Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleSupramolecular anion recognition in water: synthesis of hydrogen-bonded supramolecular frameworks†
Mahbod
Morshedi
a,
Michael
Thomas
 a,
Andrew
Tarzia
b,
Christian J.
Doonan
b and
Nicholas G.
White
a,
Andrew
Tarzia
b,
Christian J.
Doonan
b and
Nicholas G.
White
 *a
*a
aResearch School of Chemistry, The Australian National University, Canberra, ACT, Australia. E-mail: nicholas.white@anu.edu.au; Web: http://www.nwhitegroup.com
bDepartment of Chemistry and Centre for Advanced Materials, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, SA, Australia
First published on 16th February 2017
Abstract
The interaction of tetratopic amidinium-containing receptors with terephthalate anions leads to porous framework materials assembled through charge-assisted hydrogen bonds. The frameworks form in good yield within minutes in water at room temperature, but no framework material is obtained if other anions (Cl−, Br−, NO3−, SO42− or isophthalate2−) are used in place of terephthalate. Two forms of the framework can be prepared: one with a connected pore network, and a more dense phase with discrete voids. We demonstrate that these are the kinetic and thermodynamic products, respectively. Either framework can be prepared independently and can be converted to the other form in response to stimuli. Furthermore, the frameworks can be controllably disassembled and reassembled in response to acid/base triggers suggesting that this new class of materials may have applications in the selective encapsulation and release of guests.
Introduction
Encumbered by the difficulties associated with binding anions in protic solvents, the field of anion recognition has lagged behind that of cation recognition.1 Even after decades of research, there are few supramolecular hosts that can bind anions in water, and fewer still that can achieve selective recognition in this medium.2Given these difficulties, it is perhaps unsurprising that the field of anion-templated self-assembly is very much in its infancy, particularly when compared with the impressive successes of transition metal-templated self-assembly.3 However, despite the significant challenges, notable successes have been reported including the anion-templated syntheses of interlocked structures (Beer),2e,4 stimuli-responsive pseudorotaxanes and threaded architectures (Sessler),5 and very recently, cages (Kruger and Gunnlaugsson, and Wu).6
Inspired by recent developments in the field of hydrogen-bonded framework materials, in particular Ward's pioneering work on guanidinium⋯sulfonate frameworks,7 and Friščić's demonstration that imidazolium sulfate salts are “mirror images” of the transition metal imidazolate analogues,8 we have investigated the use of simple anions to assemble supramolecular framework materials.9 Herein, we describe the use of terephthalate anions to prepare porous frameworks, which we believe to be an unprecedented demonstration of anion-induced self-assembly in water.10,11
While the amidinium group has been elegantly exploited to prepare self-assembled systems,11,12 it has received relatively little attention within anion recognition chemistry.13 This is perhaps surprising, given its similarity to the thoroughly-explored guanidinium functionality.14,15 Attracted by the amidinium motif's relatively high pKa,16 strong hydrogen bonding capability and ease of synthesis, we sought to investigate whether the favourable interaction between this motif and carboxylate anions could be used to prepare self-assembled structures.
Results and discussion
While complex systems assembled by amidinum⋯carboxylate interactions have been reported,11,12 little information regarding the strength of a simple 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 amidinium⋯carboxylate interaction is available. Therefore, we initially investigated the solution anion recognition properties of simple model receptor 1·BPh4 (Fig. 1): 1H NMR titration experiments revealed that this simple host displays strong anion recognition in CD3CN (Ka for Cl− > 104 M−1, addition of oxoanions results in precipitation). Moving to a more competitive medium, isothermal calorimetry (ITC), 13C NMR experiments and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations all showed strong benzoate anion binding in 95
1 amidinium⋯carboxylate interaction is available. Therefore, we initially investigated the solution anion recognition properties of simple model receptor 1·BPh4 (Fig. 1): 1H NMR titration experiments revealed that this simple host displays strong anion recognition in CD3CN (Ka for Cl− > 104 M−1, addition of oxoanions results in precipitation). Moving to a more competitive medium, isothermal calorimetry (ITC), 13C NMR experiments and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations all showed strong benzoate anion binding in 95![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5 acetonitrile
5 acetonitrile![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) water (Ka ∼ 2900 M−1, 1H NMR experiments were precluded by disappearance of N–H resonances in this solvent mixture, see ESI† for details of anion recognition experiments).18 Negligible association was observed between 1+ and chloride anion in this competitive aqueous medium.
water (Ka ∼ 2900 M−1, 1H NMR experiments were precluded by disappearance of N–H resonances in this solvent mixture, see ESI† for details of anion recognition experiments).18 Negligible association was observed between 1+ and chloride anion in this competitive aqueous medium.
