||
| Scheme 39 Organo-CADA oxidation of C3,C2-substituted indoles by Jiang, Zhao and coworkers.73 | ||
In 2019, Zhang and coworkers reported an organo-CADA oxidation of C2-substituted indoles 169via the reaction with aldehydes or ketones 174 and TEMPO oxoammonium salt in the presence of L-proline C35, which provided oxindole derivatives 175 bearing a C2-quaternary stereogenic center in high yields and excellent stereoselectivities (Scheme 40).75 Notably, this reaction was not only applicable to C2-aryl indoles 169, but also to C2-alkyl indoles. In the suggested reaction mechanism, C2-substituted indoles 169 reacted with TEMPO oxoammonium to give a complex, which rapidly transformed into oxindol-1-ium intermediates S’ through an electron-transfer process. Then, intermediates S’ reacted with water to give 2-hydroxyloxindoles T′. In the proposed transition state (TS-1), L-proline C35 acted as a bifunctional catalyst, which not only activated aldehydes or ketones 174via enamine catalysis but also activated oxindol-1-ium intermediates via hydrogen-bonding catalysis, thus facilitating a stereoselective addition reaction between the two reaction partners to give products 175 after hydrolysis.
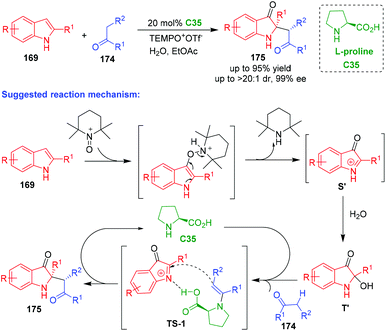 | ||
| Scheme 40 Organo-CADA oxidation of C2-substituted indoles by Zhang and coworkers.75 | ||
5. Organo-CADA reactions of 3-nitroindoles
Normally, C3- and/or C2-substituted indoles are electron-rich reactants in organo-CADA reactions. In sharp contrast, electron-poor indole derivatives have scarcely been utilized in organo-CADA reactions. In recent years, 3-nitroindoles have been utilized as electron-poor indole derivatives in organo-CADA annulations and cycloadditions. Although Chataigner and coworkers reported a CADA [4 + 2] cycloaddition of 3-nitroindole with electron-rich alkenes under the catalysis of a chiral thiourea catalyst in 2015,76 highly enantioselective reactions of 3-nitroindoles were not achieved until Yuan's group established a [3 + 2] annulation of 3-nitroindoles 176 in the same year (Scheme 41a).77 They utilized 3-isothiocyanato oxindoles 177 as three-atom reaction partners to undergo an organo-CADA [3 + 2] annulation with 3-nitroindoles 176 in the presence of chiral bifunctional catalyst C36, which offered indoline-based spirooxindoles 178 bearing multiple chiral centers in high yields and excellent stereoselectivities. In the suggested activation mode, substrates 177 were activated by the tertiary amine moiety of C36 to form enolates, and the nitro group of 3-nitroindoles 176 was activated by the NH group of C36via hydrogen-bonding interaction, thus facilitating a stereoselective addition of enolates to 176 and a subsequent cyclization to accomplish the [3 + 2] annulation.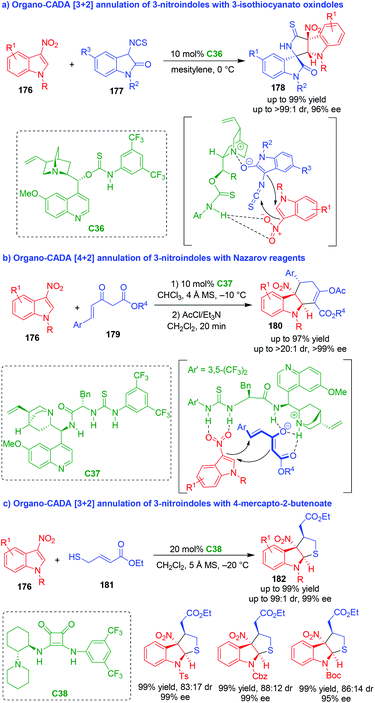 | ||
| Scheme 41 Organo-CADA [2 + n] annulations of 3-nitroindoles by Yuan's group.77–79 | ||
In 2017, the same group utilized Nazarov reagents 179 as four-atom reaction partners to undergo an organo-CADA [4 + 2] annulation with 3-nitroindoles 176 in the presence of chiral thiourea-tertiary amine catalyst C37, constructing hydrocarbazole frameworks 180 in good yields, high diastereo- and enantioselectivity (Scheme 41b).78 In the possible transition state, Nazarov reagents 179 were activated by the tertiary amine moiety of C37 to form enolates, and the nitro group of 3-nitroindoles 176 was activated by the thiourea functionality of C37via forming two hydrogen bonds. Then, the enolates of Nazarov reagents 179 attacked the C2-position of 3-nitroindoles 176 followed by an intramolecular cyclization to realize the enantioselective [4 + 2] annulation.
Recently, this group also developed organo-CADA [3 + 2] annulation of 3-nitroindoles 176 with ethyl 4-mercapto-2-butenoate 181 under the catalysis of chiral squaramide-tertiary amine C38, constructing tetrahydrothiophene-fused indoline skeletons 182 in high yields, moderate diastereoselectivities and excellent enantioselectivities (Scheme 41c).79 It should be noted that they also utilized 3-nitrobenzothiophenes in the [3 + 2] annulation with 181, which realized the CADA reaction of 3-nitrobenzothiophenes.
In 2019, nearly at the same time, the two groups of Zhang80 and Lu81 independently accomplished organo-CADA [3 + 2] cycloaddition of 3-nitroindoles 176 with allenoates 183 under the catalysis of chiral phosphine catalysts C39 and C40, which were respectively developed by their own group (Schemes 42 and 43). By these two approaches, a wide range of cyclopentaindoline scaffolds 184 were constructed in uniformly high yields and excellent enantioselectivities.
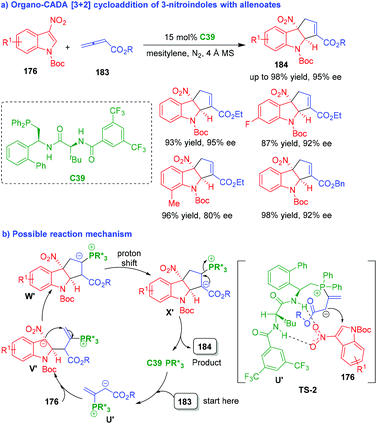 | ||
| Scheme 42 Organo-CADA [3 + 2] cycloaddition of 3-nitroindoles with allenoates by Zhang's group.80 | ||
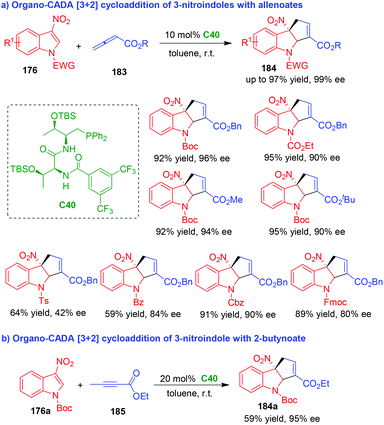 | ||
| Scheme 43 Organo-CADA [3 + 2] cycloaddition of 3-nitroindoles with allenoates by Lu's group.81 | ||
The two approaches have a similar reaction mechanism. As exemplified by C39-catalyzed CADA [3 + 2] cycloaddition (Scheme 42b),80 the addition of C39 to allenoates 183 generated phosphonium intermediates U′, which attacked the C2-position of 3-nitroindoles 176via TS-2 to form intermediates V′. In TS-2, a possible activation mode of chiral phosphine C39 to the substrates was suggested, which played an important role in controlling the enantioselectivity of the reaction. Then, intermediates V′ underwent an intramolecular cyclization to give intermediates W′, which further underwent proton shift to generate intermediates X′. Finally, intermediates X′ underwent elimination to give products 184 and regenerate catalyst C39.
