Bifunctional reusable Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticle-grafted carbon nanotubes for aqueous dye removal from contaminated water†
Abstract
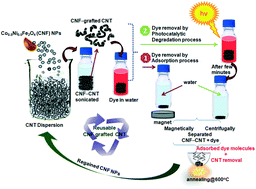
The repeated use of magnetic nanoparticles (NPs) embedded within carbon composites decreases the dye removal efficiency because the reactive surface becomes inactive and post-treatment changes the material properties. Hence, herein, we report a high-yield of sustainable, reusable Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 (CNF) NPs grafted onto carbon nanotubes (CNTs) synthesized using a microwave-assisted and sonication method. Nanocomposite samples showed a pure Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 phase and uniform distribution of ultrafine CNF NPs with sizes below 50 nm that are grafted onto CNTs for aqueous dye removal through adsorption and degradation processes. Toxic anionic and cationic dyes were removed through adsorption after treatment with the CNF-grafted CNTs and the adsorption process at higher dye concentrations was improved using a photodegradation process, demonstrating its bifunctional utility in eradicating dye molecules at lower or higher concentrations. After dye adsorption and degradation, the samples were magnetically separated and post-treated at 600 °C to remove the surface-adsorbed dye and re-activate the CNF NPs, which retained their physical and magnetic characteristics. Re-sonicating the CNF NPs with CNTs efficiently removed all dyes demonstrating their reusability for toxic-dye removal for more than 5 cycles. The high surface-area, active octahedral site, and bandgap of the CNF-grafted CNTs increase the instantaneous dye adsorption, photodegradation efficiency, and repeatability of dye removal from water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...