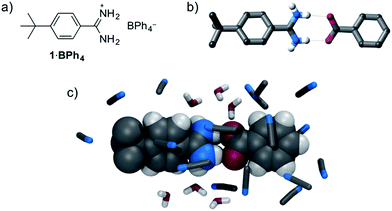 | ||
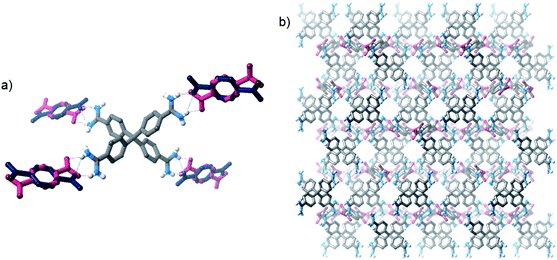
Fig. 1 (a) Structure of model compound 1·BPh4, (b) X-ray crystal structure of 1·benzoate, (c) representative snapshot from MD simulations of binding of 1+ and benzoate in 20 mM 95![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5 CH3CN 5 CH3CN![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) H2O. H2O. | ||
This strong oxoanion binding is remarkable given that 1+ contains only one amidinium motif, and an electron-donating tert-butyl group, and presumably it arises due to the highly complementary hydrogen bonding interactions possible between the amidinium N–H donors and carboxylate oxygen atoms. Single crystal X-ray diffraction (SCXRD) studies and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations reveal that in both the solid state and in solution short hydrogen bonds between the “forward-facing” amidinum N–H groups and carboxylate oxygen atoms are present (Fig. 1). Given the strong binding exhibited by simple receptor 1+, it seems likely that more complex and sophisticated anion receptors containing amidinium groups offer a route to potent anion recognition in aqueous media.
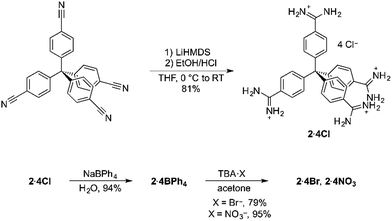
Encouraged by the strength of the interaction between our model compound and benzoate, we designed the new tetratopic tetra-cationic receptor 24+ (Scheme 1). This receptor was prepared in high yield (81%) by treating the corresponding tetra-nitrile17 with LiHMDS in THF, followed by work-up with ethanolic HCl, giving 2·4Cl. The potentially-coordinating chloride anions could be readily exchanged for non-coordinating anions by simple precipitation from water with sodium tetraphenylborate.
We next investigated whether terephthalate anions19 could be used to link 24+ receptors into a porous framework material. We initially used 2·4BPh4 and TBA2·TP, which are both soluble in a range of moderately-polar and polar organic solvents [TBA2·TP = n-tetrabutylammonium terephthalate], reasoning that using organic solvents and the non-coordinating tetraphenylborate anion and tetrabutylammonium cation would minimize unwanted interactions and maximise the strength of the amidinium⋯terephthalate interaction, thus favouring extended network formation. However, mixing 2·4BPh4 and TBA2·TP in a range of solvents resulted in the immediate precipitation of insoluble amorphous solids under all tested conditions, even when using highly polar solvents such as DMF and DMSO and/or solvothermal reactions. While the solids formed were insoluble in all tested solvents, 1H NMR analysis of the acid-digested material was consistent with the insoluble solid having the formulation [2·(TP)2]n. We hypothesize that a polymeric aggregate between 24+ and TP2− forms very rapidly in these solvents, and this speed precludes an ordered crystalline structure.
In an effort to modify the kinetics of framework formation, we next investigated the use of water as solvent; this required the use of 2·4Cl, as 2·4BPh4 is insoluble in water. Mixing aqueous solutions of 2·4Cl and TBA2·TP resulted in the formation of large needle-like crystals. Crystals were visible within 1–2 minutes, and crystal growth was complete within an hour (see ESI Video†).
The crystals were analysed by SCXRD studies, which show that the material possesses a distorted diamondoid topology with the formula [2·(TP)2]n·water (Fig. 2). The framework is constructed from parallel hydrogen bonds between the two “forward-facing” amidinium N–H groups and the two carboxylate oxygen atoms. These hydrogen bonds are short [N⋯O distances: 2.787(3) and 2.832(3) Å, 〈N–H⋯O: 171 and 165°, H⋯O distances: 1.91 and 1.99 Å, 71 and 74% of the sum of the van der Waals radii20 of H and O].