Notably, in the work of Lu's group, the N-protecting group of 3-nitroindoles 176 could be extended from Boc to other electron-withdrawing groups such as Ts, Bz, Fmoc, Cbz and ester groups (Scheme 43a).81 In addition, 2-butynoate 185 could serve as a suitable reaction partner in the CADA [3 + 2] cycloaddition with 3-nitroindole 176a, which afforded product 184a in a moderate yield with an excellent enantioselectivity (Scheme 43b).
It should be noted, in the work of Zhang's group, organo-CADA [3 + 2] cycloaddition of 2-nitrobenzofurans with Morita–Baylis–Hillman (MBH) carbonates have also been established under chiral phosphine catalysis, which constructed enantioenriched cyclopentadihydrobenzofuran scaffolds in excellent results.80 Moreover, Shi's group also reported a similar CADA [3 + 2] cycloaddition of 3-nitroindole in the presence of commercially available chiral phosphines, which gave rise to cyclopentaindoline product in a moderate enantioselectivity.82
Apart from the above mentioned three-atom building blocks, MBH carbonates could also serve as suitable three-carbon reaction partners in organo-CADA [3 + 2] annulations with 3-nitroindoles. In 2016, Chen and coworkers reported the first example of organo-CADA [3 + 2] annulation of 3-nitroindole 176b with isatin-derived MBH carbonate 186a under the catalysis of chiral DMAP-type Lewis base catalyst C41, generating cyclopentaindoline-based spirooxindole 187a in moderate enantioselectivity (Scheme 44a).83 In 2020, to solve the issue of controlling the enantioselectivity of the reaction, Tian, Lin, Ge, Gao and coworkers utilized a chiral DMAP-thiourea C42 as a bifunctional catalyst to enable a highly enantioselective CADA [3 + 2] annulation of 3-nitroindoles 176 with MBH carbonates 186, which synthesized a series of cyclopentaindoline-based spirooxindoles 187 in high yields and excellent stereoselectivities (Scheme 44b).84 Furthermore, preliminary biological evaluation discovered that product 187b displayed promising inhibition activity against pancreatic lipase.
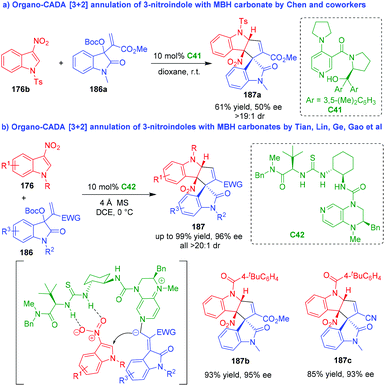 | ||
| Scheme 44 Organo-CADA [3 + 2] annulation of 3-nitroindoles with MBH carbonates.83,84 | ||
6. Organo-CADA reactions of other substituted indoles
In addition to the above mentioned organo-CADA reactions of indole derivatives, some other substituted indoles bearing well-designed functional groups could also undergo organo-CADA reactions, particularly spirocyclizations, to construct enantioenriched spiro-indole-based frameworks. In 2011, You and coworkers realized an organo-CADA spirocyclization of C3-functionalized indoles 188 in the presence of chiral primary amine C26 and 2-nitrobenzoic acid, which constructed tetracyclic indoline-containing skeletons 189 in generally high yields, good diastereoselectivities and excellent enantioselectivities (Scheme 45a).85 In the proposed reaction pathway and catalytic cycle (Scheme 45b), this CADA reaction occurred via a cascade process. Initially, C3-functionalized indoles 188 were activated by chiral primary amine C26 to generate iminium intermediates Y′, which rapidly underwent an enantioselective intramolecular 1,4-addition via iminium catalysis to give spirocyclic intermediates Z′. Subsequently, Z′ isomerized into A′′, which underwent an intramolecular Mannich reaction via enamine catalysis to give final tetracyclic products 189 after hydrolysis to regenerate C26.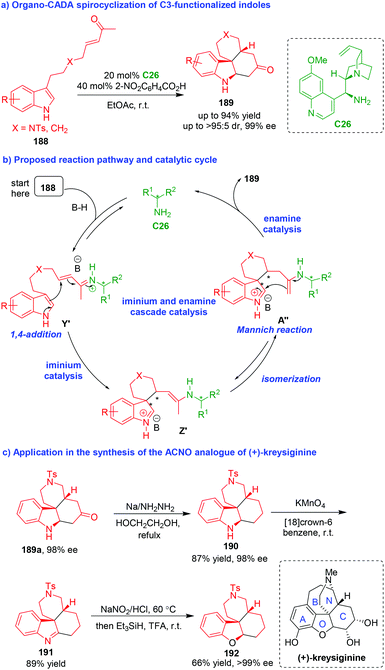 | ||
| Scheme 45 Organo-CADA spirocyclization of C3-functionalized indoles via cascade catalysis by You and coworkers.85 | ||
More importantly, this CADA methodology could be applied in the synthesis of ACNO analogue 192 of the natural product (+)-kreysiginine (Scheme 45c). In brief, compound 189a with 98% ee underwent Huang Minlon reduction to convert the ketone group into methylene group. Then, the oxidation of compound 190 afforded compound 191 bearing an imine group. Finally, the oxidation of 191 with NaNO2 and subsequent reduction with Et3SiH gave rise to compound 192 as an analogue of (+)-kreysiginine.
Apart from intramolecular reactions, intermolecular reactions could also provide opportunities for CADA spirocyclizations of indole derivatives. In 2012, Zhao, Wu, Cao and coworkers reported an organo-CADA spirocyclization of indole derivatives 193 bearing a C3-ketoamide group with α,β-unsaturated aldehydes 194 in the presence of chiral secondary amine C27, which offered spiro-indolenines 195 in good yields, moderate diastereoselectivities and excellent enantioselectivities (Scheme 46a).86 The reaction involved a cascade process, which started with the activation of aldehydes 194 by C27 to generate chiral iminium intermediates. Then, a stereoselective formal [3 + 3] cyclization occurred between chiral iminium intermediates and indole derivatives 193 to form six-membered intermediates B′′, which transformed into another iminium intermediates C′′ with the action of TFA. Finally, an intramolecular dearomative cyclization occurred, which realized the spirocyclization and afforded products 195.
