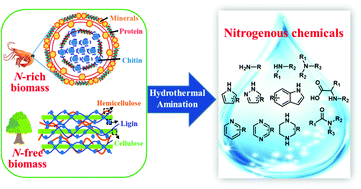
Biomass is the most abundant and low-cost renewable source for the production of value-added nitrogen-containing compounds. However, a large amount of water exists in natural biomass and relevant bio-derivatives, which often need to be removed prior to conducting valorization processes. Direct use of wet biomass and bio-derivatives as feedstocks definitely avoids energy consumption of drying processes, in which water acts as a reactive medium and is friendly to the environment and reaction devices. Hydrothermal amination of wet biomass feedstocks is thus an attractive technical strategy for producing nitrogen-containing compounds. This review summarizes state-of-the-art technologies in hydrothermal amination of natural biomass, bio-polymeric derivatives, and bio-based platform molecules with or without nitrogenous species into organonitrogen chemicals. Efforts are made to shed light on conversion routes and economic/environmental impacts of biomass hydrothermal amination. Challenges and perspectives on the large-scale production of biomass-derived nitrogenous compounds are also put forward.