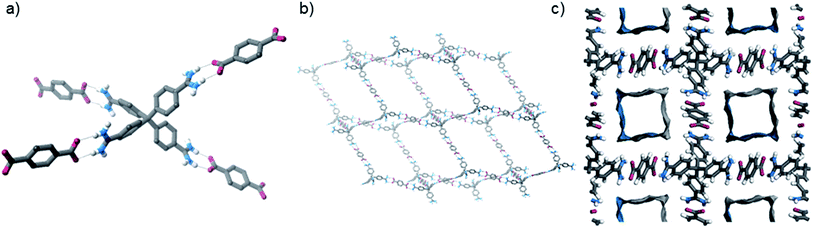 | ||
| Fig. 2 Views of the solid state structure of [2·(TP)2]n: (a) view showing hydrogen bonding interactions, (b) view of one of the interpenetrating nets, (c) view down the c-axis highlighting N2-accessible pores (solvent molecules and some hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity, see Fig. S23† for additional views of the structure). | ||
The framework crystallises in the I-centered tetragonal space group I41/a, and is significantly interpenetrated, with 11 interpenetrating nets (Fig. S23†).21 Despite this, the material contains accessible pores, which exist as square channels with a diameter of approximately 1.3 nm running down the crystallographic c-axis. In the crystalline state, the channels are filled with water molecules, which can be resolved crystallographically, and these solvents comprise about 45% of the unit cell volume. [2·(TP)2]n has a calculated Connolly surface area of 1470 m2 g−1 (using a probe radius of 1.82 Å), but unfortunately initial attempts to activate the framework via solvent exchange and evaporation, or supercritical CO2, removal appear to result in the collapse of the porous network structure (see ESI†).
The framework synthesis was repeated on a preparative scale, giving access to “bulk” quantities of [2·(TP)2]n in good yield (77%). In addition, the material was further characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) experiments, IR spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), elemental analysis (EA) and by 1H NMR spectroscopy of an acid-digested sample (see ESI†).
Given that the material is prepared from TBA2·TP, it is conceivable that the large TBA cations could have a templating effect on the structure – however, this was ruled out by preparing the framework from sodium terephthalate. Any possible structure directing effect of the chloride anions was also ruled out by preparing the framework from 2·4Br, and from 2·4NO3.
It is noteworthy that 24+ does not precipitate from water in the presence of Cl−, Br−, NO3− or even SO42− or isophthlate2− anions,22 suggesting that no extended structures form in water with these anions. We suggest that the interaction between all these anions and 24+ in water is negligible, so no insoluble aggregates form. Conversely, when terephthalate is used, the interaction between this anion and the tetra-amidinium receptor is strong enough that small “clusters” of receptors and anions can form that nucleate crystal growth.23 Remarkably, the framework could be prepared in 50 mM NaCl(aq), even though this corresponds to a greater than 100-fold excess of chloride anions relative to terephthalate anions. Surprisingly, when [2·(TP)2]n was prepared in this way, no evidence of incorporation of NaCl into the channels was observed by SCXRD.
A key advantage to preparing frameworks from terephthalate anions is that [2·(TP)2]n is prepared from solution at room temperature, unlike metal organic frameworks (MOFs) and covalent organic frameworks (COFs), which typically (although not always) require solvothermal synthesis. We sought to use these mild synthetic conditions to our advantage by reversibly “breaking” and re-forming our frameworks. Suspending crystals of [2·(TP)2]n in water and adding dilute HCl(aq) or trifluoroacetic acid caused the dissolution of the crystals, presumably due to protonation of the carboxylate anion breaking apart the favourable hydrogen bonding interactions. Neutralising the solution using NaOH(aq) caused the framework to reform within minutes. The ability to selectively “trigger” the destruction of a framework in response to a stimulus, and importantly, to re-create it, suggests that carboxylate anion-based materials may have future applications in controlled release systems, where encapsulated guests are freed by disassembling the extended network in response to acid.
To further investigate the formation of the frameworks, we next investigated the preparation of [2·(TP)2]n in the presence of an organic co-solvent. When 2·4Cl and TBA2·TP were mixed in 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 water
1 water![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) acetone, crystals did not form within minutes (as was observed in pure water), but instead several hours were required for crystal growth to commence. Analysis by SCXRD revealed that the product was again an extended framework material, but in this case the structure crystallised in the orthorhombic space group Fddd.
acetone, crystals did not form within minutes (as was observed in pure water), but instead several hours were required for crystal growth to commence. Analysis by SCXRD revealed that the product was again an extended framework material, but in this case the structure crystallised in the orthorhombic space group Fddd.