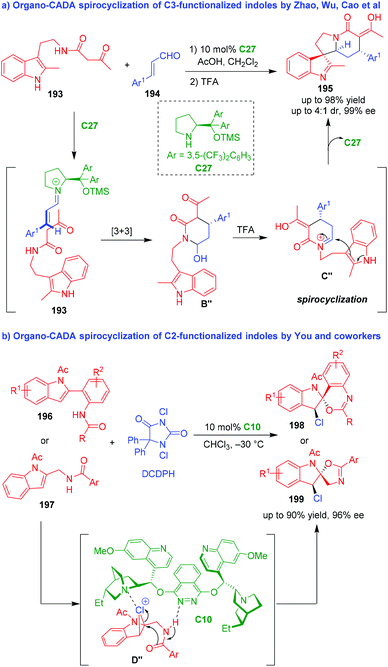 | ||
| Scheme 46 Organo-CADA intermolecular spirocyclizations of functionalized indoles.86,87 | ||
Another organo-CADA intramolecular spirocyclization of functionalized indoles was established by You and coworkers in 2013 (Scheme 46b).87 They applied the strategy of chlorocyclization in the CADA reaction of C2-functionalized indoles 196 or 197 by using DCDPH as a chlorinating reagent in the presence of (DHQD)2PHAL C10, which gave rise to spiro-indoline derivatives 198 or 199 in high yields and excellent enantioselectivities. In the suggested reaction pathway and activation mode, the chlorination of C2-functionalized indoles such as 197 with DCDPH would generate three-membered cyclic chloronium species D′′, which could be activated by C10via forming hydrogen bonds. Thus, intermediates D′′ underwent an enantioselective intramolecular nucleophilic addition and ring-opening reaction to generate spiro-products 199.
In addition to chiral amine catalysts, chiral phosphoric acids (CPAs) have proven to be suitable organocatalysts, which enabled a series of CADA spirocyclizations of C3-functionalized indoles (Scheme 47).88–90 In 2017, You and coworkers established an organo-CADA spirocyclization of indole derivatives 200 under the catalysis of CPA (S)-C43, generating spiro-indolenines 201 in good yields and moderate to high enantioselectivities (Scheme 47a).88 In the suggested activation mode, CPA (S)-C43 simultaneously activated both the NH group of the indole ring and the carbonyl group of the enone moiety, which promoted an enantioselective intramolecular Michael addition between the indole C3-position and the enone moiety, thus realizing the dearomative spirocyclization.
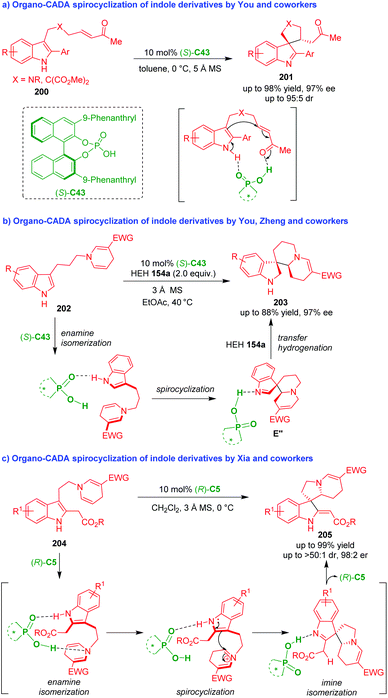 | ||
| Scheme 47 Organo-CADA spirocyclizations of C3-functionalized indoles via CPA catalysis.88–90 | ||
Based on this reaction, one year later, the same group devised a class of C3-functionalized indoles 202 bearing a dihydropyridine moiety to accomplish organo-CADA spirocyclization (Scheme 47b).89 In the presence of CPA (S)-C43, C3-functionalized indoles 202 underwent an enantioselective spirocyclization to give chiral spiro-indolenine intermediates E′′, which further underwent transfer hydrogenation with HEH 154a, thus affording spiroindolines 203 in good yields and excellent enantioselectivities. Furthermore, the authors performed DFT calculations to give some insights into the reaction mechanism and the origin of stereochemistry.
Very recently, Xia and coworkers also reported an organo-CADA spirocyclization of indole derivatives 204 bearing both a C3-dihydropyridine moiety and a C2-ester group, which delivered enantioenriched spiroindolines 205 with excellent results under the catalysis of CPA (R)-C5 (Scheme 47c).90 The reaction process was similar to You's approach,89 which involved an enamine isomerization/spirocyclization/dearomatization cascade. But the most important difference is that Xia's approach utilized a C2-ester group to facilitate an imine isomerization in the last step, thus stabilizing products 205 after spirocyclization. So, the C2-ester group in indole derivatives 204 played a crucial role in this CADA spirocyclization reaction.
7. Conclusions and outlook
In summary, organo-CADA reactions of indole derivatives have developed rapidly in recent decades, which provided efficient and enantioselective approaches for accessing optically pure heterocycles containing indoline, indolenine and other related cores, which are widely found in natural products and bioactive molecules. However, there are still some challenging issues to be solved in this research field. These issues include but are not limited to the following. (1) The organo-CADA reaction types of indole derivatives are confined to intramolecular cyclization, addition, [3 + 2], [4 + 2] and [3 + 3] cycloadditions, which resulted in the limitation of the constructed scaffolds, mainly including indoline, indolenine and five-membered-ring or six-membered-ring fused indolines. In contrast, other organo-CADA reaction types such as [4 + 3], [4 + 4], [5 + 2] cycloadditions of indole derivatives for the construction of indole-fused medium-size rings have not yet been established, which require specific design of indole-based building blocks and their involved CADA reactions. (2) In the reaction pathways of organo-CADA reactions of indole derivatives, the formation of imine, iminium, vinyl iminium and other ion-type intermediates is commonly suggested. However, radical intermediates have scarcely been involved in the reaction pathways in spite of the fact that the catalytic asymmetric radical chemistry has become an important area. Although controlling the enantioselectivity in such reactions remains a great challenge, it is highly valuable to develop radical-involved CADA reactions of indole derivatives, perhaps by the combination of asymmetric organocatalysis with visible light photoredox catalysis and electrochemical synthesis. (3) Although the frameworks of indole, indoline and indolenine exist in lots of natural alkaloids, the application of organo-CADA reactions of indole derivatives in the total synthesis of natural products are still rather limited, which only included several organo-CADA reactions of tryptamines, tryptamine-derived 2-vinylindoles and C3,C2-substituted indoles. The power and potential of organo-CADA reactions of indole derivatives in the total synthesis of natural products should be further explored and demonstrated. Therefore, great efforts are highly needed to address these challenging issues, and we have enough reason to believe that this research field will rise to a new level with the persistent endeavors of organic chemists.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
We are grateful for financial support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (21772069 and 21831007), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, and Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX20_2235).Notes and references
- For some reviews: (a) A. J. Kochanowska-Karamyan and M. T. Hamann, Marine indole alkaloids: potential new drug leads for the control of depression and anxiety, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 4489 CrossRef CAS; (b) Y. Wan, Y. Li, C. Yan, M. Yan and Z. Tang, Indole: a privileged scaffold for the design of anti-cancer agents, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2019, 183, 111691 CrossRef CAS.
