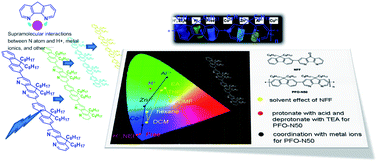
Diazafluorene (DAF) has a similar configuration to a fluorene unit except that two carbon atoms are replaced with nitrogen atoms, offering an ideal model of supramolecular conjugated polymers to investigate the structure–property relationship. Herein, a series of DAF-based oligofluorenes and polyfluorenes, including NFF, NF2F, F2NF, PFO-NO, PFO-N5, PFO-N15 and PFO-N50, have been synthesized by Suzuki and/or Yamamoto polymerization. All dioctyldiazafluorene-based copolymers show improved solubility, high quantum efficiency and good thermal stability. The 4,5-diazafluorenone (DAFone)-based oligomers exhibit solvent-dependent fluorescence and DAF-based copolymers show an optical response with a large red-shift (ca. 40–60 nm) of the absorption peak when they were protonated with trifluoroacetic acid. Their photoluminescent properties have also been obviously tuned by coordinating different metal ions to the polymers. DAF-based conjugated polymers are potential supramolecular polymer semiconductors for thin film electronics.