This orthorhombic framework is again held together by short N–H⋯O hydrogen bonds between amidinium and carboxylate groups (Fig. 3), but in this case two hydrogen bonding arrangements are observed (as 50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 disordered positions in the solid state structure). In one case, a similar “double” hydrogen bond is observed as in the tetragonal structure, in another both N–H donors bind to one carboxylate oxygen. Again, the structure is highly interpenetrated (15 interpenetrating nets), but contains significant pore space, although not as much as the tetragonal form (∼18% “free” space – i.e. space occupied by solvents). Furthermore, the Connolly surface (using a probe radius of 1.82 Å), is comprised of disconnected pore voids. We prepared this framework on preparative scales in good yield, and characterised it by PXRD, IR, TGA, EA, and by 1H NMR spectroscopy of an acid-digested sample.
50 disordered positions in the solid state structure). In one case, a similar “double” hydrogen bond is observed as in the tetragonal structure, in another both N–H donors bind to one carboxylate oxygen. Again, the structure is highly interpenetrated (15 interpenetrating nets), but contains significant pore space, although not as much as the tetragonal form (∼18% “free” space – i.e. space occupied by solvents). Furthermore, the Connolly surface (using a probe radius of 1.82 Å), is comprised of disconnected pore voids. We prepared this framework on preparative scales in good yield, and characterised it by PXRD, IR, TGA, EA, and by 1H NMR spectroscopy of an acid-digested sample.
Upon further investigation, we found that a range of percentages of acetone in water gave ortho-[2·(TP)2]n, and interestingly that even trace amounts of ethanol in water (e.g. 1% ethanol v/v) caused formation of this orthorhombic phase (as opposed to the tetragonal phase that forms in 100% water). Furthermore, when [2·(TP)2]n was prepared in 100 mM NaCl(aq), crystallisation was significantly slowed, and the major product was the orthorhombic phase. When [2·(TP)2]n was prepared in the presence of an equimolar amount of sulfate anions by adding two equivalents each of TBA2·TP and TBA2·SO4 to 2·4Cl, crystallisation was again slow and only pure ortho-[2·(TP)2]n was isolated, with no inclusion of SO42− in the product. Again this shows a remarkable degree of selectivity between two similar anions.
Given that ortho-[2·(TP)2]n appeared to be forming over a significantly longer period of time than tet-[2·(TP)2]n, we reasoned that this may be the thermodynamic form of the framework, while the more open tetragonal phase corresponds to a kinetically-trapped product.24 Consistent with this hypothesis, preparing [2·(TP)2]n in warm (50 °C) water gave the orthorhombic form, presumably due to the greater thermal energy allowing the system to overcome potential kinetic traps. Furthermore, taking crystals of tet-[2·(TP)2]n and boiling in either water or ethanol for two hours resulted in complete single-crystal-to-single-crystal conversion25 to the thermodynamic product ortho-[2·(TP)2]n, as evidenced by SCXRD and PXRD experiments. Boiling ortho-[2·(TP)2]n in either ethanol or water produced no change in the structure, which remained robust throughout (as evidenced by PXRD).
Intriguingly, the kinetic product tet-[2·(TP)2]n loses crystallinity over time when removed from solvent (after briefly becoming more crystalline, see ESI†) but this crystallinity can be recovered by addition of a drop of water. Conversely, ortho-[2·(TP)2]n is stable to solvent removal and over prolonged periods of time. When tet-[2·(TP)2]n is allowed to lose solvent and become acrystalline, it can be converted to ortho-[2·(TP)2]n by simply adding a few drops of ethanol. Once conversion is complete, this form is robust to loss of solvent. A full list of experimental conditions leading to the two different phases of the product is provided in the ESI.†
Conclusions
In this paper, we have demonstrated that a simple amidinium receptor can recognise carboxylate anions in aqueous media, and have then used these amidinum⋯carboxylate interactions to synthesise supramolecular frameworks in water. At room temperature, 2·4Cl and terephthalate anions rapidly form an open porous framework material, tet-[2·(TP)2]n, while other anions (halides, SO42−, isophthlate2−) give no framework. Formation is tolerant to the highly competitive solvent, and even to a huge excess of competing chloride anions. By varying the reaction conditions in one of several ways, we can prepare an alternative less-open framework, ortho-[2·(TP)2]n. Alternatively, ortho-[2·(TP)2]n can be prepared by the single-crystal-to-single-crystal transformation of tet-[2·(TP)2]n in response to an organic solvent, or to temperature. Both tet- and ortho-[2·(TP)2]n can be disassembled upon addition of an acid stimulus, and neutralisation of the acid results in re-assembly of the kinetic product, tet-[2·(TP)2]n when starting from either phase of the framework.We are now investigating whether more robust materials can be prepared using this anion-mediated approach with the aim of making these stable to solvent removal and thus suitable for gas/guest adsorption. We envisage that the ability to deliberately dis-assemble these frameworks and later re-assemble them will be attractive for guest storage and controlled release.