- For some reviews: (a) R. Dalpozzo, Strategies for the asymmetric functionalization of indoles: an update, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 742 RSC; (b) J.-B. Chen and Y.-X. Jia, Recent progress in transition-metal-catalyzed enantioselective indole functionalizations, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2017, 15, 3550 RSC; (c) G. Huang and B. Yin, Recent developments in transition-metal-catalyzed dearomative cyclizations of indoles as dipolarophiles for the construction of indolines, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2019, 361, 405 CrossRef CAS; (d) Y.-C. Zhang, F. Jiang and F. Shi, Organocatalytic asymmetric synthesis of indole-based chiral heterocycles: strategies, reactions, and outreach, Acc. Chem. Res., 2020, 53, 425 CrossRef CAS; (e) T.-Z. Li, S.-J. Liu, W. Tan and F. Shi, Catalytic asymmetric construction of axially chiral indole-based frameworks: an emerging area, Chem. – Eur. J., 2020, 26 DOI:10.1002/chem.202001397.
- For some recent examples: (a) Y.-L. Zhao, Y. Wang, J. Cao, Y.-M. Liang and P.-F. Xu, Organocatalytic asymmetric Michael-Michael cascade for the construction of highly functionalized N-fused piperidinoindoline derivatives, Org. Lett., 2014, 16, 2438 CrossRef CAS; (b) W. Zhao, Z. Wang, B. Chu and J. Sun, Enantioselective formation of all-carbon quaternary stereocenters from indoles and tertiary alcohols bearing a directing group, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 1910 CrossRef CAS; (c) S. Zhu, Y.-H. Chen, Y.-B. Wang, P. Yu, S.-Y. Li, S.-H. Xiang, J.-Q. Wang, J. Xiao and B. Tan, Organocatalytic atroposelective construction of axially chiral arylquinones, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 4268 CrossRef; (d) W. Xia, Q.-J. An, S.-H. Xiang, S. Li, Y.-B. Wang and B. Tan, Chiral phosphoric acid catalyzed atroposelective C-H amination of arenes, Angew. Chem., 2020, 59, 6775 CrossRef CAS; (e) X. Li and J. Sun, Organocatalytic enantioselective synthesis of chiral allenes: remote asymmetric 1,8-addition of indole imine methides, Angew. Chem., 2020, 59, 17049 CrossRef CAS; (f) Q.-Q. Hang, S.-J. Liu, L. Yu, T.-T. Sun, Y.-C. Zhang, G.-J. Mei and F. Shi, Design and application of indole-based allylic donors for Pd-catalyzed decarboxylative allylation reactions, Chin. J. Chem., 2020, 38, 1612 Search PubMed; (g) X. Wan, M. Sun, J.-Y. Wang, L. Yu, Q. Wu, Y.-C. Zhang and F. Shi, Regio- and enantioselective ring-opening reaction of vinylcyclopropanes with indoles under cooperative catalysis, Org. Chem. Front., 2020 10.1039/D0QO00699H.
- For a book: (a) S.-L. You, Asymmetric dearomatization reactions, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2016 CrossRef. For reviews: (b) C.-X. Zhou, W. Zhang and S.-L. You, Catalytic asymmetric dearomatization reactions, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 12662 CrossRef CAS; (c) C.-X. Zhuo, C. Zheng and S.-L. You, Transition-metal-catalyzed asymmetric allylic dearomatization reactions, Acc. Chem. Res., 2014, 47, 2558 CrossRef CAS; (d) W. Sun, G. Li, L. Hong and R. Wang, Asymmetric dearomatization of phenols, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2016, 14, 2164 RSC; (e) X.-W. Liang, C. Zheng and S.-L. You, Dearomatization through halofunctionalization reactions, Chem. – Eur. J., 2016, 22, 11918 CrossRef CAS; (f) C. Zheng and S.-L. You, Catalytic asymmetric dearomatization by transition-metal catalysis: a method for transformations of aromatic compounds, Chem, 2016, 1, 830 CrossRef CAS; (g) C. Zheng and S.-L. You, Catalytic asymmetric dearomatization (CADA) reaction-enabled total synthesis of indole-based natural products, Nat. Prod. Rep., 2019, 36, 1589 RSC; (h) Z.-L. Xia, Q.-F. Xu-Xu, C. Zheng and S.-L. You, Chiral phosphoric acid-catalyzed asymmetric dearomatization reactions, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 286 RSC; (i) J. An and M. Bandini, Recent advances in the catalytic dearomatization of naphthols, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2020, 4087 CrossRef CAS.
- For some recent examples: (a) K. Du, P. Guo, Y. Chen, Z. Cao, Z. Wang and W. Tang, Enantioselective palladium-catalyzed dearomative cyclization for the efficient synthesis of terpenes and steroids, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 3033 CrossRef CAS; (b) J. Nan, J. Liu, H. Zheng, Z. Zuo, L. Hou, H. Hu, Y. Wang and X. Luan, Direct asymmetric dearomatization of 2-naphthols by scandium-catalyzed electrophilic amination, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 2356 CrossRef CAS; (c) D.-C. Wang, M.-S. Xie, H.-M. Guo, G.-R. Qu, M.-C. Zhang and S.-L. You, Enantioselective dearomative [3+2] cycloaddition reactions of benzothiazoles, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 14111 CrossRef CAS; (d) Y. Wang, C. Zheng and S.-L. You, Iridium-catalyzed asymmetric allylic dearomatization by a desymmetrization strategy, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 15093 CrossRef CAS; (e) Z.-P. Yang, R. Jiang, Q.-F. Wu, L. Huang, C. Zheng and S.-L. You, Iridium-catalyzed intramolecular asymmetric allylic dearomatization of benzene derivatives, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 16190 CrossRef CAS; (f) B. Tan, L. Bai, P. Ding, J. Liu, Y. Wang and X. Luan, Palladium-catalyzed intermolecular [4+1] spiroannulation via C(sp3)-H activation and naphthol dearomatization, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 1474 CrossRef CAS; (g) X. Mu, H. Yu, H. Peng, W. Xiong, T. Wu and W. Tang, Expedite construction of various bridged polycyclic skeletons by palladium-catalyzed dearomatization, Angew. Chem., 2020, 59, 8143 CrossRef CAS.
- For some prominent reviews: (a) K. N. Houk and B. List, Asymmetric organocatalysis, Acc. Chem. Res., 2004, 37, 487 CrossRef CAS; (b) D. W. C. MacMillan, The advent and development of organocatalysis, Nature, 2008, 455, 304 CrossRef CAS; (c) A. Dondoni and A. Massi, Asymmetric organocatalysis: from infancy to adolescence, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2008, 47, 4638 CrossRef CAS; (d) J. Alemán and S. Cabrera, Applications of asymmetric organocatalysis in medicinal chemistry, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42, 774 RSC; (e) C. M. R. Volla, I. Atodiresei and M. Rueping, Catalytic C-C bond-forming multi-component cascade or domino reactions: pushing the boundaries of complexity in asymmetric organocatalysis, Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 2390 CrossRef CAS; (f) T. Wang, X. Han, F. Zhong, W. Yao and Y. Lu, Amino acid-derived bifunctional phosphines for enantioselective transformations, Acc. Chem. Res., 2016, 49, 1369 CrossRef CAS; (g) P. Chauhan, S. Mahajan and D. Enders, Achieving molecular complexity via stereoselective multiple domino reactions promoted by a secondary amine organocatalyst, Acc. Chem. Res., 2017, 50, 2809 CrossRef CAS; (h) L. Zong and C.-H. Tan, Phase-transfer and ion-pairing catalysis of pentanidiums and bisguanidiniums, Acc. Chem. Res., 2017, 50, 842 CrossRef CAS; (i) H. Ni, W.-L. Chan and Y. Lu, Phosphine-catalyzed asymmetric organic reaction, Chem. Rev., 2018, 118, 9344 CrossRef CAS; (j) Y.-B. Wang and B. Tan, Construction of axially chiral compounds via asymmetric organocatalysis, Acc. Chem. Res., 2018, 51, 534 CrossRef CAS; (k) A. J. Metrano and S. J. Miller, Peptide-based catalysts reach the outer sphere through remote desymmetrization and atroposelectivity, Acc. Chem. Res., 2019, 52, 199 CrossRef CAS.
