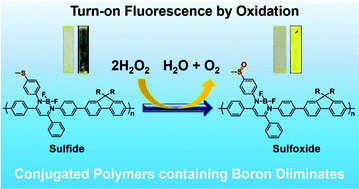
We present here the film-type chemosensors based on stimuli-responsive emissive polymers. The turn-on fluorescent conjugated polymers in the film state were designed by employing boron diiminates having aggregation-induced emission (AIE) properties to obtain strong emission from the solid state. We prepared the films with AIE-active copolymers composed of fluorenes and sulfide-substituted boron diiminates and evaluated the changes in their optical properties by oxidation. By soaking the film samples of the polymer in a H2O2 solution, a significant increase of the emission intensity was observed by oxidation. The quantum yields increased up to 3 times by oxidation at the sulfide groups. This would be attributed to the facilitating charge transfer (CT)-emissive fluorescence between the fluorene units and the boron diiminates having an enhanced electron-withdrawing ability by replacing the sulfide with the sulfoxide groups. These materials should be a suitable platform as bioprobes for longitudinal monitoring of bio-related reactions.