Experimental
General remarks
Tetra(4-cyanophenyl)methane was prepared from tetraphenylmethane as previously described.17 Additional synthetic details and characterisation data are provided in the ESI.†Synthesis of 2·4Cl
Tetra(4-cyanophenyl)methane (0.500 g, 1.19 mmol) was dissolved in dry THF (10 mL). It was cooled to −78 °C under a nitrogen atmosphere, and LiHMDS solution (1.0 M in THF, 7.1 mL, 7.1 mmol) was added resulting in the immediate formation of a precipitate. The mixture was allowed to warm to room temperature and stirred overnight, during which time the precipitate dissolved to give a yellow-orange solution. This was cooled to 0 °C and ethanolic HCl (prepared by cautiously adding 2 mL of acetyl chloride to 10 mL ethanol) was added, which resulted in the formation of a pale precipitate. This was isolated by filtration, and then suspended in ethanol (10 mL) and sonicated for 1 hour. The solid was again isolated by filtration, washed thoroughly with ethanol (5 × 10 mL) and dried in vacuo to give 2·4Cl as a cream-coloured powder. Yield: 0.612 g (0.964 mmol, 81%).
1H NMR (D2O): 7.80 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 8H), 7.66 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 8H)ppm. 13C NMR (D2O): 166.0, 150.8, 131.3, 127.8, 126.3, 65.5 ppm. HRESI-MS (pos.) 489.2530, calc. for [C29H28N8]+ (i.e. loss of 3H+ and 4Cl−) = 489.2521 Da. IR (inter alia): 1677 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N stretch) cm−1.
N stretch) cm−1.
Synthesis of tet-[2·(TP)2]n
A solution of TBA2·TP (0.103 g, 0.159 mmol) in water (20 mL) was added to a solution of 2·4Cl (0.050 g, 0.079 mmol) in water (20 mL). Within approximately one minute crystals began to grow, and crystallisation was complete within one hour (a video of this process is supplied as ESI†). The large, colourless needle-like crystals were isolated by filtration, washed with water, and air-dried to give tet-[2·(TP)2]n. Yield: 0.056 g (0.061 mmol, 77%).‡
1H NMR (d6-DMSO containing a drop of conc. DCl(aq)): δ 9.59§ (br. s), 9.34§ (br. s), 8.03 (s, 8H), 7.94 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 8H), 7.55 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 8H) ppm. IR (inter alia): 1677 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N stretch), 1555 (C
N stretch), 1555 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretch) cm−1. M. Pt: decomposition begins ∼225 °C. EA, found: C 63.6, H 5.6, N 12.8; calc. for [2·(TP)2]·2H2O (C45H44N8O10): C 63.1, H 5.2, N 13.1%.
O stretch) cm−1. M. Pt: decomposition begins ∼225 °C. EA, found: C 63.6, H 5.6, N 12.8; calc. for [2·(TP)2]·2H2O (C45H44N8O10): C 63.1, H 5.2, N 13.1%.
The structure was determined by SCXRD, and PXRD used to confirm phase purity (see ESI†).
Synthesis of ortho-[2·(TP)2]n
A solution of TBA2·TP (0.064 g, 0.099 mmol) in water![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) acetone (2
acetone (2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v, 5 mL) was added to a solution of 2·4Cl (0.030 g, 0.047 mmol) in water
1 v/v, 5 mL) was added to a solution of 2·4Cl (0.030 g, 0.047 mmol) in water![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) acetone (2
acetone (2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v, 5 mL). Crystals developed overnight, which were isolated by filtration, washed with water, and air-dried to give ortho-[2·(TP)2]n. Yield: 0.031 g (0.033 mmol, 69%).¶
1 v/v, 5 mL). Crystals developed overnight, which were isolated by filtration, washed with water, and air-dried to give ortho-[2·(TP)2]n. Yield: 0.031 g (0.033 mmol, 69%).¶
1H NMR (d6-DMSO containing a drop of conc. DCl(aq)): δ 9.53§ (br. s), 9.27§ (br. s), 8.04 (s, 8H), 7.93 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 8H), 7.56 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 8H) ppm. IR (inter alia): 1680 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N stretch), 1532 (C
N stretch), 1532 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretch) cm−1. M. Pt: 238 °C. EA, found: C 61.0, H 5.7, N 12.2; calc. for [2·(TP)2]·4H2O (C45H48N8O12): C 60.5, H 5.4, N 12.6%.