- For some recent examples: (a) W. Yang and J. Sun, Organocatalytic enantioselective synthesis of 1,4-dioxanes and other oxa-heterocycles by oxetane desymmetrization, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 1868 CrossRef CAS; (b) J. Zhang, P. Yu, S.-Y. Li, H. Sun, S.-H. Xiang, J. Wang, K. N. Houk and B. Tan, Asymmetric phosphoric acid-catalyzed four-component Ugi reaction, Science, 2018, 361, 1087 CrossRef CAS; (c) W.-L. Chan, X. Tang, F. Zhang, G. Quek, G.-J. Mei and Y. Lu, Phosphine-catalyzed (3+2) annulation of isoindigos with allenes: enantioselective formation of two vicinal quaternary stereogenic centers, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 6260 CrossRef CAS; (d) W. Guo, Y. Luo, H. H.-Y. Sung, I. D. Williams, P. Li and J. Sun, Chiral phosphoric acid catalyzed enantioselective synthesis of α-tertiary amino ketones from sulfonium ylides, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 14384 CrossRef CAS.
- J. F. Austin, S.-G. Kim, C. J. Sinz, W.-J. Xiao and D. W. C. MacMillan, Enantioselective organocatalytic construction of pyrroloindolines by a cascade addition-cyclization strategy: synthesis of (–)-flustramine B, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2004, 101, 5482 CrossRef CAS.
- For some reviews: (a) T. Akiyama, Stronger Brønsted acids, Chem. Rev., 2007, 107, 5744 CrossRef CAS; (b) M. Terada, Binaphthol-derived phosphoric acid as a versatile catalyst for enantioselective carbon-carbon bond forming reactions, Chem. Commun., 2008, 4097 RSC; (c) M. Terada, Chiral phosphoric acids as versatile catalysts for enantioselective transformations, Synthesis, 2010, 1929 CrossRef CAS; (d) A. Zamfir, S. Schenker, M. Freund and S. B. Tsogoeva, Chiral BINOL-derived phosphoric acids: privileged Brønsted acid organocatalysts for C-C bond formation reactions, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2010, 8, 5262 CAS; (e) J. Yu, F. Shi and L.-Z. Gong, Brønsted-acid-catalyzed asymmetric multicomponent reactions for the facile synthesis of highly enantioenriched structurally diverse nitrogenous heterocycles, Acc. Chem. Res., 2011, 44, 1156 CrossRef CAS; (f) D. Parmar, E. Sugiono, S. Raja and M. Rueping, Complete field guide to asymmetric BINOL-phosphate derived Brønsted acid and metal catalysis: history and classification by mode of activation; Brønsted acidity, hydrogen bonding, ion pairing, and metal phosphates, Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 9047 CrossRef CAS; (g) H. Wu, Y.-P. He and F. Shi, Recent advances in chiral phosphoric acid catalyzed asymmetric reactions for the synthesis of enantiopure indole derivatives, Synthesis, 2015, 47, 1990 CrossRef CAS; (h) F. E. Held, D. Grau and S. B. Tsogoeva, Enantioselective cycloaddition reactions catalyzed by BINOL-derived phosphoric acids and N-triflyl phosphoramides: recent advances, Molecules, 2015, 20, 16103 CrossRef CAS.
- For highlights: (a) L. Liu and J. Zhang, Catalytic asymmetric [4+3] cyclizations of 2-indolylmethanols with ortho-quinone methides, Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2019, 39, 3308 CrossRef; (b) B. Tan, Design and catalytic asymmetric construction of axially chiral aryl-alkene-indole frameworks, Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2020, 40, 1404 CrossRef. For recent examples: (c) Y.-N. Lu, C. Ma, J.-P. Lan, C. Zhu, Y.-J. Mao, G.-J. Mei, S. Zhang and F. Shi, Catalytic enantioselective and regioselective substitution of 2,3-indolyldimethanols with enaminones, Org. Chem. Front., 2018, 5, 2657 RSC; (d) C.-S. Wang, T.-Z. Li, S.-J. Liu, Y.-C. Zhang, S. Deng, Y. Jiao and F. Shi, Axially chiral aryl-alkene-indole framework: a nascent member of the atropisomeric family and its catalytic asymmetric construction, Chin. J. Chem., 2020, 38, 543 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Cai, C. Liu, X.-W. Liang and S.-L. You, Enantioselective construction of pyrroloindolines via chiral phosphoric acid catalyzed cascade Michael addition cyclization of tryptamines, Org. Lett., 2012, 14, 4588 CrossRef CAS.
- D.-H. Duan, Q. Yin, S.-G. Wang, Q. Gu and S.-Li You, Chiral phosphoric acid-catalyzed asymmetric cascade reaction of C(3) substituted indoles and methyl vinyl ketone, Acta Chim. Sin., 2014, 72, 1001 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Zhang and J. C. Antilla, Enantioselective construction of pyrroloindolines catalyzed by chiral phosphoric acids: total synthesis of (–)-debromoflustramine B, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 11778 CrossRef CAS.
- H. M. Nelson, S. H. Reisberg, H. P. Shunatona, J. S. Patel and F. D. Toste, Chiral anion phase transfer of aryldiazonium cations: an enantioselective synthesis of C3-diazenated pyrroloindolines, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 5600 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Li, T. Xia, L. Yao, H. Deng and X. Liao, Enantioselective and diastereoselective azocoupling/iminium-cyclizations: a unified strategy for the total syntheses of (–)-psychotriasine and (+)-pestalazine B, Chem. Sci., 2015, 6, 3599 RSC.
- F. Jiang, D. Zhao, X. Yang, F.-R. Yuan, G.-J. Mei and F. Shi, Catalyst-controlled chemoselective and enantioselective reactions of tryptophols with isatin-derived imines, ACS Catal., 2017, 7, 6984 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Ma, T. Zhang, J.-Y. Zhou, G.-J. Mei and F. Shi, Catalytic asymmetric chemodivergent arylative dearomatization of tryptophols, Chem. Commun., 2017, 53, 12124 RSC.
- S. Biswas, H. Kim, K. L. A. Cao and S. Shin, Enantioselective dearomative cyclization of homotryptamines with allenamides into indolo[2,3-b]quinolones, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2020, 362, 1841 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Giacinto, A. Bottoni, A. Garelli, G. P. Miscione and M. Bandini, Covalent or non-covalent? a mechanistic insight into the enantioselective Brønsted acid catalyzed dearomatization of indoles with allenamid, ChemCatChem, 2018, 10, 2442 CrossRef CAS.
- O. Lozano, G. Blessley, T. Martinez del Campo, A. L. Thompson, G. T. Giuffredi, M. Bettati, M. Walker, R. Borman and V. Gouverneur, Organocatalyzed enantioselective fluorocyclizations, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 8105 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Wei, Y.-Y. Wang, Y.-L. Du and L.-Z. Gong, Organocatalytic asymmetric selenofunctionalization of tryptamine for the synthesis of hexahydropyrrolo[2,3-b]indole derivatives, Beilstein J. Org. Chem., 2013, 9, 1559 CrossRef.
- Q. Cai, Q. Yin and S.-L. You, Chiral-amine-catalyzed asymmetric bromocyclization of tryptamine derivatives, Asian J. Org. Chem., 2014, 3, 408 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Yin and S.-L. You, Asymmetric chlorocyclization of indole-3-yl-benzamides for the construction of fused indolines, Org. Lett., 2014, 16, 2426 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Xie, G. Jiang, H. Liu, J. Hu, X. Pan, H. Zhang, X. Wan, Y. Lai and D. Ma, Highly enantioselective bromocyclization of tryptamines and its application in the synthesis of (–)-chimonanthine, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 12924 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Feng, G. Jiang, Z. Xia, J. Hu, X. Wan, J.-M. Gao, Y. Lai and W. Xie, Total synthesis of (–)-conolutinine, Org. Lett., 2015, 17, 4428 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Liu, G. Jiang, X. Pan, X. Wan, Y. Lai, D. Ma and W. Xie, Highly asymmetric bromocyclization of tryptophol: unexpected accelerating effect of DABCO-derived bromine complex, Org. Lett., 2014, 16, 1908 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) V. Rauniyar, A. D. Lackner, G. L. Hamilton and F. D. Toste, Asymmetric electrophilic eluorination using and anionic chiral phase-transfer catalyst, Science, 2011, 334, 1681 CrossRef CAS. For reviews on anionic chiral PTC strategy, see: (b) R. J. Phipps, G. L. Hamilton and F. D. Toste, The progression of chiral anions from concepts to applications in asymmetric catalysis, Nat. Chem., 2012, 4, 603 CrossRef CAS; (c) M. Mahlau and B. List, Asymmetric counteranion-directed catalysis: concept, definition, and applications, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 518 CrossRef CAS; (d) K. Brak and E. N. Jacobsen, Asymmetric ion-pairing catalysis, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 534 CrossRef CAS.
- X.-W. Liang, C. Liu, W. Zhang and S.-L. You, Asymmetric fluorinative dearomatization of tryptamine derivatives, Chem. Commun., 2017, 53, 5531 RSC.
- X.-W. Liang, Y. Cai and S.-L. You, Asymmetric fluorinative dearomatization of tryptophol derivatives by chiral anion phase-transfer catalysis, Chin. J. Chem., 2018, 36, 925 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Egami, R. Hotta, M. Otsubo, T. Rouno, T. Niwa, K. Yamashita and Y. Hamashima, Asymmetric dearomatizing fluoroamidation of indole derivatives with dianionic Phase-Transfer catalyst, Org. Lett., 2020, 22, 5656 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Kolundzic, M. N. Noshi, M. Tjandra, M. Movassaghi and S. J. Miller, Chemoselective and enantioselective oxidation of indoles employing aspartyl peptide catalysts, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 9104 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Han and M. Movassaghi, Concise total synthesis and stereochemical revision of all (–)-trigonoliimines, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 10768 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Han, K. C. Morrison, P. J. Hergenrother and M. Movassaghi, Total synthesis, stereochemical assignment, and biological activity of all known (–)-trigonoliimines, J. Org. Chem., 2014, 79, 473 CrossRef CAS.
- For some recent reviews: (a) F. Wang, P. Chen and G. Liu, Copper-catalyzed radical relay for asymmetric radical transformations, Acc. Chem. Res., 2018, 51, 2036 CrossRef CAS; (b) Q.-S. Gu, Z.-L. Li and X.-Y. Liu, Copper(I)-catalyzed asymmetric reactions involving radicals, Acc. Chem. Res., 2020, 53, 170 CrossRef CAS.
- E. C. Gentry, L. J. Rono, M. E. Hale, R. Matsuura and R. R. Knowles, Enantioselective synthesis of pyrroloindolines via noncovalent stabilization of indole radical cations and applications to the synthesis of alkaloid natural products, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 3394 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Liang, X. Tong, T. Li, B. Shi, H. Wang, P. Yan and C. Xia, Enantioselective radical cyclization of tryptamines by visible light-excited nitroxides, J. Org. Chem., 2018, 83, 10948 CrossRef CAS.
- For reviews: (a) M. Bandini, Electrophilicity: the “dark-side” of indole chemistry, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2013, 11, 5206 RSC; (b) G.-J. Mei and F. Shi, Indolylmethanols as reactants in catalytic asymmetric reactions, J. Org. Chem., 2017, 82, 7695 CrossRef CAS; (c) A. Cerveri and M. Bandini, Recent advances in the catalytic functionalization of “electrophilic” indoles, Chin. J. Chem., 2020, 38, 287 CrossRef CAS.
- For recent examples: (a) C. Li, H.-H. Zhang, T. Fan, Y. Shen, Q. Wu and F. Shi, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2016, 14, 6932 RSC; (b) H.-H. Zhang, C.-S. Wang, C. Li, G.-J. Mei, Y. Li and F. Shi, Design and enantioselective construction of axially chiral naphthyl-indole skeletons, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 116 CrossRef CAS; (c) Z.-Q. Zhu, Y. Shen, J.-X. Liu, J.-Y. Tao and F. Shi, Enantioselective direct α-arylation of pyrazol-5-ones with 2-indolylmethanols via organo-metal cooperative catalysis, Org. Lett., 2017, 19, 1542 CrossRef CAS; (d) M.-M. Xu, H.-Q. Wang, Y.-J. Mao, G.-J. Mei, S.-L. Wang and F. Shi, Cooperative catalysis-enabled asymmetric α-arylation of aldehydes using 2-indolylmethanols as arylation reagents, J. Org. Chem., 2018, 83, 5027 CrossRef CAS.
- Y.-Z. Cheng, Q.-R. Zhao, X. Zhang and S.-L. You, Asymmetric dearomatization of indole derivatives with N-hydroxycarbamates enabled by photoredox catalysis, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 18069 CrossRef CAS.
- For a recent review: E. Rossi, G. Abbiati and V. Pirovano, 2- and 3-Vinylindoles as 4πcomponents in cycloaddition reactions, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2017, 4512 CrossRef CAS.
- S. B. Jones, B. Simmons and D. W. C. MacMillan, Nine-step enantioselective total synthesis of (+)-minfiensine, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 13606 CrossRef CAS.
- B. D. Horning and D. W. C. MacMillan, Nine-step enantioselective total synthesis of (–)-vincorine, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 6442 CrossRef CAS.
- S. B. Jones, B. Simmons, A. Mastracchio and D. W. C. MacMillan, Collective synthesis of natural products by means of organocascade catalysis, Nature, 2011, 475, 183 CrossRef CAS.