O stretch) cm−1. M. Pt: 238 °C. EA, found: C 61.0, H 5.7, N 12.2; calc. for [2·(TP)2]·4H2O (C45H48N8O12): C 60.5, H 5.4, N 12.6%.
The structure was determined by SCXRD, and PXRD used to confirm phase purity (see ESI†).
Ortho-[2·(TP)2]n could also be prepared by a variety of other methods (see text of manuscript and ESI†).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Australian National University and Australian Research Council for funding. We thank Charlotte Rouse (ANU) for assistance with ITC measurements, Drs Karmen Condic-Jurkic and Megan O'Mara (ANU) for assistance with MD simulations, and Profs. Lyall Hanton (University of Otago) and Mark MacLachlan (University of British Columbia) for helpful discussions.References
- Reviews of anion recognition chemistry: (a) N. H. Evans and P. D. Beer, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 11716 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) M. J. Langton, C. J. Serpell and P. D. Beer, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 1974 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) P. A. Gale, E. N. W. Howe and X. Wu, Chemistry, 2016, 1, 351 CrossRef CAS.
- For elegant examples of anion recognition in neutral water, see: (a) F. P. Schmidtchen, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 1977, 16, 720 CrossRef; (b) A. Metzger, V. M. Lynch and E. V. Anslyn, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 1997, 36, 862 CrossRef CAS; (c) A. Schaly, R. Belda, E. Garcia-Espana and S. Kubik, Org. Lett., 2013, 15, 6238 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) H. Zhou, Y. Zhao, G. Gao, S. Li, J. Lan and J. You, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 14908 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) M. J. Langton, S. W. Robinson, I. Marques, V. Felix and P. D. Beer, Nat. Chem., 2014, 6, 1039 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) M. Lisbjerg, B. M. Jessen, B. Rasmussen, B. E. Nielsen, A. O. Madsen and M. Pittelkow, Chem. Sci., 2014, 5, 2647 RSC; (g) M. A. Yawer, V. Havel and V. Sindelar, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 276 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) P. Sokkalingam, J. Shraberg, S. W. Rick and B. C. Gibb, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 48 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) D. Philp and J. F. Stoddart, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 1996, 35, 1154 CrossRef; (b) O. M. Yaghi, M. O'Keeffe, N. W. Ockwig, H. K. Chae, M. Eddaoudi and J. Kim, Nature, 2003, 423, 705 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) T. R. Cook, Y.-R. Zheng and P. J. Stang, Chem. Rev., 2013, 113, 734 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) G. T. Spence and P. D. Beer, Acc. Chem. Res., 2013, 46, 571 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) S. W. Robinson, C. L. Mustoe, N. G. White, A. Brown, A. L. Thompson, P. Kennepohl and P. D. Beer, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 499 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) T. A. Barendt, S. W. Robinson and P. D. Beer, Chem. Sci., 2016, 7, 5171 RSC.
- (a) H.-Y. Gong, B. M. Rambo, E. Karnas, V. M. Lynch and J. L. Sessler, Nat. Chem., 2010, 2, 406 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) H.-Y. Gong, B. M. Rambo, E. Karnas, V. M. Lynch, K. M. Keller and J. L. Sessler, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 1526 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) H.-Y. Gong, B. M. Rambo, V. M. Lynch, K. M. Keller and J. L. Sessler, Chem.–Eur. J., 2012, 18, 7803 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) H.-Y. Gong, B. M. Rambo, V. M. Lynch, K. M. Keller and J. L. Sessler, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 6330 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) B. Wu, F. Cui, Y. Lei, S. Li, N. de Sousa Amadeu, C. Janiak, Y.-J. Lin, L.-H. Weng, Y.-Y. Wang and X.-J. Yang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 5096 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) D. Yang, J. Zhao, Y. Zhao, Y. Lei, L. Cao, X.-J. Yang, M. Davi, N. de Sousa Amadeu, C. Janiak, Z. Zhang, Y.-Y. Wang and B. Wu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 8658 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) K. Pandurangan, J. A. Kitchen, S. Blasco, E. M. Boyle, B. Fitzpatrick, M. Feeney, P. E. Kruger and T. Gunnlaugsson, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 4566 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) M. J. Horner, K. T. Holman and M. D. Ward, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 14640 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) Y. Liu, C. Hu, A. Comotti and M. D. Ward, Science, 2011, 333, 436 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) Y. Liu, W. Xiao, J. J. Yi, C. Hu, S.-J. Park and M. D. Ward, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 3386 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Mottillo and T. Friščić, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 8924 RSC.