- B. N. Laforteza, M. Pickworth and D. W. C. MacMillan, Enantioselective total synthesis of (–)-minovincine in nine chemical steps: an approach to ketone activation in cascade catalysis, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 11269 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Gioia, A. Hauville, L. Bernardi, F. Fini and A. Ricci, Organocatalytic asymmetric Diels–Alder reactions of 3-vinylindoles, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2008, 47, 9236 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Tan, G. Hernández-Torres and C. F. Barbas, Highly efficient hydrogen-bonding catalysis of the Diels–Alder reaction of 3-vinylindoles and methyleneindolinones provides carbazolespirooxindole skeletons, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 12354 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Enders, C. Joie and K. Deckers, Organocatalytic asymmetric synthesis of tetracyclic pyridocarbazole derivatives by using a Diels–Alder/aza-Michael/aldol condensation domino reaction, Chem. – Eur. J., 2013, 19, 10818 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Yang, Y.-H. Zhou, H. Yang, S.-S. Wang, Q. Ouyang, Q.-L. Luo and Q.-X. Guo, Asymmetric Diels–Alder reaction of 3-vinylindoles and nitroolefins promoted by multiple hydrogen bonds, Org. Lett., 2019, 21, 1161 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Wang, M. Sun, L. Yin and F. Shi, Catalytic enantioselective arylative dearomatization of 3-methyl-2-vinylindoles enabled by reactivity switch, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2015, 357, 4031 CrossRef CAS.
- For a review: G.-J. Mei and F. Shi, Design and application of 3-alkyl-2-vinylindoles in Brønsted acid-catalyzed reactions, Synlett, 2016, 27, 2515 CrossRef CAS.
- L. M. Repka, J. Ni and S. E. Reisman, Enantioselective synthesis of pyrroloindolines by a formal [3+2] cycloaddition reaction, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 14418 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Ni, H. Wang and S. E. Reisman, Direct, enantioselective synthesis of pyrroloindolines and indolines from simple indole derivatives, Tetrahedron, 2013, 69, 5622 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Wang and S. E. Reisman, Enantioselective total synthesis of (–)-lansai B and (+)-nocardioazines A and B, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 6206 CrossRef CAS.
- L.-W. Qi, J.-H. Mao, J. Zhang and B. Tan, Organocatalytic asymmetric arylation of indoles enabled by azo groups, Nat. Chem., 2018, 10, 58 CrossRef CAS.
- G.-J. Mei, X. Tang, Y. Tasdan and Y. Lu, Enantioselective dearomatization of indoles via an azoalkene enabled (3+2) reaction: facile access to pyrroloindolines, Angew. Chem., 2020, 59, 648 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Liao, C. Shu, M. Zhang, Y. Liao, X. Hu, Y. Zhang, Z. Wu, W. Yuan and X. Zhang, Highly enantioselective [3+2] coupling of indoles with quinone monoimines promoted by a chiral phosphoric acid, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 10471 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Yu, Y. Fu, J. Huang, J. Qin, H. Zuo, Y. Wu and F. Zhong, Enantioselective oxidative phenol-indole [3+2] coupling enabled by biomimetic Mn(III)/Brønsted acid relay catalysis, ACS Catal., 2019, 9, 7285 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Zhang, J. Hu, R. Xu, S. Pan, X. Zeng and G. Zhong, Catalytic asymmetric dearomative [3+2] cyclisation of 1,4-quinone with 2,3-disubstituted indoles, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2019, 361, 5449 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Cai and S.-L. You, Organocatalyzed enantioselective formal [4+2] cycloaddition of 2,3-disubstituted indole and methyl vinyl ketone, Org. Lett., 2012, 14, 3040 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Chen, B. Wang, Z. Wang, G. Zhu and J. Sun, Complex bioactive alkaloid-type polycycles through efficient catalytic asymmetric multicomponent Aza-Diels–Alder reaction of indoles with oxetane as directing group, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 2027 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Huang, L. Zhao, Y. Liu, W. Cao and X. Wu, Enantioselective intermolecular formal [3+3] cycloaddition of 2,3-disubstituted indoles with acrolein, Org. Lett., 2013, 15, 4338 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wu, J. Huang, B. Guo, L. Zhao, Y. Liu, J. Chen and W. Cao, Enantioselective Michael/aza-Michael/cyclization organocascade to tetracyclic spiroindolines: concise total synthesis of kopsinine and aspidofractine, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2014, 356, 3377 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Guo, L. Ge, G. Huang, L. Zhao, J. Chen, W. Cao and X. Wu, Expedient introduction of β-methoxyacrylate unit onto 3-substituted indoles and application of the resulting indole-dienes in organocascade toward indolino-polycyclics, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2015, 357, 4013 CrossRef CAS.
- Y.-C. Zhang, J.-J. Zhao, F. Jiang, S.-B. Sun and F. Shi, Organocatalytic asymmetric arylative dearomatization of 2,3-disubstituted indoles enabled by tandem reactions, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 13912 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Romano, M. Jia, M. Monari, E. Manoni and M. Bandini, Metal-free enantioselective electrophilic activation of allenamides: stereoselective dearomatization of indoles, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 13854 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Zhao, B. Guo, G. Huang, J. Chen, W. Cao and X. Wu, Enantioselective formation of 3-substituted indolinoazepines via organocatalyzed conjugate addition of indoloazepines to propargyl aldehyde, ACS Catal., 2014, 4, 4420 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Yang, Z. Wang, Z. He, G. Li, L. Hong, W. Sun and R. Wang, Organocatalytic enantioselective synthesis of tetrasubstituted α-amino allenoates by dearomative γ-addition of β,γ-alkynyl-α-imino esters and 2,3-disubstituted indoles, Angew. Chem., 2020, 59, 652 CrossRef.
- For recent representative examples: (a) V. Hornillos, J. A. Carmona, A. Ros, J. Iglesias-Sigüenza, J. López-Serrano, R. Fernández and J. M. Lassaletta, Dynamic kinetic resolution of heterobiaryl ketones by zinc-catalyzed asymmetric hydrosilylation, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 3777 CrossRef CAS; (b) Y. Kwon, A. J. Chinn, B. Kim and S. J. Miller, Divergent control of point and axial stereogenicity: catalytic enantioselective C-N bond-forming cross-coupling and catalyst-controlled atroposelective cyclodehydration, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 6251 CrossRef CAS; (c) Y.-S. Jang, Ł. Woźniak, J. Pedroni and N. Cramer, Access to P- and axially chiral biaryl phosphine oxides by enantioselective CpxIrIII-catalyzed C-H arylations, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 12901 CrossRef CAS; (d) C. Ma, F. Jiang, F.-T. Sheng, Y. Jiao, G.-J. Mei and F. Shi, Design and catalytic asymmetric construction of axially chiral 3,3′-bisindole skeletons, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 3014 CrossRef CAS; (e) F. Jiang, K.-W. Chen, P. Wu, Y.-C. Zhang, Y. Jiao and F. Shi, A strategy for synthesizing axially chiral naphthyl-indoles: catalytic asymmetric addition reactions of racemic substrates, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 15104 CrossRef CAS.
- For some very recent examples: (a) A. Romero-Arenas, V. Hornillos, J. Iglesias-Sigüenza, R. Fernández, J. López-Serrano, A. Ros and J. M. Lassaletta, Ir-catalyzed atroposelective desymmetrization of heterobiaryls: hydroarylation of vinyl ethers and bicycloalkenes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 2628 CrossRef CAS; (b) F.-T. Sheng, Z.-M. Li, Y.-Z. Zhang, L.-X. Sun, Y.-C. Zhang, W. Tan and F. Shi, Atroposelective synthesis of 3,3′-bisindoles bearing axial and central chirality: using isatin-derived imines as electrophiles, Chin. J. Chem., 2020, 38, 583 CrossRef CAS; (c) C. Ma, F.-T. Sheng, H.-Q. Wang, S. Deng, Y.-C. Zhang, Y. Jiao, W. Tan and F. Shi, Atroposelective access to oxindole-based axially chiral styrenes via the strategy of catalytic kinetic resolution, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 15686 CrossRef CAS.