- While conceptually quite different, a number of elegant supramolecular frameworks have been prepared by the assembly of suitably designed hydrogen bonding precursors. These have been referred to as Hydrogen Bonded Organic frameworks (HOFs) or Supramolecular Organic Frameworks (SOFs). Reviews: (a) J. D. Wuest, Chem. Commun., 2005, 5830 RSC; (b) J. Tian, L. Chen, D.-W. Zhang, Y. Liu and Z.-T. Li, Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 6351 RSC; (c) T. Adachi and M. D. Ward, Acc. Chem. Res., 2016, 49, 2669 CrossRef CAS PubMed. Selected highlights: (d) M. Simard, D. Su and J. D. Wuest, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1991, 113, 4696 CrossRef CAS; (e) P. Brunet, M. Simard and J. D. Wuest, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1997, 119, 2737 CrossRef CAS; (f) W. Yang, A. Greenaway, X. Lin, R. Matsuda, A. J. Blake, C. Wilson, W. Lewis, P. Hubberstey, S. Kitagawa, N. R. Champness and M. Schroder, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 14457 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) Y. He, S. Xiang and B. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 14570 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) M. Mastalerz and I. M. Oppel, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 5252 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) H. Wang, B. Li, H. Wu, T.-L. Hu, Z. Yhao, W. Zhou, S. Xiang and B. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 9963 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (j) A. Karmakar, R. Illathvalappil, B. Anothumakkool, A. Sen, P. Samanta, A. V. Desai, S. Kurungot and S. K. Ghosh, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 10667 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For elegant foldamers that exhibit dramatic structural changes in response to anions in aqueous media, see: (a) J.-M. Suk and K.-S. Jeong, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 11868 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) Y. Hua, Y. Liu, C-H. Chen and A. H. Flood, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 14401 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Crego-Calama and colleagues have reported elegant demonstrations that a tetra-amidinium calixarene derivate can assemble with a tetra-carboxylate or tetra-sulfonate calixarene derivative to form capsules in water, although this does not involve a discrete anion: (a) F. Corbellini, R. Fiammengo, P. Timmerman, M. Crego-Calama, K. Versluis, A. J. R. Heck, I. Luyten and D. N. Reinhoudt, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, 124, 6569 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) F. Corbellini, L. Di Costanzo, M. Crego-Calama, S. Geremia and D. N. Reinhoudt, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 9946 CAS.
- (a) M. Ikeda, Y. Tanaka, T. Hasegawa, Y. Furusho and E. Yashima, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 6806 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) H. Katagiri, Y. Tanaka, Y. Furusho and E. Yashima, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2007, 46, 2435 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) W. Makiguchi, J. Tanabe, H. Yamada, H. Iida, D. Taura, N. Ousaka and E. Yashima, Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 7236 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) Y. Nakatani, Y. Furusho and E. Yashima, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 5463 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) Y. Tanaka, H. Katagiri, Y. Furusho and E. Yashima, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2005, 44, 3867 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) T. Kusukawa, K. Matsumoto, H. Nakamura, W. Iizuka, K. Toyama and S. Takeshita, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2013, 11, 3692 RSC.
- (a) Y. Deng, J. A. Roberts, S.-M. Peng, C. K. Chang and D. G. Nocera, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 1997, 36, 2124 CrossRef CAS; (b) P. A. Gale, Tetrahedron Lett., 1998, 39, 3873 CrossRef CAS; (c) L. Sebo, B. Schweizer and F. Diederich, Helv. Chim. Acta, 2000, 83, 80 CrossRef CAS; (d) L. Sebo, F. Diederich and V. Gramlich, Helv. Chim. Acta, 2000, 83, 93 CrossRef CAS; (e) S. Camiolo, P. A. Gale, M. I. Ogden, B. W. Skelton and A. H. White, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 2001, 1294 RSC.
- For reviews of guanidinium anion receptors: (a) C. Schmuck, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2006, 250, 3053 CrossRef CAS; (b) P. Blondeau, M. Segura, R. Perez-Fernandez and J. de Mendoza, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2007, 36, 198 RSC and references therein. For a recent highlight: (c) R. Custelcean, N. J. Williams and C. A. Seipp, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 10525 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For important demonstrations of the use of guanidinium moieties in the sulfate-templated assembly of helices (one of which functions in 9
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 MeOH
1 MeOH![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) H2O), see:
(a) J. Sanchez-Quesada, C. Seel, P. Prados, J. de Mendoza, I. Dalcol and E. Giralt, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1996, 118, 277 CrossRef CAS;
(b) M. W. Peczuh, A. D. Hamilton, J. Sanchez-Quesada, J. de Mendoza, T. Haack and E. Giralt, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1997, 119, 9327 CrossRef CAS.
H2O), see:
(a) J. Sanchez-Quesada, C. Seel, P. Prados, J. de Mendoza, I. Dalcol and E. Giralt, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1996, 118, 277 CrossRef CAS;
(b) M. W. Peczuh, A. D. Hamilton, J. Sanchez-Quesada, J. de Mendoza, T. Haack and E. Giralt, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1997, 119, 9327 CrossRef CAS. - For example, the pKa of unsubsituted benzamidinium is 11.6; A. Albert, R. Goldacre and J. Phillips, J. Chem. Soc., 1948, 2240 RSC.
- B. F. Hoskins and R. Robson, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1989, 111, 5962 CrossRef CAS.
- This strong binding has some precedent: Kusukawa has shown very strong interactions in DMSO between bis(amidine) receptors and dicarboxylic acids (Ka > 105 M−1). These interactions involve proton transfer to form amidinium/carboxylate pairs
(a) T. Kusukawa, S. Tanaka and K. Inoue, Tetrahedron, 2014, 70, 4049 CrossRef CAS. Similarly, Guldi and colleagues have reported that the association constant between a porphyrin amidine and fullerene carboxylic acid (again involving proton transfer) is ∼107 M−1 in 9
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 toluene
1 toluene![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) acetonitrile:
(b) L. Sanchez, M. Sierra, N. Martín, A. J. Myles, T. J. Dale, J. Rebek, W. Seitz and D. M. Guldi, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2006, 45, 4637 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
acetonitrile:
(b) L. Sanchez, M. Sierra, N. Martín, A. J. Myles, T. J. Dale, J. Rebek, W. Seitz and D. M. Guldi, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2006, 45, 4637 CrossRef CAS PubMed. - For 1D anion coordination polymers assembled using terephthalate anions, see: (a) M. Wais Hosseini, R. Ruppert, P. Schaeffer, A. De Cian, N. Kyritsakas and J. Fischer, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1994, 2135 RSC; (b) O. Felix, M. Wais Hosseini, A. De Cian and J. Fischer, Chem. Commun., 2000, 281 RSC; (c) S. J. Brooks, P. A. Gale and M. E. Light, CrystEngComm, 2005, 7, 586 RSC; (d) J. Wang, S. Li, P. Yang, X. Huang, X.-J. Yang and B. Wu, CrystEngComm, 2013, 15, 4540 RSC; (e) N. G. White and M. J. MacLachlan, Cryst. Growth Des., 2015, 15, 5629 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Alvarez, Dalton Trans., 2013, 42, 8617 RSC.
- For COFs with a similar highly interpenetrated diamondoid network structure, see: (a) F. J. Uribe-Romo, J. R. Hunt, H. Furukawa, C. Klock, M. O'Keefe and O. M. Yaghi, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 4570 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) Y.-B. Zhang, J. Su, H. Furukawa, Y. Yun, F. Gandara, A. Duong, X. Zou and O. M. Yaghi, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 16336 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- 2·Cl, 2·Br and 2·NO3 are all soluble in water, which would not be expected if they had an extended network structure. Similarly, their 1H NMR spectra in d6-DMSO are sharply resolved, suggesting limited/no aggregation in this solvent (See Fig. S3, S8 and S9†). Addition of two equivalents of TBA2·SO4 or TBA2.isophthalate to 2·4Cl in the same manner used to prepare [2·(TP)2]n gave no precipitate even after several weeks.
- For a similar crystal growth mechanism in a MOF, see M. Jian, B. Liu, R. Liu, J. Qu, H. Wang and X. Zhang, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 48433 RSC.
- It is perhaps surprising that the orthorhombic form, which contains disordered and less linear hydrogen bonds is more stable than the tetragonal form containing linear hydrogen bonds. However, the orthorhombic form is considerably more dense, so is presumably preferred as it minimises void space. This conclusion is supported by the far greater stability of the orthorhombic phase, particularly to solvent removal.
- While the start and end points of this transformation are single crystals, we do not rule out the possibility that this process goes via an intermediate amorphous phase (see for example: T. D. Bennett, A. K. Cheetham, Acc. Chem. Res., 2014, 47, 1555).
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Experimental details, additional characterisation data. CCDC 1523337–1523341. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c7sc00201g |
| ‡ Mmol and % yield calculated accounting for 11 weight% water present after drying, as indicated by TGA. |
| § These peaks integrated to a value lower than the expected 8H, presumably due to H/D exchange. |
| ¶ Mmol and % yield calculated accounting for 13 weight% water present after drying, as indicated by TGA. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 |