- Y.-C. Xiao, C. Wang, Y. Yao, J. Sun and Y.-C. Chen, Direct asymmetric hydrosilylation of indoles: combined lewis base and Brønsted acid activation, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 10661 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Chen, C. Wang, L. Zhou and J. Sun, Chiral 2,3-disubstituted indolines from indoles and aldehydes by organocatalyzed tandem synthesis involving reduction by trichlorosilane, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2014, 356, 2224 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Yang, Y. Lou, C. Wang, L.-W. Qi, T. Fang, F. Zhang, H. Xu, L. Zhou, W. Li, G. Zhang, P. Yu and Q. Song, New chiral Brønsted acid from chiral phosphoric acid boron complex and water: asymmetric reduction of indoles, Angew. Chem., 2020, 59, 3294 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Bu, J. Li, Y. Yin, B. Qiao, G. Chai, X. Zhao and Z. Jiang, Organocatalytic asymmetric cascade aerobic oxidation and semipinacol rearrangement reaction: a visible light-induced approach to access chiral 2,2-disubstituted indolin-3-ones, Chem. – Asian J., 2018, 13, 2382 CrossRef CAS.
- For early reports: (a) X. Liu, X. Ye, F. Bureš, H. Liu and Z. Jiang, Controllable chemoselectivity in visible-light photoredox catalysis: four diverse aerobic radical cascade reactions, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 11443 ( Angew. Chem. , 2015 , 127 , 11605 ) CrossRef CAS; (b) C. Zhang, S. Li, F. Bureš, R. Lee, X. Ye and Z. Jiang, Visible light photocatalytic aerobic oxygenation of indoles and pH as a chemoselective switch, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 6853 CrossRef CAS; (c) G. Wei, C. Zhang, F. Bureš, X. Ye, C.-H. Tan and Z. Jiang, Enantioselective aerobic oxidative C(sp3)-H olefination of amines via cooperative photoredox and asymmetric catalysis, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 3708 CrossRef CAS; (d) Y. Liu, J. Li, X. Ye, X. Zhao and Z. Jiang, Organocatalytic asymmetric formal arylation of benzofuran-2(3H)-ones with cooperative visible light photocatalysis, Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 13955 RSC.
- X. Liu, X. Yan, J.-H. Yu, Y.-D. Tang, K. Wang and H. Zhang, Organocatalytic asymmetric dearomative oxyalkylation of indoles enables access to C2-quaternary indolin-3-ones, Org. Lett., 2019, 21, 5626 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Andreini, M. D. Paolis and I. Chataigner, Thiourea-catalyzed dearomatizing [4+2] cycloadditions of 3-nitroindole, Catal. Commun., 2015, 63, 15 CrossRef CAS.
- J.-Q. Zhao, M.-Q. Zhou, Z.-J. Wu, Z.-H. Wang, D.-F. Yue, X.-Y. Xu, X.-M. Zhang and W.-C. Yuan, Asymmetric Michael/cyclization cascade reaction of 3-isothiocyanato oxindoles and 3-nitroindoles with amino-thiocarbamate catalysts: enantioselective synthesis of polycyclic spirooxindoles, Org. Lett., 2015, 17, 2238 CrossRef CAS.
- D.-F. Yue, J.-Q. Zhao, X.-Z. Chen, Y. Zhou, X.-M. Zhang, X.-Y. Xu and W.-C. Yuan, Multiple hydrogen-bonding bifunctional thiourea-catalyzed asymmetric dearomative [4+2] annulation of 3-nitroindoles: highly enantioselective access to hydrocarbazole skeletons, Org. Lett., 2017, 19, 4508 CrossRef CAS.
- X.-M. Chen, C.-W. Lei, D.-F. Yue, J.-Q. Zhao, Z.-H. Wang, X.-M. Zhang, X.-Y. Xu and W.-C. Yuan, Organocatalytic asymmetric dearomatization of 3-nitroindoles and 3-nitrobenzothiophenes via thiol-triggered diastereo- and enantioselective double Michael addition reaction, Org. Lett., 2019, 21, 5452 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Wang, J. Zhang, Y. Tu and J. Zhang, Phosphine-catalyzed enantioselective dearomative [3+2]-cycloaddition of 3-nitroindoles and 2-nitrobenzofurans, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 5422 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Li, T. P. Gonçalves, K.-W. Huang and Y. Lu, Dearomatization of 3-nitroindoles via a phosphine-catalyzed enantioselective [3+2] annulation reaction, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 5427 CrossRef CAS.
- L.-W. Jin, F. Jiang, K.-W. Chen, B.-X. Du, G.-J. Mei and F. Shi, Phosphine-catalyzed regiospecific (3+2) cyclization of 3-nitroindoles with allene esters, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2019, 17, 3894 RSC.
- K.-K. Wang, W. Du, J. Zhu and Y.-C. Chen, Construction of polycyclic spirooxindoles through [3+2] annulations of Morita–Baylis–Hillman carbonates and 3-nitro-7-azaindoles, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2017, 28, 512 CrossRef CAS.
- M.-S. Mei, Y.-H. Wang, Q. Hu, Q.-H. Li, D.-Y. Shi, D. Gao, G. Ge, G.-Q. Lin and P. Tian, Enantioselective [3+2] annulation of isatin-derived MBH-carbonates and 3-nitroindoles enabled by a bifunctional DMAP-thiourea, Chem. Commun., 2020, 56, 10718 RSC.
- Q. Cai, C. Zheng, J.-W. Zhang and S.-L. You, Enantioselective Michael/Mannich polycyclization cascade of indolyl enones catalyzed by quinine-derived primary amines, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 8665 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wu, Q. Liu, H. Fang, J. Chen, W. Cao and G. Zhao, Enantioselective organocatalyzed cascade reactions to highly functionalized spirotetracyclic indolenines and oxindoles, Chem. – Eur. J., 2012, 18, 12196 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Yin and S.-L. You, Enantioselective chlorocyclization of indole derived benzamides for the synthesis of spiro-indolines, Org. Lett., 2013, 15, 4266 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhou, Z.-L. Xia, Q. Gu and S.-L. You, Chiral phosphoric acid catalyzed intramolecular dearomative Michael addition of indoles to enones, Org. Lett., 2017, 19, 762 CrossRef CAS.
- Z.-L. Xia, C. Zheng, S.-G. Wang and S.-L. You, Catalytic asymmetric dearomatization of indolyl dihydropyridines via, enamine isomerization/spirocyclization/transfer hydrogenation sequence, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 2653 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Pan, Y. Liu, F. Hu, Q. Liu, W. Shang, X. Ji and C. Xia, Enantioselective synthesis of spiroindolines via cascade isomerization/spirocyclization/dearomatization reaction, Org. Lett., 2020, 22, 1589 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † These authors contributed equally to the work. |
| This journal is © the Partner Organisations 2020 |